Manik Study Abroad Content Specialist
Study Abroad Content Specialist | Updated On - Aug 27, 2025
For Indian students planning to study abroad, one of the first decisions is whether to apply to a college or a university. This choice can shape the academic experience, career prospects, and overall return on investment.
In India, universities are degree-awarding institutions, while colleges are usually affiliated with a university. Colleges in India cannot grant degrees independently. Universities offer undergraduate, postgraduate, and doctoral programs, whereas most colleges primarily offer undergraduate courses and select postgraduate programs.
In countries such as the USA, Canada, UK, Australia, and New Zealand, the distinction between colleges and universities is different from India. In the US, for example, universities typically enroll 5,000–50,000 students and offer extensive research facilities. Whereas many colleges have fewer than 5,000 students and focus on smaller class sizes and personalized teaching. In Canada and the UK, colleges often provide diploma or vocational training, while universities offer full degree programs.
Knowing the difference between university and college will help applicants to make an informed decision, select the right study destination, and plan your higher education pathway effectively.
Also Check: Best Countries for Studying Abroad
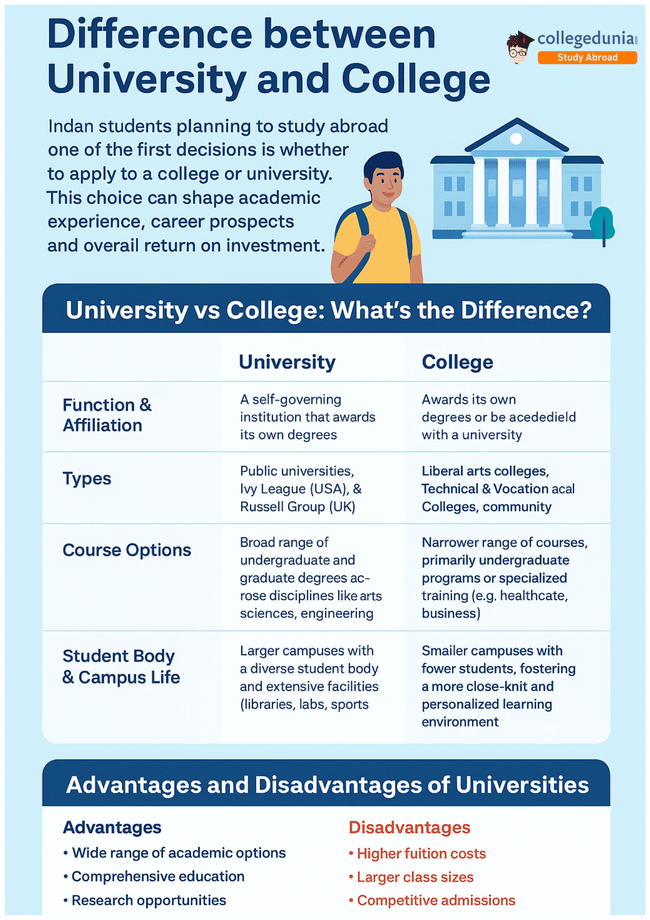
University vs College: What’s the Difference?
While “university” and “college” are often used interchangeably, they differ in structure, scope, and learning approach—especially in countries like the USA, UK, Canada, and India. Below is a side-by-side comparison to help you understand these differences better.
| Key Parameter | University | College |
|---|---|---|
| Function & Affiliation | A self-governing institution that awards its own degrees and often contains multiple colleges or faculties. Engages in teaching, research, and societal development. | May award its own degrees or be affiliated with a university for accreditation. Typically, offers fewer programs, often with a focus on undergraduate education. |
| Types | Public Universities, Private Universities, Ivy League (USA), Russell Group (UK), Open Universities. | Liberal Arts Colleges, Technical & Vocational Colleges, Community Colleges, Art & Design Colleges, Military Colleges. |
| Course Options | Broad range of undergraduate and graduate degrees across disciplines like arts, sciences, engineering, and business. Often offers flexible formats like online and distance learning. | Narrower range of courses, primarily undergraduate programs or specialized training (e.g., healthcare, business). Designed for quick workforce entry. |
| Common Courses | Humanities, Social Sciences, Engineering, Business & Economics, Fine Arts, Media Studies, Political Science, Linguistics, Architecture & Design. | Humanities, Mathematics, Computer Science, Business, Engineering, Health Sciences, Education, Fine Arts, Public Administration, Linguistics. |
| Learning Approach | Emphasis on research-based learning, independent study, and critical thinking. | Focus on hands-on, practical training and experiential learning for job readiness. |
| Student Body & Campus Life | Larger campuses with a diverse student body and extensive facilities (libraries, labs, sports arenas). | Smaller campuses with fewer students, fostering a more close-knit and personalized learning environment. |
| Cost | Generally higher tuition fees due to broader facilities, research infrastructure, and program diversity. | More affordable, as infrastructure and program range are limited. |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Universities
Choosing a university education comes with both opportunities and challenges. Below is a detailed breakdown to help students make an informed decision.
Advantages of Universities
- Wide Range of Academic Options – Universities offer diverse programs across multiple disciplines, enabling students to explore different fields and even change majors.
- Comprehensive Education – Combines general education with specialized studies, ensuring a well-rounded academic foundation.
- Research Opportunities – Access to cutting-edge research, laboratories, and funded projects.
- Extensive Resources and Facilities – Well-equipped libraries, labs, advanced technology, and career centers.
- Networking Opportunities – Large, diverse student bodies and alumni networks provide valuable professional connections.
- Interdisciplinary Learning – Opportunities to integrate and connect knowledge across different fields.
- Graduate & Professional Programs – Pathways to advanced degrees in law, medicine, engineering, and more.
- Global Exposure – International exchange programs and global partnerships foster cultural learning.
- Prestige & Recognition – Well-known universities often carry a strong brand image that can boost career prospects.
- Extracurricular Activities – Access to student clubs, sports teams, and leadership organizations.
Disadvantages of Universities
- Higher Tuition Costs – University education is often more expensive compared to community colleges or vocational schools.
- Larger Class Sizes – Less one-on-one interaction with professors, especially in the first years.
- Competitive Admissions – Stricter entry requirements and limited acceptance rates.
- Bureaucratic Processes – Administrative procedures can be slow and complex.
- Research-Focused Curriculum – May not align with students seeking more career-focused training.
- High Academic Pressure – Rigorous coursework and demanding assessments can lead to stress.
- Limited Access to Professors – Faculty availability may be constrained due to research commitments.
- Increased Competition – A highly competitive environment among peers.
- Impersonal Lectures – Large lecture halls may reduce interactive learning experiences.
- Less Flexibility in Courses – Rigid degree structures may limit elective choices.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Colleges
Colleges offer a more focused and accessible path to higher education, but like universities, they have unique strengths and challenges. Below is a breakdown of the key advantages and disadvantages of attending a college.
| Advantages of Colleges | Disadvantages of Colleges |
|---|---|
| Lower Tuition Fees – Generally more affordable than universities, making them attractive for budget-conscious students. | Limited Academic Options – Fewer degree programs and majors compared to universities. |
| Smaller Class Sizes – Allows for more personalized attention and interaction with professors. | Fewer Research Opportunities – Less emphasis on large-scale research projects and innovation. |
| Career-Focused Programs – Strong emphasis on practical skills and job readiness, especially for vocational fields. | Limited Advanced Degrees – Often do not offer master’s or doctoral programs. |
| Easier Admission Requirements – More accessible entry criteria compared to competitive university admissions. | Fewer Resources and Facilities – Smaller libraries, labs, and extracurricular infrastructure. |
| Flexible Learning Paths – Many offer part-time, evening, or online courses for working students. | Lower Global Recognition – May lack the prestige and international reputation of major universities. |
| Close-Knit Community – Encourages stronger relationships between students, faculty, and staff. | Narrower Networking Scope – Alumni and industry connections may be smaller in scale. |
| Faster Entry into the Workforce – Programs are often shorter, enabling quicker employment. | Limited Campus Life – Fewer extracurricular activities and cultural exchange opportunities. |
Popular Colleges and Universities Abroad
Indian students have a wide range of international higher education options, from research-focused universities to skill-oriented colleges. Below are some of the most notable institutions, grouped by country and type, along with their key benefits.
USA – Community Colleges
Community colleges (junior or two-year colleges) offer affordable pathways to higher education or vocational training. They award associate degrees, certificates, and often provide transfer routes to four-year universities.
Notable Institutions:
- Santa Monica College
- Pasadena City College
- Miami Dade College
- Valencia College
- Lone Star College
- Austin Community College
- Cuyahoga Community College
- Community College of Philadelphia
- Montgomery College
- Northern Virginia Community College
Also Read: Community Colleges in USA
Canada – SPP Colleges
The Student Partners Program (SPP) is a joint initiative between the Association of Canadian Community Colleges (ACCC) and Citizenship and Immigration Canada (CIC), designed to simplify visa processing for Indian students. These institutions are known for their technical, vocational, and diploma programs, with some also offering degrees.
Notable SPP Colleges:
- Algonquin College
- Bow Valley College
- Cambrian College
- Camosun College
- Canadore College
- Durham College
- Lakeland College
Know More: SSP Program in Canada
Australia – TAFE Institutes
Technical and Further Education (TAFE) institutes provide vocational training ranging from short courses to multi-year diplomas. They are ideal for students aiming to develop job-ready skills and enter the workforce quickly.
Popular TAFE Institutes:
- South Metropolitan TAFE
- Northern Sydney Institute of TAFE
- William Angliss Institute of TAFE
- Central Regional TAFE
- Hunter Institute of TAFE
- TAFE Queensland
- TAFE NSW
New Zealand – Institutes of Technology and Polytechnics (ITPs)
Government-owned and funded, ITPs focus on applied learning and practical skills, making them an attractive option for students seeking employment after graduation.
Well-Known ITPs:
- Eastern Institute of Technology
- Manukau Institute of Technology
- Nelson Marlborough Institute of Technology
- North Tec
- Otago Polytechnic
UK – Sixth Form Colleges
Sixth Form Colleges cater to students aged 16–19 and focus on A-levels, BTECs, and other pre-university qualifications. Known for smaller class sizes and strong academic support.
Top Sixth Form Colleges:
- Oxford International College
- Brampton College
- King’s College London Mathematics School
- Cardiff Sixth Form College
- Hurtwood House
- Abbey College Cambridge
- Ashbourne Independent Sixth Form College
Also Read:
Top Universities in the World 2026
The QS World University Rankings 2026 highlight institutions excelling in research, teaching quality, employability, and global engagement. Below are the top-ranked universities globally:
| Rank | University Name | Location |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) | Cambridge, United States |
| 2 | Imperial College London | London, United Kingdom |
| 3 | Stanford University | Stanford, United States |
| 4 | University of Oxford | Oxford, United Kingdom |
| 5 | Harvard University | Cambridge, United States |
| 6 | University of Cambridge | Cambridge, United Kingdom |
| 7 | ETH Zurich – Swiss Federal Institute of Technology | Zürich, Switzerland |
| 8 | National University of Singapore (NUS) | Singapore, Singapore |
| 9 | University College London (UCL) | London, United Kingdom |
| 10 | California Institute of Technology (Caltech) | Pasadena, United States |
Check Out: Top Universities in the World
Choosing between a university and a college depends on academic goals, career aspirations, and preferred learning environment. Universities often provide a wider range of programs, research opportunities, and global recognition. Colleges may offer smaller class sizes, lower tuition costs, and a more personalized approach. By carefully considering the advantages and disadvantages of each, students can make an informed decision that aligns with their future plans.
FAQs
Ques: What is the main difference between a college and a university abroad?
Ans: A university is typically a larger institution offering undergraduate, postgraduate, and research programs, while a college often focuses on undergraduate or vocational training with smaller class sizes.
Ques: Which is better for Indian students — college or university?
Ans: It depends on your goals. Universities offer broader academic options, research opportunities, and global recognition. Colleges provide lower costs, more personal attention, and career-focused programs.
Ques: Are colleges abroad less prestigious than universities?
Ans: Not always. While universities often have stronger global reputations, many colleges—especially in the USA, Canada, and the UK—are well-regarded for their specialized programs and industry connections.
Ques: Which option is cheaper for studying abroad?
Ans: Colleges generally have lower tuition fees compared to universities, making them a more affordable option for budget-conscious students.
Ques: Can I transfer from a college to a university abroad?
Ans: Yes. Many community colleges and vocational institutions have transfer agreements with universities, allowing students to complete their degrees at a four-year institution.
Ques: Do universities offer more job opportunities than colleges?
Ans: Universities often have wider alumni networks and more global recognition, which can open more career opportunities. However, colleges excel in practical training for direct workforce entry.
Ques: What are the top universities in the world in 2026?
Ans: The top three are Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Imperial College London, and Stanford University.



Comments