Muskan Shafi Education Content Expert
Education Content Expert
Displacement is the shortest distance between the initial and final position of an object. It is the change in the position of the object along with the direction of motion.
- Displacement always has a straight path as the initial and final points are directly connected to find displacement.
- It is represented using the symbol ‘S’.
- Displacement can be positive, negative, or zero.
- It is a vector quantity as it has both magnitude and direction.
Displacement Formula is used to calculate the measure of the displacement of an object. Displacement Formula is given as S = Sf – Si. Here, S refers to displacement, Sf is the final position and Si is the initial position of the object.
Read More: NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Motion in a Straight Line
Key Terms: Displacement, Distance, Velocity, Vector, Motion, Magnitude, Displacement Formula, Acceleration, Time
What is Displacement?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Displacement is the change in the position of an object. The term ‘Displacement’ means that the object has been moved or displaced from its position.
- Displacement deals with motion in a straight line.
- It is the difference in the position of an object from an initial position to the final position.
- It has a direction as well as magnitude, thus, it is a vector quantity.
- It can have a positive, negative, or zero value.
Motion in a Straight Line Video Explanation
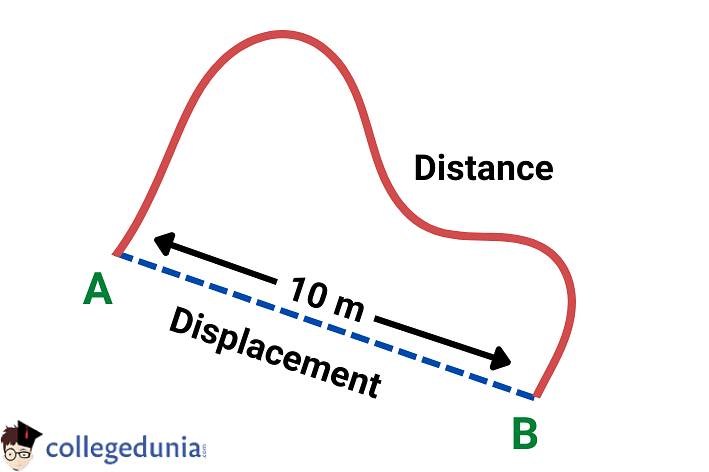
Example: A boy moves from Position A to Position B during a walk in a park. Thus, the displacement will be 10 m.
Read More:
Displacement Formula
[Click Here for Previous Years' Questions]
Displacement is the change of the position of an object from its original position to its final position.
Displacement Formula is given as
| S = Sf – Si |
Where,
- S: Displacement
- Sf: Final Position of the Object
- Si: Initial Position of the Object
Displacement can also be calculated using the given formula derived from equations of motion:
| S = ut + ½ at2 |
Where
- u: Initial Velocity
- v: Final Velocity
- a: Acceleration
- t: Time Taken
Solved ExampleExample: Anjali travels 300 m North to reach a mall, however, she had to travel back to the same track south 125 m to pick up a friend. What will be the total displacement of Anjali? Solution: The initial position of Anjali is S i= 0. The final position Sf is the distance traveled North minus the distance traveled South. Using the Displacement Formula, we get S = (Sf - Si) S = (350 - 125) - 0 S = 225 m Thus, the total displacement of Anjali is 225 m North. |
Read More: Motion in a Straight Line Important Questions
Difference between Distance and Displacement
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Distance and Displacement are two very important terms in motion and related concepts. Both terms are often used interchangeably, however, they are totally different concepts in Physics.
The difference between distance and displacement is as follows:
| Parameter | Distance | Displacement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Distance is the complete length of the path an object travels. | Displacement is the shortest distance between the initial and the final position of the object. |
| Magnitude | Distance is always positive or zero. | It can be positive, negative, or zero. |
| Quantity | It is a scalar quantity as it only depends upon the magnitude. | It is a vector quantity as it depends upon both magnitude and direction. |
| Value | The value of the distance is never less than displacement. | Displacement is either equal to or less than the distance. |
| Symbol | Distance is denoted by the symbol ‘d’. | ‘Displacement is denoted by the symbol ‘s’. |
| Route Information | Distance gives complete information about the route that is followed while traveling from one point to another. | Displacement does not give complete information about the route as it only refers to the shortest path. |
| Formula | Distance Formula: Speed × Time | Displacement: Velocity × Time |
Solved Examples on Displacement Formula
[Click Here for Previous Years' Questions]
Here are a few solved examples of the Displacement Formula in order to understand the concept better:
Example 1: A bus traveling at 25 m/s starts accelerating at 3 m/s2 in a time period of 4 seconds. What is the displacement of the bus?
Solution: It is given that
- Initial Position (u): 25 m/s
- Acceleration (a): 3 m/s2
- Time (t): 4 sec
Using the Displacement formula
S = ut + ½ at2
S = 25 x 4 + ½ x 3 x 42
S = 124 m
Thus, the displacement of the bus is 124 m.
Example 2: A cyclist rides his cycle from position A to position B. The distance between A and B is 5 km. He turned back and then travels from position B to position C. The distance between B and C is 4 km. What will be the displacement?
Solution: It is given that
- Distance from A to B: 5 km
- Distance from B to C: 4 km
Using the Displacement Formula,
S = Sf – Si
S = 5 km – 4 km
S = 1 km
Thus, the displacement of the cyclist is 1 km.
Example 3: A car moves from A to B for 4 km and then from B to C at a right angle for 3 Km. It then returns from point C to A for 5 km. What will be the distance and displacement?
Solution: Given that
- Distance from A to B: 4 km
- Distance from B to C: 3 km
- Distance from C to A: 5 km
We know that distance is the total path covered by an object. So,
Distance Covered = AB + BC + AC = 4 + 3 + 5 = 12km
Displacement is the difference between the initial and final position. However, here the final position and initial position are the same i.e. A.
Thus, the displacement here will be 0.
Read More:
Motion in a Straight Line Class 11 Handwritten Notes
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Here are the handwritten notes on Motion in a Straight Line and related concepts:




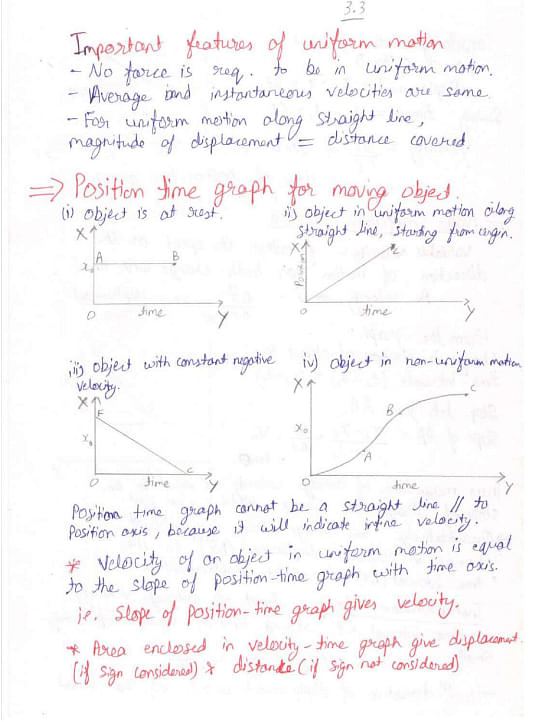



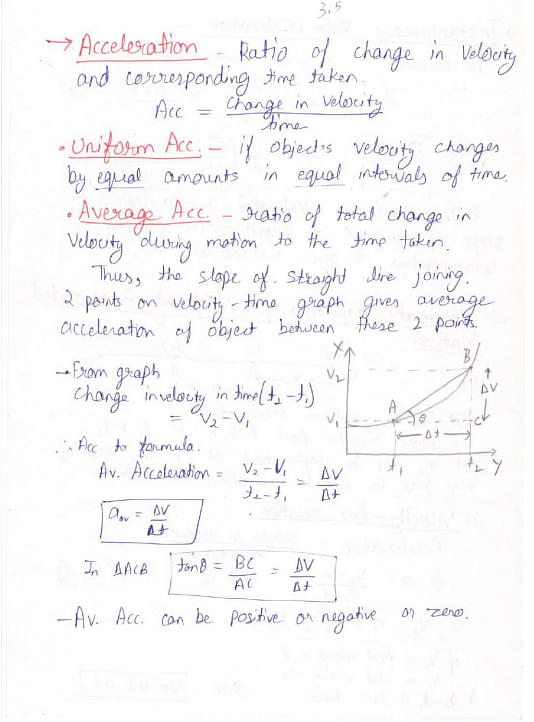







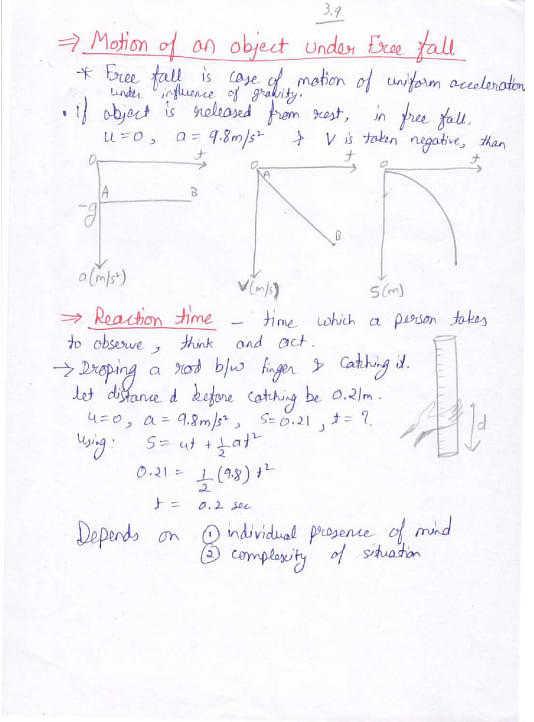
Things to Remember
- Displacement is the change in the position of an object.
- It is a vector quantity because it depends on both magnitude and direction.
- It can be positive, negative, and even zero.
- Displacement can be zero where the distance is covered but no change in position.
- Displacement is directly proportional to velocity.
- Displacement Formula is given as S = Sf – Si.
- It can also be calculated using the formula S = ut + ½ at2.
Previous Years’ Questions
- Displacement time graph cannot be…
- If the displacement of a particle is zero, the distance covered by it…
- The displacement-time graph of a particle executing… (KCET 2003)
- The displacement of a body is given to be proportional… (AIIMS 1996)
- If the equation for the displacement of a particle… (AIIMS 1998)
- To get a resultant displacement of 10 m two displacement vectors…
- Displacement x versus t2 graph is shown for a… (UPSEE 2017)
- The displacement-time graphs of two moving particles… (KCET 2011)
- A particle moves along a straight line such that its displacement… (NEET 1994)
- A particle moving in a straight line covers half the distance… (KEAM)
Sample Questions
Ques. A plane traveling with an initial speed of 40 m/s, takes 13 seconds to reach the end of the runway. How long will be the flight path if the plane is traveling at 10 m/s2? (3 Marks)
Ans. Given that,
- Initial Speed of the Plane = 40 m/s
- Time taken to reach the end of the Runway = 13 sec
- Acceleration = 10 m/s2
Put the given values in the displacement formula,
S = ut + ½ at2
S = 40 x 13 + ½ x 10 x (13)2
S = 1365 meters
Thus, the flight path will be 1365 m long.
Ques. Suyash throws a cricket ball 30 feet east for his pet dog. The dog catches the ball and takes it past Ayushi who is standing 38 feet to the west of where Suyash is. Calculate the displacement of the cricket ball. (3 Marks)
Ans. It is given that
- Initial Position = 0 km
- Final position = 38 − 30 = − 8 km
Using the Displacement Formula,
S = Sf − Si = − 8 − 0 = − 8 m
Thus, the displacement of the ball is 8 m from Mithila’s initial position.
Ques. What is Displacement? (3 Marks)
Ans. Displacement is the shortest distance between the initial position and the final position of the body along with the direction. Displacement is always measured along a straight path and direction is taken into consideration while calculating displacement.
- It is denoted by the symbol ‘S’.
- Since displacement means the shortest path, it does not give complete details about the path covered.
- It only depends upon the initial and final position of the body and not on the path.
Ques. What is Displacement Formula? (3 Marks)
Ans. The Displacement Formula is given as
S = Sf – Si
Here
- Sf is the final position of the object.
- Si is the initial position of the object.
- S is the displacement or change in the position of the object.
Ques. What does Displacement depend on? (2 Marks)
Ans: Displacement depends on the initial and final position of the path taken which is taken by the object. Delta x or Delta y is the symbol for displacement and Delta refers to the change in position. Thus, speed depends on the distance traveled while velocity depends on the displacement.
Ques. Is displacement a scalar quantity or a vector quantity? (2 Marks)
Ans. Distance is a scalar quantity referring to how much path the object has covered during its movement while displacement is a vector quantity that depends on how far the object reaches. It refers to the change in overall position. It is a physical vector quantity as it has both magnitude as well as direction.
Ques. Can Displacement be Zero? (3 Marks)
Ans. Yes, displacement can be zero as it is a change in position.
For instance,
- When the object starts from point A and goes through points B and C and again comes back to point A. Here the displacement will be zero.
- Object completing the journey over a circular path, the displacement will be zero.
Ques. How is distance different from displacement? (2 Marks)
Ans. The difference between distance and displacement is direction. In distance, one does not need direction but in calculating displacement, one does require direction. Displacement can be measured; thus it is a physical quantity but here direction is also given thus making it a vector quantity.
Ques. Can displacement be negative? (3 Marks)
Ans. Generally, displacement can be negative because displacement refers to the change in position in while considering the direction. In calculating the displacement, the direction is necessary. For example,
If the initial position is 8 m and the final position is 2 m
Then, here the displacement will be 2m – 6m = -4 m
Ques. Is displacement proportional to velocity? Explain? (3 Marks)
Ans. Yes, the displacement is directly proportional to velocity keeping the time constant.
This can be explained by the velocity formula:
Velocity = Displacement / Time
Thus, Displacement = Velocity X Time
If the time is constant then,
- Displacement is directly proportional to velocity.
- Thus, if the velocity is increased then more distance can be covered at the same time.
Check-Out:






Comments