Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert | Updated On - Sep 25, 2025
The global competition for skilled workers has intensified. On one side, the United States has imposed a $100,000 one-time fee on all new H-1B visa petitions filed after September 21, 2025. On the other hand, China has launched a new K-Visa effective October 1, 2025, designed to attract international STEM graduates with simpler rules and longer stays.
For Indian students, who make up 71% of all H-1B approvals, this clash of policies raises a pressing question: stick with the prestige of Silicon Valley or explore Beijing’s new, more accessible alternative?
Check Out: H1B Visa Fee Raised to $100,000: Trump’s New Order Could Impact Indian Tech Workers
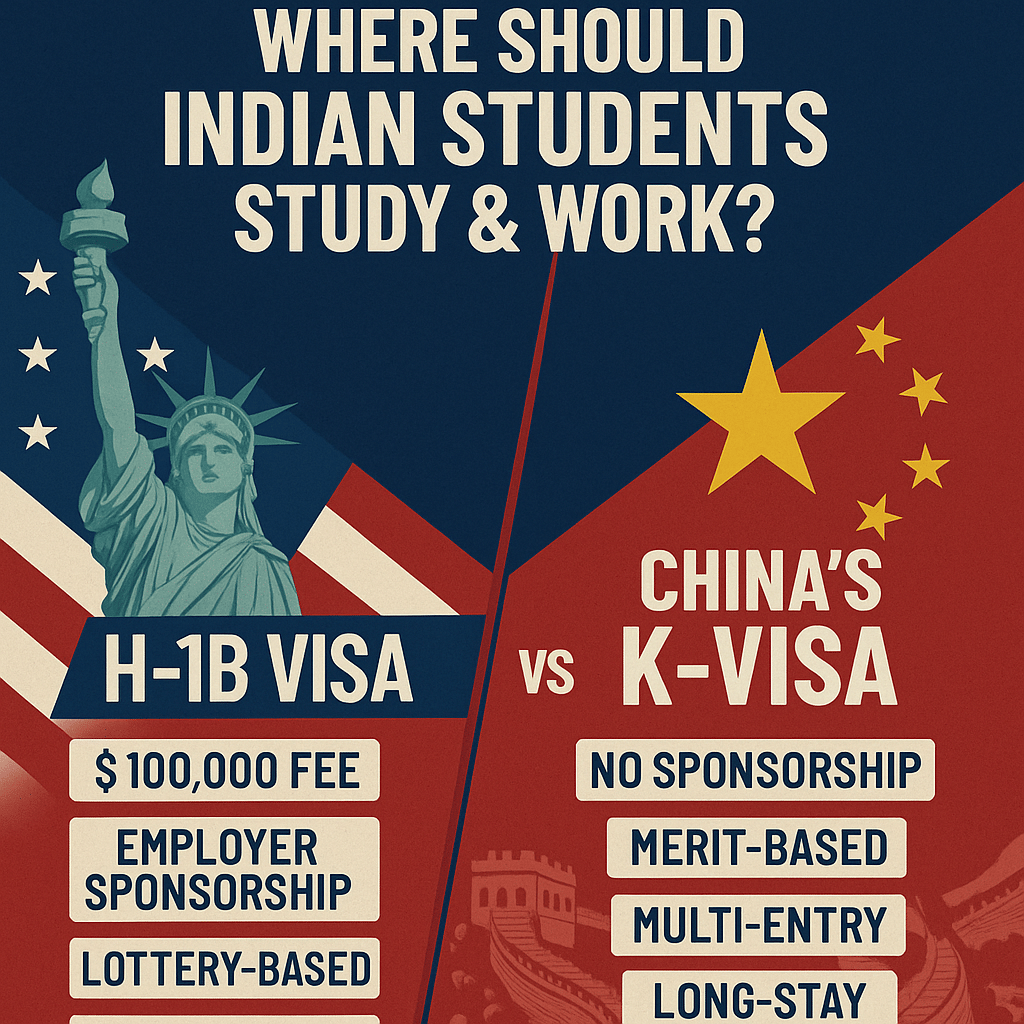
The H-1B Visa: From Opportunity to Obstacle
The H-1B visa once represented the dream pathway into top U.S. tech and research jobs. Today, it is more uncertain and expensive than ever.
- New Cost Barrier: Employers must now pay $100,000 with every new petition, drastically raising hiring costs.
- Political Overtones: Trump’s administration has framed foreign workers as competitors to “American jobs,” making sponsorships politically sensitive.
- Impact on Students: Indian graduates moving from F-1 (student) and OPT (work-training) visas to H-1B now face a shrinking window of opportunity.
This shift risks discouraging early-career professionals and placing additional strain on Indian IT firms and U.S. research labs.
The K-Visa: China’s Counter-Move
China’s new K-Visa offers an alternative narrative. Unlike the U.S. lottery-based H-1B, it is sponsorship-free, rooted in education and expertise rather than employer backing.
Key Features of K-Visa:
- No employer sponsorship required.
- Multi-entry, long-stay validity.
- Open to academic, research, entrepreneurial, and cultural work.
- Designed specifically for young STEM graduates.
Beijing’s strategy is clear: turn Washington’s restrictions into China’s opportunities, capturing the next generation of engineers, coders, and scientists.
Check: STEM Education Abroad
What This Means for Indian Students?
For India’s massive STEM talent pool, the trade-offs are stark:
| Factor | United States (H-1B) | China (K-Visa) |
|---|---|---|
| Visa Cost | $100,000 per petition | Minimal fees |
| Sponsorship | Mandatory (employer-backed) | Not required |
| Selection Process | Lottery-based | Merit-based (STEM qualification) |
| Stay & Entry | Restricted, tied to the employer | Multi-entry, long-stay |
| Career Prospects | Silicon Valley, global VC ecosystem | Research parks, industrial hubs |
For Indian students:
- U.S. = Prestige + Risk: Top-ranked universities, deep tech ecosystems, but high cost and political unpredictability.
- China = Accessibility + Speed: Faster entry, research-focused pathways, but less international brand recognition.
Visa Policy as a Geopolitical Tool
This isn’t just about immigration—it’s geopolitics of talent.
- The U.S. is restricting access, tightening its visa system, and raising barriers.
- China is lowering hurdles, offering predictability, and using visas to recruit global STEM talent.
For Indian students and graduates, the decision could determine not only career opportunities but also which global power they contribute to.
As Trump’s H-1B fee turns the U.S. into a costly gamble, China’s K-Visa opens a new door for Indian students abroad. The choice ahead is sharper than ever: pursue the prestige of U.S. opportunities despite the risks, or explore China’s emerging, state-backed ecosystem with fewer bureaucratic barriers. Either way, the global battle for STEM talent has begun — and Indian students are right at the center of it.











Comments