The CLAT Syllabus for PG has 120 questions, which have to be completed in a 2-hour time limit. The CLAT PG Syllabus is based on the LLB core subjects. CLAT PG syllabus 2026 covers detailed subjects for the Postgraduate admission to a 1-year integrated LLM program at 21 National Law Universities (NLUs) across India.
The CLAT PG Syllabus 2026 mainly focuses on understanding core law subjects from the LL.B. studies, along with analytical and comprehension skills.
Now, if we look at the CLAT PG syllabus, it is divided into 13 subjects. Each subject has its sub-topics and different weightage in the exam.
- Every right response has 1 mark, and for every incorrect response, 0.25 marks are cut.
- Constitution, Jurisprudence, Contract, and Criminal combined constitute 50% of the paper.
- Subjects like Tax or Public International Law have 4–6 marks per passage.
- The exam is passage-based and has from extracts from Supreme Court judgments, statutes, and regulations.

Key Summary
In this article, we have given details regarding the CLAT PG syllabus, exam pattern, topic-wise weightage, crucial books, and tips for preparation.
- The CLAT PG syllabus contains 13 varying subjects.
- Subjects such as Constitution, Jurisprudence, Contract, and Criminal Law collectively cover over 50% of the paper.
- The CLAT PG Exam is held offline and consists of 120 multiple-choice questions (MCQs). It is to be answered within 2 hours.
- Candidates should practice high-weightage subjects and comprehension-type questions. It will assist candidates in performing well in the exam.
Also Check:
CLAT PG 2026 Exam Pattern
The CLAT PG exam is based on objective-type questions. It is held once every year, mostly in December, in the offline mode. The candidates have to attempt a total of 120 questions in 2 hours. The table mentioned below shows the CLAT PG exam pattern, providing a clear overview of the subjects, number of questions, and marks distribution for the upcoming exam.
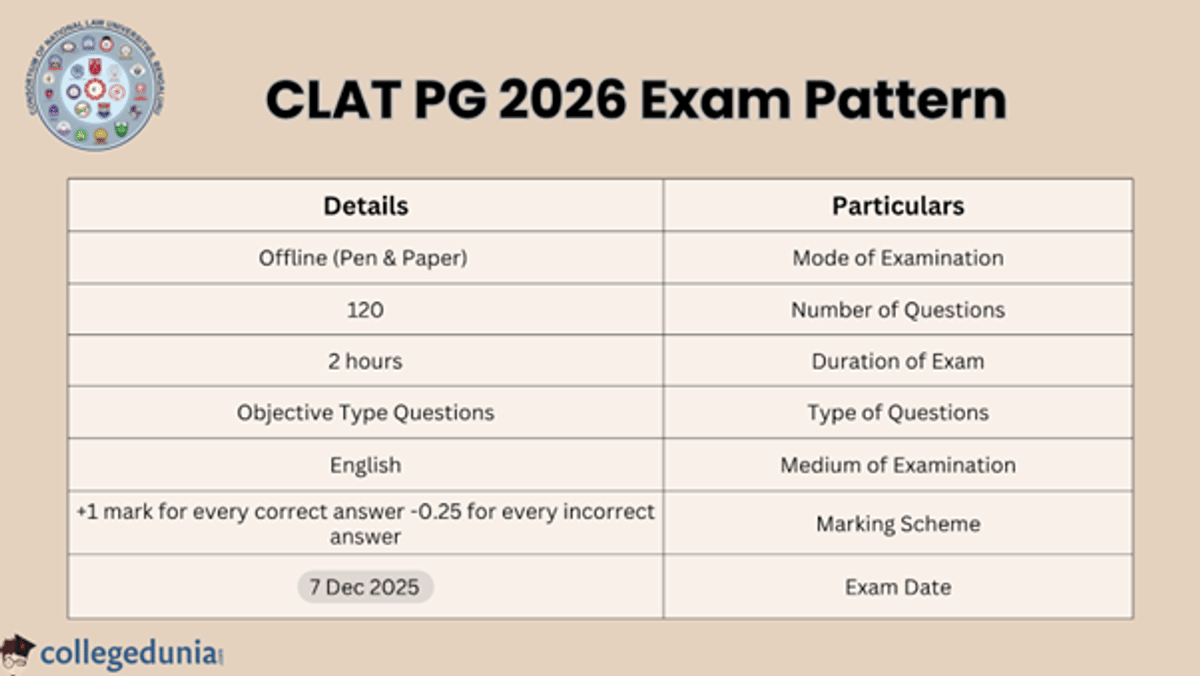
| Details | Particulars |
|---|---|
| Offline (Pen & Paper) | Mode of Examination |
| 120 | Number of Questions |
| 2 hours | Duration of Exam |
| Objective Type Questions | Type of Questions |
| English | Medium of Examination |
| +1 mark for every correct answer -0.25 for every incorrect answer | Marking Scheme |
| Which Skills will be tested? |
What is CLAT PG Syllabus 2026?
The CLAT Postgraduate syllabus is divided into many subtopics. The exam will test you on the core law subjects from LL.B., and the subtopics for the CLAT syllabus for PG are mentioned below:
- Constitutional Law
- Jurisprudence
- Administrative Law
- Law of Contract
- Torts
- Family Law
- Criminal Law
- Property Law
- Corporate Law
- Public International Law
- Tax Law
- Environmental Law
- Labour & Industrial Law
The sub-topics for CLAT PG subjects are mentioned below in the table:
| Subjects | Sub-Topics |
|---|---|
| Constitutional Law |
|
| Jurisprudence |
|
| Administrative Law |
|
| Law of Contract |
|
| Torts |
|
| Family Law |
|
| Criminal Law |
|
| Property Law |
|
| Corporate Law |
|
| Public International Law |
|
| Tax Law |
|
| Environmental Law |
|
| Labour & Industrial Law |
|
CLAT PG Syllabus Subject-Wise Importance & Weightage
The CLAT PG Syllabus has 13 subjects. Each subject has its own weightage and some main topics that the candidates should focus on. Subjects such as Constitution, Jurisprudence, Contract, and Criminal Law collectively cover over 50% of the paper. The table given below shows the subject-wise weightage for the CLAT PG test, which will help candidates to understand how the marks are distributed for different topics.
| Subject | What to Cover? | Estimated Weightage (out of 120) |
|---|---|---|
| Criminal Law |
| 10–15 marks |
| Constitutional Law |
| 10 marks |
| Jurisprudence |
| 10 marks |
| Family Law |
| 5–10 marks |
| Public International Law |
| 5–10 marks |
| Corporate Law |
| 5–10 marks |
| Environmental Law |
| 5–10 marks |
| Law of Contract |
| 5–10 marks |
| Property Law |
| 5 marks |
| Arbitration & Conciliation |
| 5 marks |
| Intellectual Property Rights |
| 5 marks |
| Labour & Industrial Law |
| 5 marks |
| Administrative Law |
| 5 marks |
| Tax Law |
| 5 marks |
| Law of Torts |
| 5 marks |
CLAT PG 2026 Important Books
Preparing for the exam is very important, but having the right books is equally crucial. The table below shows the important books that are essential for CLAT PG 2026 preparation.
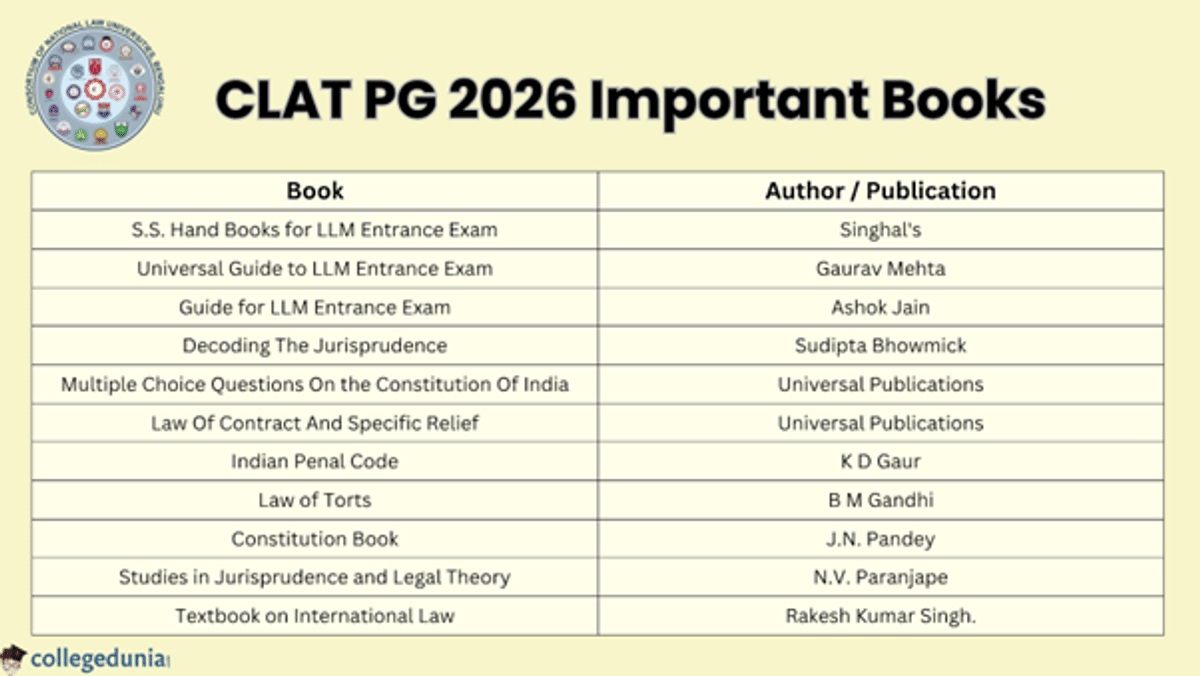
| Book | Author / Publication |
|---|---|
| S.S. Hand Books for LLM Entrance Exam | Singhal's |
| Universal Guide to LLM Entrance Exam | Gaurav Mehta |
| Guide for LLM Entrance Exam | Ashok Jain |
| Decoding The Jurisprudence | Sudipta Bhowmick |
| Multiple Choice Questions On the Constitution Of India | Universal Publications |
| Law Of Contract And Specific Relief | Universal Publications |
| Indian Penal Code | K D Gaur |
| Law of Torts | B M Gandhi |
| Constitution Book | J.N. Pandey |
| Studies in Jurisprudence and Legal Theory | N.V. Paranjape |
| Textbook on International Law | Rakesh Kumar Singh. |
In addition to physical books, online resources and e-books should be utilized:
- Legal Databases: Access court cases, laws, and legal documents via databases like Westlaw, LexisNexis, and Manupatra.
- YouTube Video Tutorials: The LegalEdge After College YouTube channel can be a visual help in understanding difficult concepts.
- E-Libraries: Platforms like JSTOR and the National Digital Library offer academic journals and research papers.
- E-Books and Study Guides: E-books from publishers like Pearson, Wolters Kluwer, and Oxford University Press that are often updated with the latest exam patterns are also helpful.
CLAT PG Syllabus 2026 - Important Topics
The CLAT PG Syllabus has remained consistent for years, and it has not been changed for 2026 either. But there are some topics that are important for the CLAT PG 2026 exam.
Important topics for CLAT PG 2026
Uniform Civil Code - Uttarakhand (2024)
- First Indian State to implement a full UCC.
- Uniform laws on marriage, divorce, and inheritance across all religions.
- Excludes Scheduled Tribes.
- Relevant for debates on Articles 14, 25-28, 44.
Waqf (Amendment) Act, 2025 + Repeal of Mussalman Waqf Act, 1923
- Introduces new governance mechanisms for Waqf properties.
- Adds mandatory representation for Muslim Women.
- Allows appeal in the High Court.
- Controversial due to the involvement of non-Muslims in boards.
New Labour Codes
Four consolidated codes:
- Codes on Wages
- Industrial Relations Code
- Social Security Code
- Occupational Safety Code
Aim: Simplification and digitization of compliance.
Yet to be implemented in full across states.
Immigration and Foreigners Bill, 2025
- Replaces outdated laws on immigration.
- Compulsory documentation for entry/exit.
- Establishment of a centralized Bureau of immigration.
- Security-based screening provisions.
Criminal Law Reforms (In Force from July 1, 2024)
- Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS) - Replaces IPC
- Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS) - Replaces CrPC
- Bharatiya Sakshya Adhiniyam (BSA) - Replaces the Indian Evidence Act.
Key Changes:
- New definitions (e.g., terrorism, mob lynching)
- Sedition removed
- Electronic evidence emphasis
- Timelines for investigation and trial.
- Community service as punishment.
Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023
- First comprehensive data protection law in India.
- Interlinks with Article 21 (Right to Privacy)
- Based on the consent architecture and the rights of data principals.
- Replaces previous Personal Data Protection Bill proposals.
Apart from these, there are some other important topics that the candidates should look for in CLAT PG 2026:
Landmark Judgments for CLAT PG 2026
Many major court judgments are mostly asked in the CLAT PG exam. The candidates should know about the cases and their key significances, and the major changes they have made in our law.
| Case | Year | Key Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Navtej Singh Johar v. Union of India | 2018 | Decriminalized consensual homosexuality; Section 377 read down |
| K.S. Puttaswamy v. Union of India | 2017, 2018 | Right to privacy is fundamental; limits on Aadhaar usage |
| Indian Young Lawyers Association v. State of Kerala | 2018 | Allowed women of all ages into Sabarimala temple |
| Shayara Bano v. Union of India | 2017 | Declared instant triple talaq unconstitutional |
| In Re: Article 370 | 2023 | Upheld removal of J&K special status; reorganisation valid |
| Association for Democratic Reforms v. Union of India | 2024 | Cancelled Electoral Bonds Scheme; political funding transparency |
| Janhit Abhiyan v. Union of India | 2022 | Upheld 10% EWS reservation in education/jobs |
| M. Nagaraj v. Union of India | 2006 | Allowed reservations in promotions with conditions |
| Shreya Singhal v. Union of India | 2015 | Struck down Section 66A; protected online free speech |
| Common Cause v. Union of India | 2018 | Legalised passive euthanasia; living will recognised |
| Vineeta Sharma v. Rakesh Sharma | 2020 | Daughters have equal rights in ancestral property |
| BALCO v. Kaiser Aluminium | 2012 | Indian courts can’t interfere in foreign-seated arbitrations |
| Swiss Ribbons Pvt. Ltd. v. Union of India | 2019 | Upheld Insolvency & Bankruptcy Code (IBC) |
| Kulbhushan Jadhav Case (ICJ) | 2017 | Pakistan violated consular access; ICJ ruled in India’s favour |
| Jarnail Singh v. Lachhmi Narain Gupta | 2018 | SC/ST promotions: creamy layer excluded, no fresh proof needed |
| Steel Authority of India Ltd. v. National Union Waterfront Workers | 2001 | Contract workers don’t automatically become permanent |
| Lily Thomas v. Union of India | 2013 | MPs/MLAs disqualified immediately if convicted of 2+ yrs |
| NALSA v. Union of India | 2014 | Recognised transgender persons as third gender |
| T.M.A. Pai Foundation v. State of Karnataka | 2002 | Defined minority educational institutions’ rights |
| Bilkis Yakub Rasool v. Union of India | 2024 | Quashed remission of convicts in Bilkis Bano case |
| Anuradha Bhasin v. Union of India | 2020 | Set limits on internet shutdowns; must be reasonable |
| Arnesh Kumar v. State of Bihar | 2014 | Prevented unnecessary arrests; police must follow CrPC |
| Kaushal Kishor v. State of UP | 2023 | Ministers’ hate speech: individuals accountable, not government |
Supreme Court Judgments of 2025 for CLAT PG 2026
Some important Supreme Court Judgments of 2025 that can be asked in CLAT PG 2026 are mentioned below. Candidates should understand clearly the main issues and the judgments passed on those issues.
| Case Name | Key Issue(s) | Judgment / Principle |
|---|---|---|
| Gayatri Balasamy v ISG Novasoft | Can courts modify arbitral awards under Sections 34 & 37 of 1996 Act? | Limited modification allowed: clerical errors, interest, severable parts; Article 142 can be invoked in exceptional cases. Dissent: No power to modify, only set aside. |
| All India Judges Association v Union of India | Restore 3-year practice requirement for Civil Judge (Jr.) eligibility | 3-year practice mandatory, counted from provisional Bar registration; law clerk experience considered; applies prospectively. |
| Varshatai v State of Maharashtra | Use of additional language (Urdu) on municipal signboard | Permissible; 2022 Act does not prohibit additional languages alongside Marathi. |
| Imran Pratapgarhi v State of Gujarat | Posting a poem promoting sacrifice & non-violence | FIR quashed; no offense under BNS; violated Article 19(1)(a) rights. |
| State of Tamil Nadu v Governor of TN | Governor’s delay in assenting to state bills | Delay unconstitutional; Article 142 used to deem assent; timelines fixed; Governor has no absolute veto. |
| Rakesh Kumar Verma & Deepti Bhatia v HDFC Bank | Validity of exclusive jurisdiction clauses in employment contracts | Exclusive jurisdiction clauses valid; suits outside agreed forum dismissed; Section 28 Contract Act not violated. |
| Jitender @ Kalla v State (NCT of Delhi) | Criteria for Senior Advocate designation | Holistic assessment required (integrity, ethics, mentorship, skill); gown differences have no legal basis. |
| Jharkhand Urja Utpadan Nigam Ltd v Heavy Electricals Ltd | Limitation period for commercial appeals | Limitation starts from pronouncement date, not receipt of judgment copy. |
| Amlesh Kumar v State of Bihar | Narco-analysis test rights & admissibility | Cannot force narco-test; voluntary request allowed but not absolute; cannot be sole basis for conviction. |
| Mahnoor Fatima Imran v Visweswara Infrastructure | Effect of unregistered sale deeds | Registration ≠ title; invalid agreements cannot transfer ownership; writ relief denied if no lawful title. |
| Independent Sugar Corp Ltd v Girish Juneja | CCI approval under IBC | Prior CCI approval mandatory before CoC approval; NCLAT’s “directory” view overturned. |
| Urmila Dixit v Sunil Sharan Dixit | Senior citizen’s right to reclaim transferred property | Gift deed can be cancelled under Section 23 if maintenance obligations not met; possession can be restored. |
| Jyotsnamayee Mishra v State of Odisha | Negative discrimination in promotion | Employee cannot claim promotion to direct-recruit post; internal circulars cannot bypass open recruitment; Article 14 violation prevented. |
| Vihaan Kumar v State of Haryana | Arrest procedure & treatment | Arrest illegal due to violation of Art 22(1); handcuffing in hospital violated Art 21; immediate release ordered. |
| Sunil Kumar Singh v Bihar Legislative Assembly | Challenge to legislative expulsion | Expulsion quashed as disproportionate; Art 212(1) bars procedural review, not legality of punishment. |
CLAT PG Previous Year Question Paper
Solving CLAT PG previous year question papers is an important strategy, as it will make the candidates familiar with the pattern of the exam, types of questions, and difficulty level of the CLAT PG exam.
| CLAT PG PYQs | Download Question Paper | Download Solution |
|---|---|---|
| 2025 (Set A) | Download Question Paper | Download Solution |
| 2025 (Set B) | Download Question Paper | Download Solution |
| 2025 (Set C) | Download Question Paper | Download Solution |
| 2025 (Set D) | Download Question Paper | Download Solution |
| 2024 (Set A) | Download Question Paper | Download Solution |
| 2024 (Set B) | Download Question Paper | Download Solution |
| 2024 (Set C) | Download Question Paper | Download Solution |
| 2024 (Set D) | Download Question Paper | Download Solution |
| 2023 | Download Question Paper | Download Solution |
| 2022 | Download Question Paper | Download Solution |
CLAT PG 2026 Preparation Tips
The following table shows the effective preparation strategies for CLAT PG 2026 that the candidates need to adapt to improve their performance and utilize their study time effectively.
| Tip | Details |
|---|---|
| Focus on Major Subjects | Constitution, Jurisprudence, Contract, and Criminal together make up more than 50% of the paper. |
| Tackle Smaller Subjects | Revise quickly using one-liners, case briefs, and bare provisions. |
| Practice Like a Real Test | Solve previous year papers and passage-based timed mocks. |
| Don’t Ignore Small Marks | Subjects like Tax or PIL can give easy 4–6 marks per passage. |
| Read Recent + Landmark Judgments | Regularly read Supreme Court judgments and legal current affairs. |
| Practice Comprehension + Application | Focus on passage-based MCQs, not just memorization. |
| Stay Updated with Current Affairs | Keep track of changes in laws like the RTI Act. |
| Dedicated Time for Jurisprudence | Spend enough time, as it’s important for the exam and the practical legal field. |
| Read Newspapers Regularly | Helps with comprehension skills and staying updated with current affairs. |
| Regular Mock Tests | Take mocks to understand the exam pattern and find strong/weak areas. |
Mostly Asked Questions
Ques: Is CLAT PG held twice a year?
Ans: No, CLAT PG is not organized twice a year. It is organized once a year, generally in December.
Ques: Who is eligible for CLAT PG?
Ans: Applicants should have passed LL.B. (Bachelor of Laws) or equivalent degree from a recognized university.
Minimum Marks:
- General / OBC / PwD / NRI / PIO / OCI candidates: LL.B. with minimum 50% marks.
- SC / ST candidates: LL.B. with minimum 45% marks.
- Applicants who are appearing in the final year of the LL.B. course can also apply, subject to the provision that they furnish proof of qualification at the time of admission.
Ques: How many marks is CLAT PG?
Ans: The total marks for the CLAT PG exam are 120, 1 mark for each question.
Ques: What are the subjects in CLAT PG?
Ans: The CLAT PG syllabus consists of 13 compulsory law subjects from the LL.B. curriculum. The subjects are designed to gauge a candidate's knowledge of basic legal principles and their application. They cover the following subjects: Constitutional Law, Jurisprudence, Contract Law, Criminal Law, Torts, Administrative Law, Family Law, Property Law, Company Law, Public International Law, Tax Law, Environmental Law, Labour and Industrial Law.
Ques: Can CLAT PG be given without LLB?
Ans: No, you cannot provide CLAT PG without an LL.B. (or equivalent law qualification) degree.
Ques: Can I crack the exam without CLAT PG coaching?
Ans: Yes, you can crack CLAT PG without coaching by making the most of online resources. The test evaluates your knowledge of main law topics from your LL.B., as well as comprehension and analytical capability.
Ques: Can I do LLM without CLAT?
Ans: Yes, it is possible to do an LL.M. without appearing for CLAT, but this depends on the university you apply for.
While the majority of National Law Universities (NLUs) in India need CLAT PG for admission, some other universities and private law colleges provide LL.M. courses through their own entrance examinations or through merit-based admission.







Comments