Jasmine Grover Content Strategy Manager
Content Strategy Manager | Updated On - Oct 14, 2025
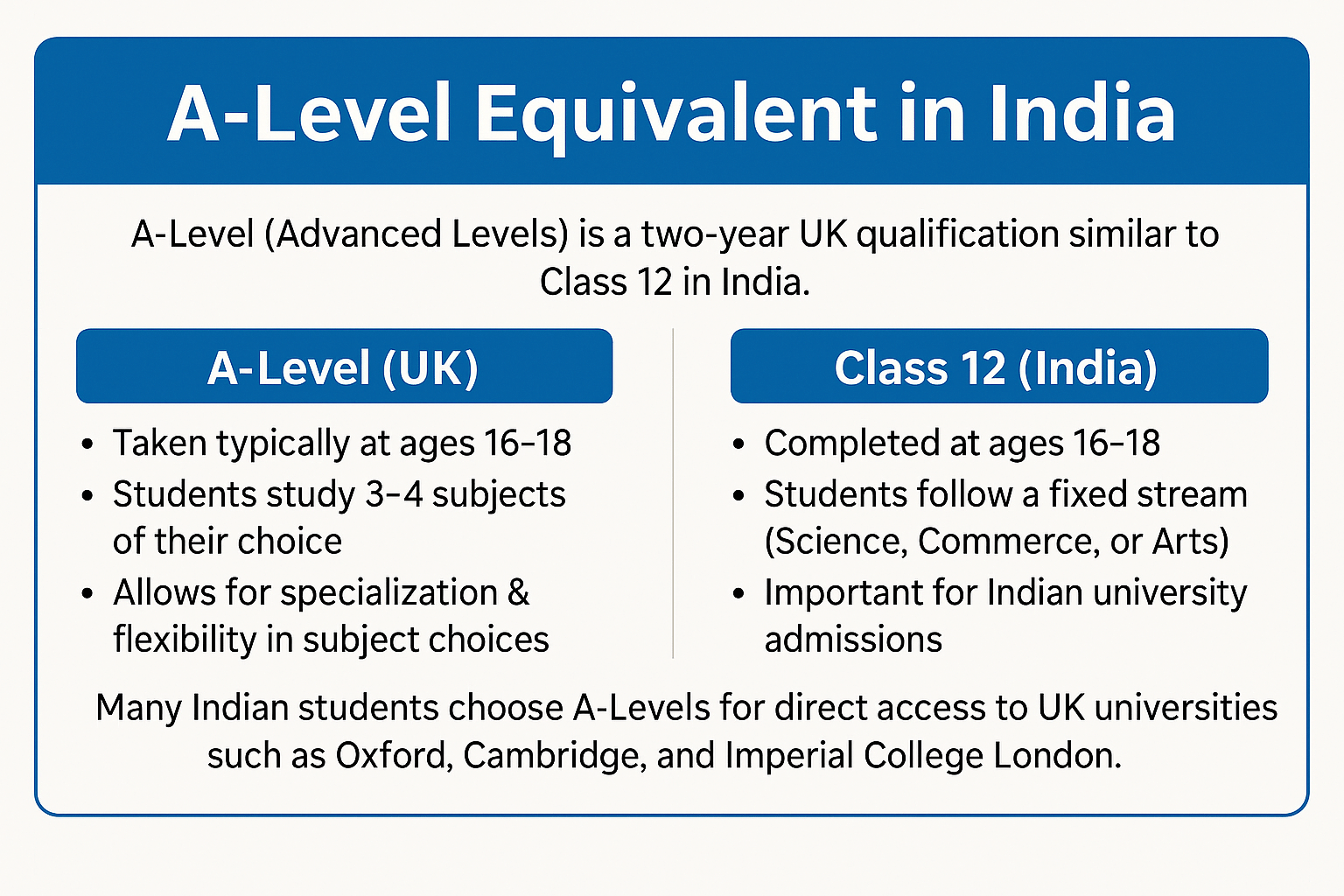
A-Level (Advanced Levels) is a two-year qualification in the UK, equivalent to Class 12 in India, where students focus on 3–4 subjects of their choice. It is a key admission requirement for many Indian students applying to UK universities, including prestigious institutions like Oxford, Cambridge, and Imperial College London.
Wondering what the A-Level equivalent is in India?
If you're comparing education systems in the UK and India, A-Levels and Class 12 often stand side by side.
For Indian students, A-Levels are especially beneficial because they provide a direct pathway to top UK universities, aligning closely with the academic rigor of India’s Class 12 exams. A-Levels also offer flexibility in subject choices, allowing students to pick courses that match their career aspirations—whether it's Engineering, Medicine, Business, or Law. This flexibility and international recognition make A-Levels an ideal option for Indian students looking to study abroad in the UK.
In A-Levels, students typically study 3–4 subjects of their choice over two years. These subjects are selected based on their interests and future career plans. For example, if you want to study engineering, you might pick Mathematics, Physics, and Chemistry. If your goal is to pursue law, subjects like History, English, or Economics could be your focus. This flexibility allows you to tailor your studies to match your university and career aspirations.
Many Indian students planning to study abroad ask: Is A-Level equal to Class 12 in India? While both are school-leaving qualifications taken at age 16–18, they differ significantly in flexibility, global recognition, and university pathways. In this guide, we compare UK A-Levels with Indian Class 12 boards like CBSE, ISC, and HSC to help you decide what’s right for your goals.
Check Out: Student Guide to Study in UK
- Understanding A-Levels: An Overview of the Qualification System in the UK
- Subjects Offered in A-Levels
- The Grading System of A-Levels
- How A-Levels Compare to Indian Education Systems (CBSE, ICSE, and State Boards)
- The Role of A-Levels in UK University Applications
5.1 How Universities Evaluate A-Level Grades
- A-Level grade requirements for Top UK Universities
- FAQs
What are A-Levels?
A-Levels are a key qualification system in the UK, similar to Class 12 or pre-university courses in India. Designed for students aged 16–18, A-Levels prepare you for entry into top UK universities and are recognized globally. It is a two-year program where students specialize in 3-4 subjects they want to focus on. These subjects are often chosen based on career goals, such as medicine, engineering, law, or business.
Two-Year Program:
- AS-Level (Year 1): In the first year, you learn the basics of your chosen subjects, building a strong foundation and understanding your strengths.
- A2-Level (Year 2): In the second year, you dive deeper into the subjects, focusing on advanced concepts and critical thinking.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Program Duration | 2 years (AS-Level in Year 1 and A2-Level in Year 2) |
| Subjects | Students choose 3–4 subjects based on their career goals. |
| Structure | AS-Level: Foundation-level study in chosen subjects- A2-Level: Advanced-level study |
| Assessment | Primarily written exams; some subjects include coursework or practical assessments. |
| Grading System | A* (highest), A, B, C, D, E (pass grades), U (ungraded) |
| Flexibility | Mix subjects across categories like Sciences, Arts, and Social Sciences. |
| Recognition | Globally recognized; essential for UK university admissions and accepted worldwide. |
| Focus | In-depth subject knowledge and critical thinking skills. |
What is the A-Level Equivalent in India?
In India, the qualification equivalent to the UK's A-Level is the Higher Secondary Certificate (HSC), commonly known as Class 12. This includes:
- CBSE Class 12 (Central Board of Secondary Education)
- ISC (Indian School Certificate)
- State Boards (Maharashtra HSC, Tamil Nadu Board, etc.)
| UK Qualification | Indian Equivalent | Age Group | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| A-Levels | Class 12 (CBSE/ISC/HSC) | 16–18 | 2 years |
These are completed after 12 years of schooling and typically include subjects based on chosen streams: Science, Commerce, or Arts. Like A-Levels, these exams play a crucial role in university admissions.
A-Levels vs Indian Class 12 (CBSE/ISC)
| Feature | UK A-Levels | Indian Class 12 (CBSE/ISC) |
|---|---|---|
| Curriculum Flexibility | Choose any 3–4 subjects from any stream | Subjects are pre-grouped by stream (Science/Commerce/Arts) |
| Global Recognition | Highly recognized internationally, especially in UK & US | Recognized in India, accepted by many foreign universities with conditions |
| Admission Route | Direct entry to UK universities | Often needs additional entrance exams (SAT, UCAS, IELTS) |
| Teaching Style | Analytical and application-based | Mix of rote and application-based learning |
| Examination Format | Two-stage: AS + A2, mostly written exams | Final board exams after 2 years |
Also Check:
| Study in UK Guides | ||
|---|---|---|
| Top UK universities with highest ROI | Foundation Course in UK | UK Grading System |
| Study gap accepted in UK | UK University Application Deadlines | India to UK Travel Checklist |
Subjects Offered in A-Levels in UK
A-Levels offer a broad selection of subjects, allowing students to specialize in areas that align with their interests and future aspirations. Unlike the rigid stream system of selecting from a few subject options, A-Levels let you mix subjects across disciplines, giving you the flexibility to tailor your education.
The table below shows the popular subject categories in A-Levels often opted by students, along with example subjects and the career paths they lead to:
| Subject Category | Subjects | Potential Career Fields |
|---|---|---|
| Sciences | Biology, Chemistry, Physics, Mathematics | Medicine, Engineering, Research |
| Humanities | History, Geography, Psychology, Philosophy | Law, Teaching, Civil Services |
| Languages | English Literature, French, Spanish, German | Literature, Translation, Linguistics |
| Social Sciences | Economics, Sociology, Political Science | Business, International Relations |
| Creative Arts | Art and Design, Drama and Theatre Studies, Music | Media, Design, Performing Arts |
| Technology and Computing | Computer Science, Design and Technology | IT, Software Development, Engineering |
| Business and Law | Business Studies, Accounting, Law | Finance, Corporate Law, Entrepreneurship |
The Grading System of A-Levels in UK
The table below shows the A-Level grading system, explaining each grade, and its description:
| Grade | Description | Percentage Range |
|---|---|---|
| A* | Exceptional performance | 90% and above |
| A | Excellent performance | 80% – 89% |
| B | Very good performance | 70% – 79% |
| C | Good performance | 60% – 69% |
| D | Sufficient performance | 50% – 59% |
| E | Basic passing grade | 40% – 49% |
| U | Ungraded | Below 40% |
Also Check: UK Grading System
How A-Levels Compare to Indian Education Systems
The table below compares A-Levels in the UK with the Indian education system, highlighting key differences and similarities. It reflects both parameters for students who studied under the traditional pre-NEP system and those adapting to the flexible post-NEP approach:
| Aspect | A-Levels (UK) | Post-NEP Indian System | Pre-NEP Indian System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subject Choices | Choose 3–4 subjects from any field. | Choose subjects from different streams, like Math with Music. | Had to pick fixed streams like Science, Commerce, or Arts. |
| Depth of Study | Focuses on a few subjects deeply. | Allows deeper study of chosen subjects. | Covers many subjects but with less focus on depth. |
| Learning Style | Practical and application-based learning. | Mix of practical and theoretical learning. | Mostly focused on memorizing theory. |
| Exams and Assessment | Exams at the end of the year with grades (A* to E). | Includes regular assessments, projects, and final exams. | Board exams with marks; fewer regular assessments. |
| Grading System | Grades from A* (top) to E (pass). | Uses grades and detailed feedback along with marks. | Mostly percentages, with some boards using grades. |
| Global Recognition | Accepted worldwide, especially in the UK and US. | CBSE and ICSE are accepted globally; State Boards less so. | Recognized mostly within India; limited international use. |
| University Focus | Prepares for UK and international universities. | Works for both Indian and international universities. | Focused on Indian universities and entrance exams. |
| Flexibility in Subjects | Mix any subjects you like. | Can now combine different subjects from various streams. | Fixed combinations depending on your stream. |
| Skill Development | Builds practical and thinking skills. | Focuses on skills, projects, and practical knowledge. | Little focus on practical skills; mostly academic knowledge. |
| Career Preparation | Prepares for global education and jobs. | Prepares for careers in India and abroad. | Mainly geared for Indian jobs and education. |
The Role of A-Levels in UK University Applications
For Indian students, A-Levels provide a direct pathway to UK universities without additional entrance exams like SAT or ACT. If you’re aiming for a globally recognized degree and a streamlined admission process, A-Levels can be your stepping stone to success. UK universities use A-level results as a primary way to evaluate students. Admissions teams look at the grades you achieve in your chosen subjects, with requirements varying depending on the course and university.
How Universities Evaluate A-Level Grades
A-level grade requirements for UK universities are usually written as combinations like A*AA, AAA, or ABB. These indicate the grades you need in your chosen subjects to qualify for a course. Here's what they mean:
- A*AA: This means you need one A* (highest grade) and two A grades. For example, if you're taking Mathematics, Physics, and Chemistry, you must achieve an A* in one subject and A grades in the other two.
- AAA: This requires three A grades across your subjects. For instance, you might need A grades in Biology, Chemistry, and Psychology for a course like Biomedical Sciences.
- ABB: This asks for one A grade and two B grades. For example, in subjects like Business, Economics, and History, you must get an A in one subject and B grades in the other two.
- BBB: Three B grades are required. This is typically for less competitive courses, where achieving consistent good performance is key.
A-Level Grade Requirements for Top UK Universities
The table below outlines the A-Level grade requirements for popular courses at top UK universities:
| University | Course | A-Level Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| University of Oxford | Medicine | A*AA |
| Law | AAA | |
| Engineering | AAA | |
| University of Cambridge | Computer Science | AAA |
| Economics | A*AA | |
| Natural Sciences | AAA | |
| Imperial College London | Mechanical Engineering | AAA |
| Chemistry | A*AA | |
| Mathematics | AAA | |
| University College London (UCL) | Architecture | AAB |
| Psychology | AAA | |
| History | AAA | |
| University of Manchester | Business Management | AAB |
| Biomedical Sciences | AAA | |
| Law | AAA |
Also Check: Exams to Study in UK for International Student
Students should know that it is not mandatory for Indian students to have A-Level qualifications to get into UK universities, but having them is advantageous. Since A-Levels are specifically designed to align with UK university requirements, they simplify the admission process by allowing universities to assess students' performance in subjects directly related to their chosen courses.
FAQs
Ques: Is it mandatory to take A-Levels for admission to UK universities?
Ans: No, A-Levels are not mandatory for Indian students applying to UK universities. Indian qualifications like CBSE or ICSE are also accepted by UK Universities, but you may need to meet additional requirements, such as taking tests like the SAT/ACT or IELTS/TOEFL to prove your academic ability and English proficiency. However, having an A-Level qualification can ease the application process for auditors and improve your chances of admission.
Ques: Can A-Levels help me get into Ivy League universities?
Ans: Yes, A-Levels are widely recognized by Ivy League universities in the US. Achieving top grades (like A*AA or higher) in A-Levels, along with meeting other requirements like SAT/ACT scores and essays, can boost your chances of admission.
Ques: Can I get scholarships for A-Levels in the UK?
Ans: Yes, scholarships are available for A-Level students in the UK. For example, universities like the University of Oxford and University of Cambridge offer scholarships such as the Cambridge International Scholarships and the Oxford Bursary. Many schools, like Dulwich College and Sevenoaks School, also provide financial support based on academic merit or financial need to help international students with tuition fees.
Ques: How many subjects do most students take for their A-levels in the UK?
Ans: Most students take 3–4 subjects for their A-Levels. Three subjects are usually enough for university admission, but some students take a fourth to strengthen their applications or explore additional interests.



Comments