Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Exercise 6.2 Solutions are based on alternate interior angles, alternate exterior angles, corresponding angles, Interior angles on the same side of the transversal and more.
Download PDF: NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.2 Solutions
Check out NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.2 Solutions
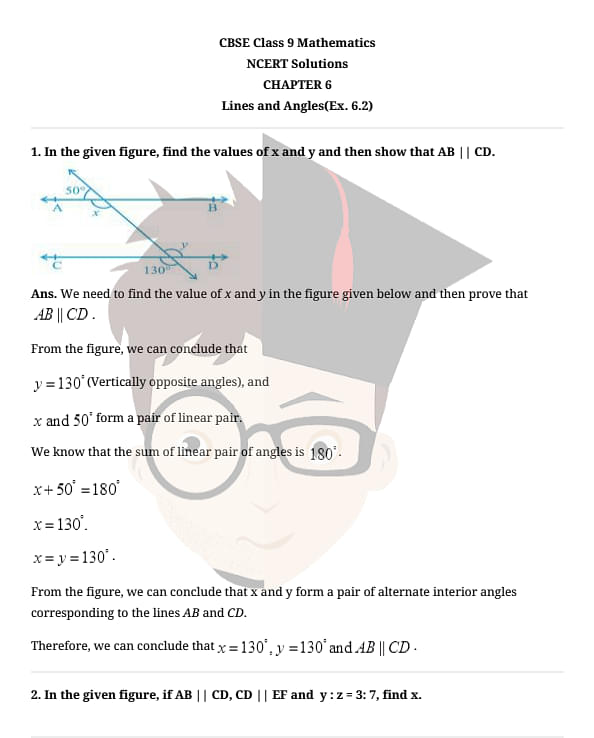





Read More: NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles
Exercise Solutions of Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles
Also check other Exercise Solutions of Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Exercise 6.1 Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Exercise 6.3 Solutions
Also Check:
Also check:




Comments