Antidiuretic hormone aids in regulating some important internal processes in the body. This hormone mostly controls physical processes. It also helps in keeping several life-threatening conditions in control. Antidiuretic hormone is sometimes also referred to as Vasopressin.
- Antidiuretic hormone has important functions in human body.
- It is involved in maintaining blood pressure and cardiac cyce.
- It is also responsible for homeostasis in the body.
Read More Uremia
Key words: Antidiuretic hormone, ADH, Vaspressinn, Blood, Pituitary gland
Antidiuretic Hormone
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) helps in balancing and controlling the volume of water in the blood. It is also responsible for the increase of glomerular blood flow. This hormone is also known as Vasopressin.
- Antidiuretic Hormone is released by neurohypophysis.
- The secretion of Antidiuretic hormone is regulated by the posterior part of the pituitary gland.
- Hypothalamus produces this hormone and the pituitary gland stores it.
- The ADH hormone is activated by the posterior pituitary lobe.
- The normal range for Anti Diuretic hormone in the bloodstream is between 1 to 5 picograms per millimeter.
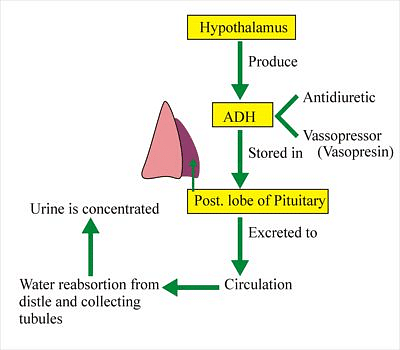
Secretion of Antidiuretic Hormone
Functions of Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Antidiuretic Hormone performs various functions. Some of the functions of antidiuretic hormone are-
- Antidiuretic hormone controls the circadian cycle.
- It helps in the maintenance of cellular functions of the body.
- Antidiuretic hormone monitors and controls the volume of water in the body.
- It regulates blood pressure.
- Antidiuretic hormone is responsible for homeostasis.
- It retains the level of fluid in the body by conserving the water in the kidney.
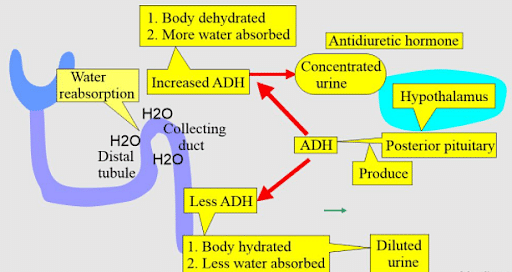
Functions of ADH
Hormonal levels of Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The levels of Antidiuretic hormone in blood cells should remain consistent.
If the Anti Diuretic hormone levels are higher than desired, it can lead to some acute conditions such as vomiting, dehydration, nausea, and headache; or in more severe conditions it can also lead to seizures and coma. A high level of Antidiuretic hormone in blood cells can also result in lung cancer, brain cancer, bladder cancer, blood cancer, pancreatic cancer, tuberculosis, cystic fibrosis, multiple sclerosis, emphysema, lymphoma, etc.
If the Anti Diuretic hormone levels are lower than desired, it can lead to low blood pressure, frequent urination due to excretion of a large amount of water by the kidney, diabetes insipidus, may also cause harm to the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, or primary polydipsia.
Read More
| Related Articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Tumor | Nephritis | Human Health and Diseases |
| Pituitary Adenoma | Thyroid Gland | Pineal Gland |
Regulation of Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
There are several factors that regulate the release of Antidiuretic hormone into the bloodstream. These factors are:
- The receptors and blood vessels present in the heart detect the change in blood pressure and blood volume and control the release of Antidiuretic hormone.
- When the level of Antidiuretic hormone in the bloodstream is higher than normal, the kidney retains the water in the body.
- This leads to an increase in the hormone in the blood and thus there is a dilution in blood.
Factors Affecting Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
ADH can be affected by below mentioned factors.
Side effects of drugs:
The level of Antidiuretic hormone in the bloodstream can also be high due to the side effects of certain drugs or lung diseases. This high level of antidiuretic hormone can cause brain cancer, blood cancer, leukemia, pancreatic cancer, etc.
The concentration of salt in the bloodstream:
When there is an increase in the concentration of salt, the secretion of Antidiuretic hormone in the bloodstream is affected.
Regular intake of alcoholic drinks:
Intake of alcohol can prevent the release of Antidiuretic hormone in the bloodstream, which can result in frequent urination and dehydration.
Disorders of Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The disorders caused by the increase or decrease of the antidiuretic hormone levels include.:
- Infertility
- Insomnia
- Autoimmune disorders
- Frequent urination
- Fluctuations in body temperature
- Fluctuations in blood pressure
- Head injuries
- Delayed puberty
- Genetic disorders
- Change in appetite
- Tumours in the hypothalamus or regions near the pituitary gland
Things to Remember
- Antidiuretic hormone helps in regulating some important internal processes in the body.
- It is also referred to as Vasopressin.
- Antidiuretic hormone helps in balancing and controlling the volume of water in the blood.
- The secretion of Antidiuretic hormone is controlled by the posterior part of the pituitary gland.
- Antidiuretic Hormone performs functions such as monitoring and controlling the volume of water in the blood and controlling the circadian cycle.
- It maintains the level of fluid in the body by conserving the water in the kidney.
- The levels of Antidiuretic hormone in blood cells should remain within the normal range.
- Both high and low levels of Antidiuretic Hormone can lead to various acute or severe illnesses.
Sample Questions
Ques: Which gland is responsible for storing Antidiuretic Hormone? (1 Mark)
- Pineal Gland
- Pituitary Gland
- Parathyroid Gland
- Thyroid Gland
Ans: b) Pituitary Gland
Ques: What is the normal range for Anti Diuretic Hormone in the bloodstream? (1 Mark)
Ans: The normal range for Anti Diuretic hormone is between 1 to 5 picograms per millimeter of blood.
Ques: Define Hormone. (1 Mark)
Ans: Hormones are chemical messengers that are produced and synthesized by endocrine glands to regulate the functioning of the body.
Ques: What are some of the disorders caused due to increase or decrease of Antidiuretic Hormone levels? (2 Marks)
Ans: If the Antidiuretic hormone levels are higher or lower than desired, it can lead to many disorders. These disorders include: delay in puberty, autoimmune disorders, genetic disorders, change in body temperature, fluctuations in blood pressure, insomnia, a shift in appetite, infertility, tumors in the pituitary gland, injuries on the head, and frequent urination.
Ques: What are the functions of the parathyroid hormone? (2 Marks)
Ans: The parathyroid gland increases the level of calcium ions in the bloodstream. It is also responsible for triggering the bone resorption process. It maintains the amount of calcium in the body.
Ques: Mention three factors that regulate the Antidiuretic hormone? (3 Marks)
Ans: The three factors that affect the release of Antidiuretic hormone into the bloodstream are:
- Intake of alcohol can prevent the release of Antidiuretic hormone in the bloodstream, which can result in frequent urination and dehydration.
- When there is an increase in the concentration of salt, the secretion of Antidiuretic hormone in the bloodstream is affected.
- When the level of Antidiuretic hormone in the bloodstream is higher than normal, the kidney retains the water in the body. This can dilute the blood.
Ques: Write a short note on the thyroid gland. (4 marks)
Ans: The Thyroid gland is located in the anterior part of the neck. It is an endocrine gland. The thyroid gland is responsible for secreting two hormones: Thyroxine hormone and Triiodothyronine hormone.

The thyroid hormones affect physiological processes such as metabolism and growth. Goitre: The enlargement of the thyroid gland can cause various problems.
Ques: List out the hormones secreted by the Pituitary gland. (3 Marks)
Ans: The pituitary gland secretes the following hormones:
- Antidiuretic hormone
- Growth hormone
- Follicle-stimulating hormone
- Oxytocin
- Neurohypophysis
- Adenohypophysis
- Melanocyte-stimulating hormone
- Thyroid stimulating hormone
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone
- Luteinizing hormone
Ques: Write a short note on Acromegaly. (3 Marks)
Ans: Acromegaly is a hormonal disorder that leads to unusual growth in body parts and organs. It is caused by excessive secretion of growth hormone by the pituitary gland.
Some of the symptoms of acromegaly are constant headaches, croaky voice, sweating, fatigue, enlargement of sebaceous glands, and painful joints.
Acromegaly can be treated through medicines, surgery, or radiation therapy.
Ques: What happens if the Antidiuretic hormone levels fluctuate? (3 Marks)
Ans: The levels of Antidiuretic hormone in blood cells should remain consistent.
If the Antidiuretic hormone levels are higher than desired, it can lead to some acute conditions such as vomiting, and headache; or in more severe conditions it can lead to seizures and coma. High levels of Antidiuretic hormone in blood cells can also result in lung cancer, brain cancer, bladder cancer, blood cancer, pancreatic cancer, etc.
If the Anti Diuretic hormone levels are lower than desired, it can lead to low blood pressure, frequent urination due to excretion of a large amount of water by the kidney, diabetes insipidus, harm to the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, or primary polydipsia.
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Check-Out:





Comments