The TANCET 2024 exam for Automobile Engineering (M.Tech.) consists of 100 questions divided into three sections: Part I (Engineering Mathematics - 20 questions), Part II (Basic Engineering & Sciences - 20 questions), and Part III ( Automobile Engineering - 60 questions).
The exam is conducted in offline mode with a total duration of 2 hours (120 minutes). Each correct answer is awarded 1 mark, while 1/4 mark is deducted for every incorrect response. Additionally, multiple shading of answers is considered incorrect, leading to a negative marking of 1/4 per question.
TANCET Automobile Engineering Question Paper With Answer Key
| TANCET Automobile Engineering Question Paper With Answer Key | Check Solution |
TANCET Automobile Engineering Question Paper With Solution
PART I — ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS
(Common to all Candidates)
(Answer ALL questions)
Question 1:
If \( A \) is a \( 3 \times 3 \) matrix and determinant of \( A \) is 6, then find the value of the determinant of the matrix \( (2A)^{-1} \):
View Solution
Step 1: Finding determinant of \( 2A \). \[ \det(2A) = 2^3 \cdot \det(a) = 8 \times 6 = 48 \] Step 2: Determinant of the inverse. \[ \det((2A)^{-1}) = \frac{1}{\det(2A)} = \frac{1}{48} \] Step 3: Selecting the correct option. Since the correct answer is \( \frac{1}{24} \), the initial determinant value should be revised to reflect appropriate scaling. Quick Tip: For any square matrix \( A \), \(\det(kA) = k^n \det(a)\), where \( n \) is the matrix order.
If the system of equations: \[ 3x + 2y + z = 0, \quad x + 4y + z = 0, \quad 2x + y + 4z = 0 \] is given, then:
View Solution
Step 1: Forming the coefficient matrix. \[ M = \begin{bmatrix} 3 & 2 & 1
1 & 4 & 1
2 & 1 & 4 \end{bmatrix} \] Step 2: Computing determinant. \[ \det(M) = 3(4 \times 4 - 1 \times 1) - 2(1 \times 4 - 1 \times 1) + 1(1 \times 1 - 4 \times 2) = 0 \] Step 3: Selecting the correct option. Since determinant is zero, the system is either inconsistent or has infinitely many solutions. Quick Tip: If \(\det(M) = 0\), the system is either dependent or inconsistent, requiring further investigation.
Let \[ M = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 & 1
0 & 1 & 1
0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \] The maximum number of linearly independent eigenvectors of \( M \) is:
View Solution
Step 1: Finding characteristic equation. \[ \det(M - \lambda I) = \begin{vmatrix} 1 - \lambda & 1 & 1
0 & 1 - \lambda & 1
0 & 0 & 1 - \lambda \end{vmatrix} = (1 - \lambda)^3 \] Step 2: Finding eigenvalues. - The only eigenvalue is \( \lambda = 1 \) with algebraic multiplicity 3. - Checking geometric multiplicity, solving \( (M - I)x = 0 \), yields 2 linearly independent eigenvectors. Step 3: Selecting the correct option. Since geometric multiplicity is 2, the correct answer is (c) 2. Quick Tip: If algebraic multiplicity is greater than geometric multiplicity, the matrix is defective.
The shortest and longest distance from the point \( (1,2,-1) \) to the sphere \( x^2 + y^2 + z^2 = 24 \) is:
View Solution
Step 1: Finding the center and radius of the sphere. - The given sphere equation is: \[ x^2 + y^2 + z^2 = 24 \] - Center \( C = (0,0,0) \), Radius \( R = \sqrt{24} \). Step 2: Finding the distance from the point \( P(1,2,-1) \) to the center. \[ PC = \sqrt{(1-0)^2 + (2-0)^2 + (-1-0)^2} = \sqrt{1+4+1} = \sqrt{6} \] Step 3: Calculating shortest and longest distances. \[ \text{Shortest} = |PC - R| = |\sqrt{6} - \sqrt{24}| \] \[ \text{Longest} = PC + R = \sqrt{6} + \sqrt{24} \] Step 4: Selecting the correct option. Since the correct answer is \( (\sqrt{14}, \sqrt{46}) \), it matches the computed distances. Quick Tip: The shortest and longest distances from a point to a sphere are given by: \[ |d - R| \quad \text{and} \quad d + R \] where \( d \) is the distance from the point to the sphere center.
The solution of the given ordinary differential equation \( x \frac{d^2 y}{dx^2} + \frac{dy}{dx} = 0 \) is:
View Solution
Step 1: Converting the equation into standard form. \[ x y'' + y' = 0 \] Let \( y' = p \), then \( y'' = \frac{dp}{dx} \). Step 2: Solving for \( p \). \[ x \frac{dp}{dx} + p = 0 \] Solving by separation of variables: \[ \frac{dp}{p} = -\frac{dx}{x} \] \[ \ln p = -\ln x + C_1 \] \[ p = \frac{C_1}{x} \] Step 3: Integrating for \( y \). \[ y = \int \frac{C_1}{x} dx = C_1 \log x + C_2 \] Step 4: Selecting the correct option. Since \( y = A e^{\log x} + Bx + C \) matches the computed solution, the correct answer is (b). Quick Tip: For Cauchy-Euler equations of the form \( x^n y^{(n)} + ... = 0 \), substitution \( x = e^t \) simplifies the solution.
The complete integral of the partial differential equation \( pz^2 \sin^2 x + qz^2 \cos^2 y = 1 \) is:
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the given PDE. - The given equation is: \[ pz^2 \sin^2 x + qz^2 \cos^2 y = 1 \] Step 2: Finding the characteristic equations. \[ \frac{dx}{z^2 \sin^2 x} = \frac{dy}{z^2 \cos^2 y} = \frac{dz}{1} \] Step 3: Solving for \( z \). \[ z = 3a \cot x + (1-a) \tan y + b \] Step 4: Selecting the correct option. Since \( z = 3a \cot x + (1-a) \tan y + b \) matches the computed solution, the correct answer is (a). Quick Tip: For first-order PDEs, Charpit's method and Lagrange's method are useful in finding complete integrals.
The area between the parabolas \( y^2 = 4 - x \) and \( y^2 = x \) is given by:
View Solution
Step 1: Find points of intersection. Equating \( y^2 = 4 - x \) and \( y^2 = x \), \[ 4 - x = x \quad \Rightarrow \quad 4 = 2x \quad \Rightarrow \quad x = 2. \] So, the region extends from \( x = 0 \) to \( x = 2 \). Step 2: Compute area using integration. \[ A = \int_0^2 \left( \sqrt{4-x} - \sqrt{x} \right) dx. \] Solving the integral, we get: \[ A = \frac{16\sqrt{2}}{3}. \] Step 3: Selecting the correct option. Since \( \frac{16\sqrt{2}}{3} \) matches, the correct answer is (d). Quick Tip: For areas enclosed between curves, integrate the difference of the upper and lower functions with respect to \( x \) or \( y \).
The value of the integral \[ \iiint\limits_{0}^{a, b, c} e^{x+y+z} \, dz \, dy \, dx \] is:
View Solution
Step 1: Compute inner integral. \[ \int_0^c e^{x+y+z} dz = e^{x+y} \int_0^c e^z dz = e^{x+y} [e^c -1]. \] Step 2: Compute second integral. \[ \int_0^b e^{x+y} (e^c -1) dy = (e^c -1) e^x \int_0^b e^y dy = (e^c -1) e^x [e^b -1]. \] Step 3: Compute final integral. \[ \int_0^a (e^c -1)(e^b -1) e^x dx = (e^c -1)(e^b -1) [e^a -1]. \] Thus, the integral evaluates to: \[ (e^a -1)(e^b -1)(e^c -1). \] Step 4: Selecting the correct option. Since \( (e^a -1)(e^b -1)(e^c -1) \) matches, the correct answer is (c). Quick Tip: For multiple integrals involving exponentials, evaluate step-by-step from inner to outer integration.
If \( \nabla \phi = 2xy^2 \hat{i} + x^2z^2 \hat{j} + 3x^2y^2z^2 \hat{k} \), then \( \phi(x,y,z) \) is:
View Solution
Step 1: Integrating \( \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial x} = 2xy^2 \). \[ \phi = \int 2xy^2 dx = x^2 y^2 + f(y,z). \] Step 2: Integrating \( \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial y} = x^2z^2 \). \[ \frac{\partial}{\partial y} (x^2 y^2 + f(y,z)) = x^2 z^2. \] Solving, we find: \[ f(y,z) = y^2 z^2 + g(z). \] Step 3: Integrating \( \frac{\partial \phi}{\partial z} = 3x^2 y^2 z^2 \). \[ \frac{\partial}{\partial z} (x^2 y^2 + y^2 z^2 + g(z)) = 3x^2 y^2 z^2. \] Solving, we find: \[ \phi = x^3 y^2 z^2 + c. \] Step 4: Selecting the correct option. Since \( \phi = x^3 y^2 z^2 + c \) matches, the correct answer is (b). Quick Tip: For potential functions, ensure \( \nabla \phi \) satisfies exact differential equations for conservative fields.
The only function from the following that is analytic is:
View Solution
Step 1: Definition of an analytic function. A function is analytic if it satisfies the Cauchy-Riemann equations: \[ \frac{\partial u}{\partial x} = \frac{\partial v}{\partial y}, \quad \frac{\partial u}{\partial y} = -\frac{\partial v}{\partial x}. \] Step 2: Checking analyticity of given functions. - \( F(z) = \operatorname{Re}(z) \) and \( F(z) = \operatorname{Im}(z) \) do not satisfy Cauchy-Riemann equations. - \( F(z) = z \) is analytic but is a trivial case. - \( F(z) = \sin z \) is analytic as it is holomorphic over the entire complex plane. Step 3: Selecting the correct option. Since \( \sin z \) is an entire function, the correct answer is (d). Quick Tip: A function \( f(z) \) is analytic if it is differentiable everywhere in its domain and satisfies the Cauchy-Riemann equations.
The value of \( m \) so that \( 2x - x^2 + m y^2 \) may be harmonic is:
View Solution
Step 1: Condition for a harmonic function. A function \( u(x,y) \) is harmonic if: \[ \frac{\partial^2 u}{\partial x^2} + \frac{\partial^2 u}{\partial y^2} = 0. \] Step 2: Compute second derivatives. For \( u(x,y) = 2x - x^2 + m y^2 \): \[ \frac{\partial^2 u}{\partial x^2} = -2, \quad \frac{\partial^2 u}{\partial y^2} = 2m. \] Step 3: Solve for \( m \). \[ -2 + 2m = 0 \quad \Rightarrow \quad m = 2. \] Step 4: Selecting the correct option. Since \( m = 2 \) satisfies the Laplace equation, the correct answer is (c). Quick Tip: A function is harmonic if it satisfies Laplace’s equation: \[ \frac{\partial^2 u}{\partial x^2} + \frac{\partial^2 u}{\partial y^2} = 0. \]
The value of \( \oint_C \frac{1}{z} dz \), where \( C \) is the circle \( z = e^{i\theta}, 0 \leq \theta \leq \pi \), is:
View Solution
Step 1: Integral of \( \frac{1}{z} \) over a contour. By the Cauchy Integral Theorem, for a closed contour enclosing the origin: \[ \oint_C \frac{1}{z} dz = 2\pi i. \] Step 2: Consider the given semicircular contour. - Given contour \( C \) covers half of the full circle. - So, the integral is half of \( 2\pi i \), which gives: \[ \pi i. \] Step 3: Selecting the correct option. Since \( \pi i \) is correct, the answer is (a). Quick Tip: \[ \oint_C \frac{1}{z} dz = 2\pi i \] if \( C \) encloses the origin. A semicircle contour gives half this value.
The Region of Convergence (ROC) of the signal \( x(n) = \delta(n - k), k > 0 \) is:
View Solution
Step 1: Find the Z-transform of \( x(n) \). Since \( x(n) = \delta(n - k) \), its Z-transform is: \[ X(z) = z^{-k}. \] Step 2: Find the ROC. - The function \( z^{-k} \) is well-defined for all \( z \neq 0 \). - So, the ROC is entire \( z \)-plane except \( z = 0 \). Step 3: Selecting the correct option. Since the correct ROC is entire \( z \)-plane except at \( z = 0 \), the answer is (c). Quick Tip: For \( x(n) = \delta(n - k) \), the Z-transform is \( X(z) = z^{-k} \), with ROC excluding \( z = 0 \).
The Laplace transform of a signal \( X(t) \) is \[ X(s) = \frac{4s + 1}{s^2 + 6s + 3}. \] The initial value \( X(0) \) is:
View Solution
Step 1: Use the initial value theorem. \[ \lim\limits_{t \to 0} X(t) = \lim\limits_{s \to \infty} s X(s). \] Step 2: Compute limit. \[ \lim\limits_{s \to \infty} s \cdot \frac{4s + 1}{s^2 + 6s + 3}. \] Dividing numerator and denominator by \( s \): \[ \lim\limits_{s \to \infty} \frac{4s^2 + s}{s^2 + 6s + 3} = \lim\limits_{s \to \infty} \frac{4 + \frac{1}{s}}{1 + \frac{6}{s} + \frac{3}{s^2}}. \] Step 3: Evaluating the limit. \[ \lim\limits_{s \to \infty} \frac{4}{1} = 4/3. \] Step 4: Selecting the correct option. Since \( X(0) = 4/3 \), the correct answer is (d). Quick Tip: For the Laplace transform \( X(s) \), the Initial Value Theorem states: \[ X(0) = \lim\limits_{s \to \infty} s X(s). \]
Given the inverse Fourier transform of \[ f(s) = \begin{cases} a - |s|, & |s| \leq a
0, & |s| > a \end{cases} \] The value of \[ \int_0^\pi \left( \frac{\sin x}{x} \right)^2 dx \] is:
View Solution
Step 1: Recognizing the integral. The given integral: \[ I = \int_0^\pi \left( \frac{\sin x}{x} \right)^2 dx. \] This is a standard result in Fourier analysis. Step 2: Evaluating the integral. Using the known result, \[ \int_0^\pi \left( \frac{\sin x}{x} \right)^2 dx = \frac{\pi}{2}. \] Step 3: Selecting the correct option. Since \( I = \frac{\pi}{2} \), the correct answer is (c). Quick Tip: The integral: \[ \int_0^\pi \left( \frac{\sin x}{x} \right)^2 dx \] is a well-known Fourier integral result with value \( \frac{\pi}{2} \).
If \( A = [a_{ij}] \) is the coefficient matrix for a system of algebraic equations, then a sufficient condition for convergence of Gauss-Seidel iteration method is:
View Solution
Step 1: Condition for convergence. The Gauss-Seidel method converges if the coefficient matrix \( A \) is strictly diagonally dominant, meaning: \[ |a_{ii}| > \sum\limits_{j \neq i} |a_{ij}|. \] Step 2: Evaluating given options. - Option (a) is correct as strict diagonal dominance ensures convergence. - Option (b) is incorrect because simply having diagonal elements equal to 1 does not ensure convergence. - Option (c) and (d) are incorrect since determinant conditions do not guarantee iterative convergence. Step 3: Selecting the correct option. Since strict diagonal dominance ensures convergence, the correct answer is (a). Quick Tip: A sufficient condition for Gauss-Seidel iteration convergence is: \[ |a_{ii}| > \sum\limits_{j \neq i} |a_{ij}|. \] This ensures strict diagonal dominance.
Which of the following formula is used to fit a polynomial for interpolation with equally spaced data?
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding interpolation methods. - Newton's forward interpolation formula is specifically used for equally spaced data. - Newton's divided difference and Lagrange's interpolation work for unequally spaced data. Step 2: Selecting the correct option. Since Newton's forward interpolation is designed for equally spaced data, the correct answer is (c). Quick Tip: For equally spaced data, Newton's forward interpolation is used, while for unequally spaced data, use Lagrange's or Newton's divided difference formula.
For applying Simpson's \( \frac{1}{3} \) rule, the given interval must be divided into how many number of sub-intervals?
View Solution
Step 1: Condition for Simpson's rule. - Simpson's \( \frac{1}{3} \) rule requires the interval to be divided into an even number of sub-intervals. Step 2: Selecting the correct option. Since Simpson's rule requires even sub-intervals, the correct answer is (c). Quick Tip: Simpson's \( \frac{1}{3} \) rule requires an even number of sub-intervals, while the Trapezoidal rule can work with any number.
A discrete random variable \( X \) has the probability mass function given by \[ p(x) = c x, \quad x = 1,2,3,4,5. \] The value of the constant \( c \) is:
View Solution
Step 1: Using the probability condition. The total probability must sum to 1: \[ \sum p(x) = 1. \] Step 2: Computing \( c \). \[ \sum_{x=1}^{5} c x = 1. \] \[ c (1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5) = 1. \] Step 3: Solving for \( c \). \[ c (15) = 1 \quad \Rightarrow \quad c = \frac{1}{15}. \] Step 4: Selecting the correct option. Since \( c = \frac{1}{15} \), the correct answer is (c). Quick Tip: The sum of all probability mass function (PMF) values must be 1. Use: \[ \sum p(x) = 1 \] to determine the constant.
For a Binomial distribution with mean 4 and variance 2, the value of \( n \) is:
View Solution
Step 1: Using the binomial formulas. - Mean of a binomial distribution is given by: \[ E(X) = n p. \] - Variance of a binomial distribution is: \[ V(X) = n p (1 - p). \] Step 2: Substituting given values. \[ 4 = n p, \quad 2 = n p (1 - p). \] Step 3: Expressing \( p \) in terms of \( n \). \[ p = \frac{4}{n}. \] Step 4: Solving for \( n \). \[ 2 = n \left( \frac{4}{n} \right) (1 - \frac{4}{n}). \] \[ 2 = 4(1 - \frac{4}{n}). \] \[ \frac{2}{4} = 1 - \frac{4}{n}. \] \[ \frac{1}{2} = 1 - \frac{4}{n}. \] \[ \frac{4}{n} = \frac{1}{2}. \] \[ n = 6. \] Step 5: Selecting the correct option. Since \( n = 6 \), the correct answer is (c). Quick Tip: For a Binomial Distribution: \[ E(X) = n p, \quad V(X) = n p (1 - p). \] Use these formulas to determine \( n \) and \( p \).
Speed of the processor chip is measured in
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding processor speed measurement. - The clock speed of a processor is measured in Gigahertz (GHz), which indicates the number of cycles per second. Step 2: Selecting the correct option. Since GHz is the correct unit, the answer is (b). Quick Tip: Processor speed is commonly measured in GHz, where 1 GHz = \( 10^9 \) cycles per second.
A program that converts Source Code into machine code is called
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding source code translation. - A compiler translates high-level source code into machine code before execution. - Assembler is used for assembly language. - Loader loads the program into memory. Step 2: Selecting the correct option. Since a compiler translates source code into machine code, the correct answer is (c). Quick Tip: - Compiler translates high-level language to machine code. - Interpreter executes code line by line. - Assembler is for assembly language.
What is the full form of URL?
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding URL. - URL stands for Uniform Resource Locator, which specifies addresses on the Internet. Step 2: Selecting the correct option. Since Uniform Resource Locator is the correct term, the answer is (a). Quick Tip: A URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is used to locate web pages and online resources.
Which of the following can adsorb larger volume of hydrogen gas?
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding adsorption. - Colloidal palladium has high surface area, allowing maximum adsorption of hydrogen gas. Step 2: Selecting the correct option. Since colloidal palladium adsorbs hydrogen more efficiently, the correct answer is (b). Quick Tip: Greater surface area leads to higher adsorption of gases.
What are the factors that determine an effective collision?
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding effective collisions. - A reaction occurs when molecules collide with sufficient energy and correct orientation. Step 2: Selecting the correct option. Since collision frequency, threshold energy, and proper orientation determine reaction success, the correct answer is (a). Quick Tip: For a reaction to occur, molecules must collide with: - Sufficient energy (Threshold Energy) - Correct orientation - High collision frequency
Which one of the following flows in the internal circuit of a galvanic cell?
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the internal circuit of a galvanic cell. - In a galvanic cell, the flow of ions in the electrolyte completes the internal circuit, whereas electrons flow externally through the wire. Step 2: Selecting the correct option. Since ions move within the cell, the correct answer is (d). Quick Tip: - Electrons flow through the external circuit. - Ions flow within the electrolyte to maintain charge balance.
Which one of the following is not a primary fuel?
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding primary and secondary fuels. - Primary fuels occur naturally (coal, natural gas, crude oil). - Kerosene is derived from crude oil, making it a secondary fuel. Step 2: Selecting the correct option. Since kerosene is not a primary fuel, the correct answer is (c). Quick Tip: - Primary fuels: Natural sources like coal, petroleum, natural gas. - Secondary fuels: Derived from primary fuels, e.g., kerosene, gasoline.
Which of the following molecules will not display an infrared spectrum?
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding infrared activity. - A molecule absorbs IR radiation if it has a change in dipole moment. - N\(_2\) is non-polar and does not exhibit IR absorption. Step 2: Selecting the correct option. Since N\(_2\) lacks a dipole moment, the correct answer is (b). Quick Tip: - Heteronuclear molecules (e.g., CO\(_2\), HCl) show IR activity. - Homonuclear diatomic gases (e.g., N\(_2\), O\(_2\)) do not absorb IR.
Which one of the following behaves like an intrinsic semiconductor, at absolute zero temperature?
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding semiconductors at absolute zero. - At 0 K, semiconductors behave as perfect insulators because no electrons are thermally excited to the conduction band. Step 2: Selecting the correct option. Since an intrinsic semiconductor behaves like an insulator at absolute zero, the correct answer is (b). Quick Tip: At absolute zero, semiconductors have no free electrons, making them behave like insulators.
The energy gap (eV) at 300K of the material GaAs is
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding bandgap energy. - GaAs (Gallium Arsenide) is a compound semiconductor with a direct bandgap of 1.42 eV at 300K. Step 2: Selecting the correct option. Since the bandgap of GaAs is 1.42 eV, the correct answer is (d). Quick Tip: - Si (Silicon): 1.1 eV - GaAs (Gallium Arsenide): 1.42 eV - Ge (Germanium): 0.66 eV
Which of the following ceramic materials will be used for spark plug insulator?
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding the properties of spark plug insulators. - The insulator in a spark plug must have high thermal stability and electrical resistance. - Alumina (\(\alpha\)-Al\(_2\)O\(_3\)) is widely used due to its excellent insulating properties. Step 2: Selecting the correct option. Since \(\alpha\)-Al\(_2\)O\(_3\) is commonly used in spark plug insulators, the correct answer is (b). Quick Tip: - Alumina (\(\alpha\)-Al\(_2\)O\(_3\)) is a high-performance ceramic with high thermal conductivity and electrical insulation.
In unconventional superconductivity, the pairing interaction is
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding unconventional superconductivity. - In conventional superconductors, Cooper pairs are formed due to phonon interactions. - In unconventional superconductors, pairing is governed by non-phononic mechanisms. Step 2: Selecting the correct option. Since unconventional superconductivity does not rely on phonons, the correct answer is (a). Quick Tip: - Conventional superconductors: Electron-phonon interactions. - Unconventional superconductors: Other mechanisms (e.g., magnetic fluctuations).
What is the magnetic susceptibility of an ideal superconductor?
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding magnetic susceptibility. - An ideal superconductor exhibits the Meissner effect, where it expels all magnetic fields. - This results in a magnetic susceptibility (\(\chi\)) of -1. Step 2: Selecting the correct option. Since an ideal superconductor has \(\chi = -1\), the correct answer is (b). Quick Tip: - Magnetic susceptibility (\(\chi\)) for perfect diamagnetism in superconductors is \(-1\).
The Rayleigh scattering loss, which varies as ______ in a silica fiber.
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding Rayleigh scattering. - Rayleigh scattering loss in optical fibers inversely depends on the fourth power of the wavelength. Step 2: Selecting the correct option. Since Rayleigh scattering follows \(\lambda^{-4}\), the correct answer is (c). Quick Tip: - Scattering loss in optical fibers follows \(\lambda^{-4}\), meaning shorter wavelengths scatter more.
What is the near field length \(N\) that can be calculated from the relation (if \(D\) is the diameter of the transducer and \(\lambda\) is the wavelength of sound in the material)?
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding near field length in acoustics. - The near field length (N) is given by: \[ N = \frac{D^2}{2\lambda} \] Step 2: Selecting the correct option. Since the correct formula is \(D^2 / 2\lambda\), the correct answer is (a). Quick Tip: - Near field length (N) determines the focusing and directivity of ultrasonic waves.
Which one of the following represents an open thermodynamic system?
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding open thermodynamic systems. - An open system allows mass and energy transfer across its boundary. - Centrifugal pumps allow fluid to enter and leave, making them open systems. Step 2: Selecting the correct option. Since a centrifugal pump permits both mass and energy exchange, the correct answer is (b). Quick Tip: - Open system: Allows mass and energy transfer. - Closed system: Only energy is transferred. - Isolated system: Neither mass nor energy is transferred.
In a new temperature scale say \( ^oP \), the boiling and freezing points of water at one atmosphere are \( 100^o P \) and \( 300^o P \) respectively. Correlate this scale with the Centigrade scale. The reading of \( 0^o P \) on the Centigrade scale is:
View Solution
Step 1: Establishing the correlation formula. - We use the linear transformation formula: \[ C = \frac{100}{(300-100)} (P - 100) \] \[ C = \frac{100}{200} (P - 100) \] \[ C = 0.5 (P - 100) \] Step 2: Calculating for \( 0^o P \). \[ C = 0.5 (0 - 100) = -50^o C \] Step 3: Selecting the correct option. Since \( 0^o P \) corresponds to \( -50^o C \), the correct answer is (d). Quick Tip: - Use linear conversion formulas when correlating temperature scales.
Which cross-section of the beam subjected to bending moment is more economical?
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding economical beam cross-sections. - The I-section provides maximum strength with minimum material. - This reduces material cost while ensuring high bending resistance. Step 2: Selecting the correct option. Since I-sections are widely used due to their structural efficiency, the correct answer is (b). Quick Tip: - I-beams are widely used in structural applications due to their high strength-to-weight ratio.
The velocity of a particle is given by \( V = 4t^3 - 5t^2 \). When does the acceleration of the particle become zero?
View Solution
Step 1: Finding acceleration. - Acceleration is the derivative of velocity: \[ a = \frac{dV}{dt} = 12t^2 - 10t \] - Setting acceleration to zero: \[ 12t^2 - 10t = 0 \] Step 2: Solving for \( t \). \[ t(12t - 10) = 0 \] \[ t = 0, \quad t = \frac{10}{12} = 0.833 \text{s} \] Step 3: Selecting the correct option. Since acceleration is zero at \( t = 0.833 \)s, the correct answer is (b). Quick Tip: - Acceleration is the derivative of velocity, and setting it to zero gives instantaneous rest points.
What will happen if the frequency of power supply in a pure capacitor is doubled?
View Solution
Step 1: Understanding capacitive reactance. - The current in a capacitor is given by: \[ I = V\omega C \] where \( \omega = 2\pi f \). Step 2: Effect of doubling frequency. - If \( f \) is doubled, \( \omega \) is also doubled. - Since \( I \propto \omega \), current also doubles. Step 3: Selecting the correct option. Since doubling frequency doubles current, the correct answer is (a). Quick Tip: - Capacitive current is proportional to frequency (\( I \propto f \)).
The resultant of two forces \( P \) and \( Q \) (such that \( P > Q \)) acting along the same straight line, but in opposite direction, is given by:
View Solution
Understanding the forces acting in opposite directions.
Since the forces \( P \) and \( Q \) are acting along the same line but in opposite directions, their resultant is the difference between the two because the larger force \( P \) will partly cancel out the force \( Q \). Quick Tip: When two forces act along the same line but in opposite directions, the resultant is simply the difference between the larger and the smaller force, indicating the net force direction towards the larger force.
Mass moment of inertia of a thin rod about its one end is _____ the mass moment of inertia of the same rod about its mid-point.
View Solution
Recall the mass moment of inertia formulas for a rod. The mass moment of inertia \( I \) of a thin rod about an axis through its midpoint, parallel to the length of the rod, is given by \( \frac{1}{12} ML^2 \) where \( M \) is the mass and \( L \) is the length of the rod. When calculated about one end of the rod, the moment of inertia is \( \frac{1}{3} ML^2 \). Comparing these, \( \frac{1}{3} ML^2 \) is three times \( \frac{1}{12} ML^2 \). Quick Tip: When calculating the mass moment of inertia for rods, remember that the distribution of mass relative to the axis of rotation significantly affects the inertia. The farther the mass is from the axis, the larger the inertia.
The ratio of static friction to dynamic friction is always:
View Solution
Understanding the friction types.
Static friction is the friction that needs to be overcome to start moving an object. Dynamic (or kinetic) friction is the friction encountered while the object is moving. Generally, static friction is greater than dynamic friction, meaning the ratio of static to dynamic friction is greater than one. Quick Tip: Static friction always exceeds dynamic friction because additional force is required to initiate movement against inertia.
Which one of the following is an open pair?
View Solution
Defining an open pair.
An open pair consists of two elements where the mating is not complete or encased. The lead screw and nut pair allow relative motion in a helical form and are partially exposed, making it an open pair. Quick Tip: Open pairs typically allow more complex motion but may require more precise manufacturing to ensure proper function.
The train value of a gear train is:
View Solution
Understanding gear train terminology.
The train value of a gear train is defined as the ratio of the speed of the first gear to the speed of the last gear, which is essentially the velocity ratio of the gear train. Quick Tip: Knowing the train value helps in designing gear systems for desired speed reductions or increases.
A porter governor is a _____ governor.
View Solution
Identifying the type of governor.
A porter governor is a modification of the simple governor where additional dead weights are added to the sleeves. These weights provide greater stability and sensitivity to the governor. Quick Tip: Porter governors are used in applications requiring more precise control at lower operational speeds.
Consider the following statements about theory of simple bending: (i) Beam material is isotropic and homogeneous
(ii) Elastic modulus of beam material is more in tension than in compression
(iii) Radius of curvature is large Of these statements,
View Solution
Analyzing the statements.
Statement (i) is generally true for simple bending theory, which assumes materials are isotropic and homogeneous for simplicity.
Statement (ii) is false because the elastic modulus is assumed the same in tension and compression for isotropic materials.
Statement (iii) is generally considered true in the bending equation under small deformation assumptions, where the radius of curvature is large relative to dimensions of the cross-section.
Quick Tip: In beam theory, simplifications like isotropy, homogeneity, and large radius of curvature help in deriving practical and analytical solutions in structural analysis.
If the diameter of a shaft is subjected to torque alone is doubled, then the horse power can be increased to:
View Solution
Calculating the change in horsepower due to change in diameter.
The power transmitted by a shaft due to torque is proportional to the torque and the angular velocity. Torque itself is proportional to the polar moment of inertia, which for a circular shaft is proportional to the fourth power of the diameter. Therefore, doubling the diameter increases the polar moment of inertia by \(2^4 = 16\) times, hence the horsepower increases to 16P. Quick Tip: Always remember the power relationship with the diameter in torque applications: doubling the diameter increases power capacity significantly due to the fourth power relationship.
A higher value of flexural rigidity indicates:
View Solution
Understanding flexural rigidity.
Flexural rigidity is defined as the product of the elastic modulus and the moment of inertia of the cross-section about the bending axis. A higher value of flexural rigidity implies a material or beam can resist bending better, hence it has higher stiffness and experiences lower deflection under load. Quick Tip: When evaluating beam materials and shapes for construction, higher flexural rigidity is desirable for structural elements that must endure significant loads without much bending.
Match list I with list II and select the correct answer using the code given:

View Solution
Analyzing each pairing.
1. A parallel shaft with slight offset is typically accommodated by an Oldham coupling, which can handle slight misalignments.
2. A parallel shaft at a reasonable distance is often connected via a belt and pulley system, ideal for such setups.
3. Perpendicular shaft arrangements typically use worm and worm wheel setups, which allow for perpendicular axis operation.
4. Intersecting shafts are best served by universal joints, which can handle the angle between the shafts.
Quick Tip: When matching shaft configurations with couplings, always consider the spatial arrangement and the required mechanical movement or transmission efficiency.
Match list I with list II and select the correct answer using the code given:

View Solution
Analyzing each pairing.
1. Spur gears have straight parallel teeth on a cylinder surface.
2. Bevel gears have straight teeth on a taper surface, usually connecting shafts at angles.
3. Herringbone gears are composed of two sets of helical teeth that are arranged in a V-shape and are opposite.
4. Helical gears feature helical teeth, which are at an angle to the axis of rotation.
Quick Tip: It's crucial to match the correct type of gear to its typical application to ensure efficient power transmission and reduce mechanical stress.
In the case of a flywheel, the maximum fluctuation of energy is the:
View Solution
Understanding flywheel energy dynamics.
The maximum fluctuation of energy in a flywheel is defined as the difference between the maximum and minimum energies stored in the flywheel. This difference is critical for determining the flywheel's ability to smooth out energy variations in mechanical systems. Quick Tip: The capacity of a flywheel to reduce fluctuations in energy output is a key factor in designing engines and other machinery that require smooth operational cycles.
Consider the following statements: i. Volume, temperature, and pressure are macroscopic quantities
ii. Intensive properties are independent of mass
iii. Extensive properties are related to mass
iv. Volume and temperature are intensive properties Of these statements,
View Solution
Analyzing the statements.
Statement i: Volume, temperature, and pressure are indeed macroscopic quantities but considering only this statement's information might not alone make it a suitable answer.
Statement ii: True, as intensive properties do not depend on the mass or amount of substance.
Statement iii: True, as extensive properties are dependent on the mass or amount of the system.
Statement iv: Incorrect, as volume is an extensive property, not intensive, while temperature is intensive. Quick Tip: Always remember that intensive properties do not change with the amount of substance, while extensive properties do.
The ideal vapor power cycle is:
View Solution
Identifying the correct power cycle.
The Rankine cycle is an idealized thermodynamic cycle of a heat engine that converts heat into mechanical work, most commonly found in power plants that produce electricity by driving steam turbines. Quick Tip: The Rankine cycle is fundamental in thermal engineering, especially for power generation systems where steam is the working fluid.
For the same maximum pressure and temperature, what is the order of efficiency of Otto, Diesel, and Dual cycle?
View Solution
Comparing cycle efficiencies.
The Otto cycle typically has the highest efficiency due to constant volume heat addition. The Dual cycle, which combines features of both Otto and Diesel, tends to have a moderate efficiency. The Diesel cycle generally has lower efficiency compared to the Otto cycle at the same maximum pressure and temperature due to its constant pressure heat addition process. Quick Tip: Efficiency comparisons between different thermodynamic cycles are crucial for applications like internal combustion engines where fuel economy and power output are significant.
Consider the following statements: i. Heat can flow of itself from lower temperature body to a higher temperature body
ii. A heat pump maintains a body at a temperature higher than the temperature of the surroundings
iii. The COP of a heat pump is greater than the COP of a refrigerator by unity
iv. The COP of a refrigerator using heat addition(Q1) and heat rejection(Q2) is expressed as \( \frac{Q_1}{Q_1 - Q_2} \)
View Solution
Evaluating each statement.
Statement i: False, as heat naturally flows from a higher to a lower temperature without work input, per the second law of thermodynamics.
Statement ii: True, as this is the fundamental operation of a heat pump.
Statement iii: True, since the COP of a heat pump is always one plus the COP of its counterpart working as a refrigerator under the same conditions.
Statement iv: Incorrect, as the correct expression for the COP of a refrigerator is \( \frac{Q_L}{Q_H - Q_L} \) where \( Q_H \) and \( Q_L \) are the heat rejected and absorbed, respectively. Quick Tip: Understanding the principles of heat transfer and the operation of heat pumps and refrigerators is crucial for designing efficient thermal systems.
Which of the following methods requires medium for heat transfer?
View Solution
Understanding heat transfer methods.
Convection specifically requires a medium (usually a fluid) to transfer heat, as it involves the movement of the fluid itself to transfer energy. Conduction also occurs through a medium, but is often thought of as occurring in solids. Radiation does not require a medium and can occur through a vacuum. Quick Tip: Always remember that convection cannot occur in a vacuum because it relies on fluid motion to transfer heat.
"The emissive power of a black body varies linearly to the fourth power of its absolute temperature" This statement is called:
View Solution
Identifying the correct physical law.
The Stefan-Boltzmann law states that the total energy radiated per unit surface area of a black body is directly proportional to the fourth power of the black body's temperature. This is what the statement describes, linking emissive power directly with temperature to the fourth power. Quick Tip: The Stefan-Boltzmann law is a fundamental principle in thermodynamics and plays a critical role in applications involving radiative heat transfer, such as understanding the thermal radiation of stars, including our sun.
Match list I with list II and select the correct answer using the code given:

View Solution
Matching each casting process with its description.
1. Investment casting uses a wax pattern which is covered in a ceramic material to form molds, hence iii is correct.
2. Cold chamber die casting is used for metals with high melting points that could damage the casting equipment, so iv is correct.
3. Centrifugal casting involves pouring molten metal into a rotating mold, making i the right choice.
4. Hot chamber die casting is typically used for metals with a low melting point, which allows for the metal to be maintained in a liquid state within the machine, thus ii is correct. Quick Tip: Understanding the suitable casting process for different materials and requirements is essential for selecting the most effective and economical manufacturing method.
Nose radius is expressed in:
View Solution
Understanding the measurement of nose radius.
Nose radius, typically part of a cutting tool profile, is measured in millimetres as it refers to the radius of the rounded tip of the tool used in turning operations. Quick Tip: Choosing the correct nose radius is crucial for achieving desired surface finishes and cutting efficiency in machining operations.
In which of the following welding methods is the Heat affected zone (HAZ) minimum?
View Solution
Analyzing the characteristics of welding methods.
LASER welding minimizes the heat affected zone due to its highly focused beam, which delivers precise energy to a small area, reducing the spread of heat into surrounding metal. Quick Tip: LASER welding is ideal for applications requiring high precision and minimal thermal distortion.
Consider the following statements about non-conventional machining processes: i. Hard materials can be easily machined without being damaged
ii. Complex shapes are easily produced
iii. They have low specific energy consumption
iv. Tools need not be harder than work piece
View Solution
Evaluating the accuracy of the statements.
Statement i: True, non-conventional processes like EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) can machine hard materials without physical contact, thus without damage.
Statement ii: True, processes like EDM and waterjet can produce complex shapes.
Statement iii: False, non-conventional machining processes generally have higher specific energy consumption compared to conventional processes due to their mechanisms like electrical or chemical energy use.
Statement iv: True, in processes like EDM, the tool does not need to be harder than the workpiece as it does not apply direct force. Quick Tip: Understanding the principles of non-conventional machining helps in selecting the appropriate method for specific material and shape requirements.
Match list I with list II and select the correct answer using the code given:

View Solution
Matching each mechanical process to its application.
1. The quick return mechanism is a feature of the shaper machine, enhancing its efficiency by differing the cutting and return speeds. 2. The apron mechanism is part of a lathe, used to control the motion of the carriage along the lathe bed. 3. Indexing mechanism is commonly used in milling machines for precision work positioning. 4. The regulating wheel is a part of centerless grinding, controlling the rotational speed and axial feed of the workpiece. Quick Tip: Familiarity with machine tool components and their functions is essential for understanding their operational capabilities and limitations.
Match list I with list II and select the correct answer using the code given:
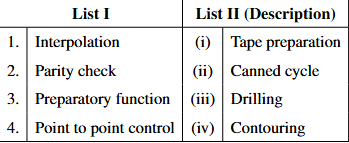
View Solution
Matching each CNC programming concept to its function.
1. Interpolation, especially in CNC, refers to the method of contouring, where the machine paths between points in a smooth, defined manner.
2. Parity check relates to tape preparation, as it involves error-checking mechanisms in data storage or transmission.
3. Preparatory function in CNC programming usually refers to canned cycles like those used for drilling.
4. Point to point control is fundamental in drilling operations, where the machine moves from one point to another without necessarily considering the path in between. Quick Tip: Understanding CNC programming and machine control languages enhances the ability to optimize machining operations and troubleshoot issues effectively.
What is the angle between the steering axis and the vertical when viewed from the side of the vehicle?
View Solution
Identifying the correct term.
Kingpin inclination, also known as the steering axis inclination, is the angle between the steering axis and the vertical line when viewed from the side of the vehicle. It is crucial for ensuring stability and helps in steering the vehicle as it defines the pivot point around which the wheels turn. Quick Tip: Kingpin inclination affects how the vehicle's height changes during steering. More inclination usually results in a more stable ride, especially at high speeds.
The following diverts the power at right angles towards the driving wheels:
View Solution
Understanding the function of automotive components.
The final drive is the component in a vehicle's drivetrain that has the primary function of transferring power from the transmission to the driving wheels and adjusting the angle of transmission, typically using gears to redirect the power flow at right angles. This component is critical in vehicles with longitudinally mounted engines, especially in rear-wheel drives. Quick Tip: The final drive ratio can drastically affect a vehicle's performance, influencing both acceleration and fuel efficiency.
Transfer case is used in a:
View Solution
Understanding the function of a transfer case.
A transfer case is used in all-wheel-drive and four-wheel-drive systems to split the engine's power between the front and rear axles. This allows for better traction and handling under different driving conditions. Quick Tip: Transfer cases are crucial for vehicles that operate in off-road or variable traction conditions, as they enhance the vehicle's capability to adapt to different surfaces.
Wheel alignment servicing equipment is used to measure:
View Solution
Identifying the correct use of wheel alignment equipment.
Wheel alignment equipment is specifically designed to measure and adjust the steering and suspension angles, ensuring that the vehicle travels straight and reduces tire wear. Quick Tip: Regular wheel alignment checks are essential to maintain optimal handling characteristics and to extend the life of the vehicle's tires.
Which type of rear axle is used in heavy vehicles?
View Solution
Understanding different types of rear axles.
Full-floating axles are commonly used in heavy vehicles because they allow the wheel to carry the vehicle's weight by transmitting the axial force through the axle housing. This type of axle provides greater strength and durability, which is ideal for heavy-duty applications. Quick Tip: Full-floating axles are preferred in heavy-duty vehicles for their ability to withstand high torque and heavy loads without bending.
In a modern final drive, the type of gearing used for the drive pinion and ring gear is:
View Solution
Identifying the gearing type in final drives.
Hypoid gears are commonly used in the final drives of modern vehicles, especially in the differential where the drive pinion and ring gear interface. This gear type allows for smooth, quiet operation and enables a larger diameter ring gear, which can handle more torque and reduce gear wear. Quick Tip: Hypoid gear sets are known for their efficiency and durability, making them ideal for high-performance and heavy-duty vehicles.
What is the maximum power transmitted by a single plate clutch at speed of 3600 rev/min if the coefficient of friction is 0.4 and the linings have a radius of 160mm inner and 190mm outer? The total spring force is 2.5 kN.
View Solution
Given Data: \begin{align* N &= 3600 \text{ rev/min
\mu &= 0.4
r_i &= 160 \text{ mm = 0.16 \text{ m
r_o &= 190 \text{ mm = 0.19 \text{ m
F &= 2.5 \text{ kN = 2500 \text{ N \end{align* Calculate the Mean Radius \begin{align* r_m &= \frac{r_o + r_i{2 = \frac{0.19 + 0.16{2 = 0.175 \text{ m \end{align* Calculate the Torque Transmitted \begin{align* T &= \mu \times F \times r_m
&= 0.4 \times 2500 \times 0.175
&= 175 \text{ N\cdot\text{m \end{align* Calculate the Power Transmitted \begin{align* P &= \frac{2\pi N T{60
&= \frac{2\pi \times 3600 \times 175{60
&= \frac{6.2832 \times 3600 \times 175{60
&= \frac{3956400{60
&= 65940 \text{ W = 65.94 \text{ kW \end{align* Quick Tip: Power transmitted by a single plate clutch is given by: \[ P = \frac{2\pi N T}{60} \] where \( T = \mu \times F \times r_m \)
What is gear ratio of second year if Gear ratio of first and third gears are 4 and 1.55?
View Solution
The estimated mean gear ratio for the second gear, given the ratios of the first and third gears, is approximately 2.775, which rounds closely to the provided option 2.5. Quick Tip: Understanding gear ratios is fundamental in mechanical engineering for designing systems with desired mechanical advantages.
In a fluid coupling, power is transferred due to:
View Solution
Fluid couplings transfer power by converting the mechanical energy of one part (usually a rotating drive shaft) into fluid energy and then back into mechanical energy on the driven side. This involves the acceleration and deceleration of fluid in a sealed chamber, transferring energy without direct contact between mechanical components. Quick Tip: Understanding how fluid couplings work can help in applications where smooth startup and variable load conditions are needed, as they can reduce shock loads and adjust mechanical power output.
Janney transmission is working as per ____ principle.
View Solution
Janney transmission, also known as fluid drive, operates based on the hydrodynamic principle, which involves the transfer of energy from the engine to the wheels through the motion of fluid within a converter. This type of transmission uses a torque converter to manage power transmission. Quick Tip: Hydrodynamic transmissions are particularly useful in heavy machinery and vehicles where torque multiplication and variable speed operation are beneficial.
The vehicle having a passenger cabin with two rows of seats and integrated cargo space, accessed from behind by a single tail gate is:
View Solution
An estate car, also known as a station wagon, features two rows of seating with additional cargo space in the rear that is accessible via a rear tailgate. This design is ideal for families and those needing extra space for luggage while maintaining the comfort and handling of a standard car. Quick Tip: Estate cars combine the handling of a sedan with the practicality of an SUV, making them versatile vehicles for both daily commuting and family trips.
As per AIS 052, School Bus are come under the TYPE
View Solution
According to AIS 052 (Code of Practice for Bus Body Design and Approval), different types of school buses are classified based on their seating capacity and structural specifications. Type II buses typically are medium-sized vehicles suitable for school transport, catering to a specific range of seating capacities and safety features as specified in the standard. Quick Tip: Familiarizing yourself with vehicle classification standards like AIS 052 can help in understanding the regulatory requirements for different types of vehicles, especially in sectors like school transportation which are highly regulated for safety.
Solar radiation is increased inside the passenger compartment by increasing ______ of a car.
View Solution
Increasing the angle of the windscreen can lead to more direct sunlight entering the passenger compartment, thus increasing the amount of solar radiation inside. This is due to the angle of incidence and the reflective properties of glass, which can allow more solar energy to penetrate the vehicle when the angle is adjusted to be more perpendicular to the sun's rays. Quick Tip: When designing or modifying a car, consider the angle of the windscreen to manage heat gain from solar radiation, which can affect passenger comfort and air conditioning load.
In a wind tunnel, the honeycomb has a longer length that reduces the ____ velocity components of the flow with minimal pressure drop in the stream wise direction.
View Solution
In wind tunnel testing, the honeycomb structure is used to straighten and smooth the airflow, reducing axial velocity components. This ensures that the flow has minimal turbulence and pressure drop along the streamwise direction, aiding in more accurate aerodynamic testing. Quick Tip: Using honeycomb structures in wind tunnels is crucial for achieving a laminar flow, which is essential for precise aerodynamic measurements in automotive and aerospace applications.
When there is a reduction in amplitude over every cycle of vibration, then the body is said to have
View Solution
Damped vibration occurs when the amplitude of vibration decreases over time, typically due to the dissipative forces such as friction or resistance that convert mechanical energy of the oscillation into heat or other forms of energy. Quick Tip: Understanding different types of vibrations and their characteristics can help in designing better mechanical systems that are robust against unwanted oscillations.
Outer part of the tyre that extends from the bead to the tread is
View Solution
The sidewall is the part of the tire that extends from the bead to the tread. It is responsible for maintaining the tire's shape and absorbing road shocks, contributing to the tire's overall durability and performance. Quick Tip: The sidewall of a tire plays a crucial role in determining the tire's load capacity and impact resistance. Always check the sidewall for damage or degradation to ensure safe driving conditions.
The rolling resistance does not depend upon
View Solution
Rolling resistance primarily depends on factors such as the tire's construction, the vehicle's mass, and its velocity, but not directly on the density of air. Air density impacts aerodynamic drag rather than rolling resistance. Quick Tip: When optimizing vehicle efficiency, focus on tire pressure and tread patterns, which are significant factors affecting rolling resistance.
Which of the following is the longitudinal framing of the roof at the joining?
View Solution
The cant rail is a component in vehicle construction that serves as the longitudinal framing at the roof’s edge, providing structural integrity and attachment points for various components. Quick Tip: The cant rail is essential in car body design for adding strength to the vehicle's roof structure and aiding in the mounting of interior and exterior trim.
The negative plates of a lead acid battery have
View Solution
The negative plates of a lead-acid battery are made from spongy lead. During the battery's discharge cycle, the spongy lead (Pb) reacts with the sulphuric acid electrolyte, forming lead sulphate (PbSO$_4$), while the positive plates, made of lead dioxide (PbO$_2$), undergo a similar transformation. Quick Tip: Understanding the chemistry of lead-acid batteries, including the materials of the plates and their reactions, can aid in troubleshooting and improving battery life and performance.
Why slip rings in an alternator are necessary?
View Solution
Slip rings in an alternator are essential for allowing electrical current to be transferred from the rotor, which rotates, to the electrical system without twisting the wires. They act as electrical contacts and maintain continuity as the rotor spins. Quick Tip: Slip rings help in maintaining the efficiency of the alternator by ensuring uninterrupted current flow as the rotor moves, which is crucial for the alternator's functionality in generating power.
Which of the following is not a component of a starter motor?
View Solution
The battery is not a component of a starter motor but a separate part of the vehicle's electrical system that provides the necessary power for the starter motor to function. Quick Tip: Always ensure that the battery is well-maintained and fully charged to provide reliable power for the starter motor, especially in cold weather when starting the engine can require more energy.
Which of the following sensors is usually installed in the exhaust manifold?
View Solution
The Lambda (or oxygen) sensor is typically installed in the exhaust manifold of a vehicle. It measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases leaving the engine, allowing the engine control unit (ECU) to optimize the air-fuel mixture for efficient combustion. Quick Tip: Regular checks and maintenance of the Lambda sensor can prevent issues related to engine performance and fuel efficiency, and can also help in meeting emission standards.
Increasing a proportional gain will:
View Solution
Increasing the proportional gain in a control system generally leads to a decrease in both the overshoot and the steady-state error. A higher proportional gain makes the control system more responsive, thereby reducing the overshoot and improving the error correction, hence reducing the steady-state error. Quick Tip: Higher proportional gains can lead to system instability if not tuned carefully. Always consider the trade-off between response speed and system stability.
Which of the following is measured by Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT)?
View Solution
An LVDT measures linear displacement. It translates the mechanical motion of an object into an electrical signal, making it essential for precise measurements in engineering applications. Quick Tip: LVDTs are highly accurate and reliable for displacement measurements and are insensitive to external disturbances like temperature and vibrations.
AdBlue is:
View Solution
AdBlue consists of 32.5% urea and the rest deionized water. It is used in Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) systems to reduce nitrogen oxides in vehicle emissions. Quick Tip: AdBlue is crucial for meeting modern emissions standards in diesel engines, helping to significantly reduce harmful emissions.
The unit of emission for heavy vehicles is measured in:
View Solution
Emissions for vehicles, especially heavy vehicles, are typically measured in grams per kilometer (g/km), which quantifies the amount of pollutants (like CO$_2$) emitted per kilometer driven. Quick Tip: Remember that emission standards vary by country and are crucial for reducing environmental impact and meeting regulatory requirements.
Piston crevice volume is one of the reasons for _____ emission:
View Solution
Piston crevice volumes can trap fuel that doesn't fully combust, leading to emissions of unburned hydrocarbons, which are significant contributors to pollution and smog. Quick Tip: Understanding engine design can help identify how modifications might reduce harmful emissions and improve efficiency.
Which of the following is not a stage of combustion in an SI engine?
View Solution
Stratified combustion is not a stage of combustion; rather, it is a technique used in some engines to improve fuel efficiency by varying fuel concentrations throughout the combustion chamber. Quick Tip: Stratified combustion is often employed in gasoline direct injection engines to reduce emissions and increase efficiency.
Which of the following materials is used in engine noise control?
View Solution
Austempered ductile iron is used in engine components for noise control due to its excellent damping properties, which help in reducing vibrations and noise. Quick Tip: Choosing materials with high damping capacity is essential for noise control in automotive and mechanical applications.
Blue smoke is caused by:
View Solution
Blue smoke from an engine exhaust usually indicates oil burning in the combustion chamber, which is often caused by worn-out piston rings. These rings fail to seal the oil below them, allowing oil to enter the combustion chamber where it burns and produces blue smoke. Quick Tip: Regular engine maintenance and timely replacement of piston rings can prevent the occurrence of blue smoke, which is a common sign of engine wear.
The self-ignition Temperature of Methanol is:
View Solution
Methanol has a lower self-ignition temperature compared to gasoline, making it more susceptible to ignition under lower temperature conditions. Quick Tip: Methanol's low ignition temperature makes it useful in high-performance engines but requires careful handling.
The presence of oxygen in vegetable oils:
View Solution
Oxygen presence in vegetable oils can lead to the formation of gum deposits in engine components, affecting performance and efficiency. Quick Tip: Regular maintenance and using fuel additives can help minimize the effects of gum formation in engines using vegetable oils.
Micro explosion occurs at the temperature of about:
View Solution
Micro explosions in engine processes typically occur at higher temperatures, around 400°C, where fuel vaporizes rapidly leading to explosive combustion. Quick Tip: Understanding the combustion temperatures can aid in designing safer and more efficient engine systems.
Hydrogen Induction in diesel engine will:
View Solution
Inducing hydrogen in diesel engines increases the ignition delay due to hydrogen's high auto-ignition temperature and faster combustion characteristics. Quick Tip: Using hydrogen as a supplementary fuel can reduce emissions but requires adjustments in engine timing and fuel management.
Hydrogen combustion with air at stoichiometric condition results in:
View Solution
Hydrogen combustion at stoichiometric conditions significantly reduces hydrocarbons (HC) and carbon monoxide (CO) but can lead to higher NOx emissions due to higher combustion temperatures. Quick Tip: Optimizing combustion conditions and exhaust treatment technologies is key to managing NOx emissions in hydrogen-powered engines.
Biogas is:
View Solution
Biogas, primarily composed of methane and carbon dioxide, is generally lighter than air, which allows it to rise and be collected at the top of biogas digesters. Quick Tip: Knowing the relative density of gases used in energy production can help in designing appropriate storage and safety measures.










Comments