
Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Zoology is a study that collects data or information about both the inquiry into an individual animal and their whole parts. The zoology also contains it to the molecular level, and the inquiry into entire faunas, animal populations, the relationships of animals with each other and with the plants, and to the non-living environment also.
| Table of Content |
Keyterms: Animal kingdom, Animalia, Plants, faunas, Phylum, botany, Biodiversity, Ecological diversity
Read More: Animalia Lower Invertebrates
History of Zoology
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Living things were segmented into plants and animals, and later, Zoology went through research for further classifications. Later words like botany, biology, and zoology found their existence. Zoology includes animals’ physiology, their interactions, their habits, their behavior with other species of the environment. It is a vast course that includes the distribution of all the animal species present on earth including extinct animals also.
Few years later, the animal category was separated into two categories: one with the red blood and the other without the red blood like insects and crustaceans. Other creatures were further separated into categories like those who were able to flow or swim or walk.
Now, Zoology is becoming very extensive where the living things are classified into five kingdoms, also in which animal kingdom is also classified further into some smaller categories of Phylum, Order, Family, Genus, Class, and, finally, Species.

History of Zoology
Read More: Animal Kingdom Important Questions
Branches of Zoology
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Zoology has branches that focus on some particular animal types' life divisions.
And those branches of zoology are given below:
- Entomology- the study of insects.
- Paleontology- the study of fossils.
- Ornithology- the study of birds.
- Primatology- the study of primates.
- Socio-biology- this studies the behavioral ecology, and evolution of social animals like schooling bees, ants, fish, and humans.
- Ethology- this studies the behavior of animals.
- Herpetology- the study of amphibians and reptiles.
- Ichthyology- the study of fishes.
- Invertebrate zoology- the study of these animals who do not have a backbone.
- Malacology- the study of mollusks.
- Mammalogy- the study of mammals.
- Ecology- this studies how animals interact with the environment.
- Embryology- the study of animal development before birth.
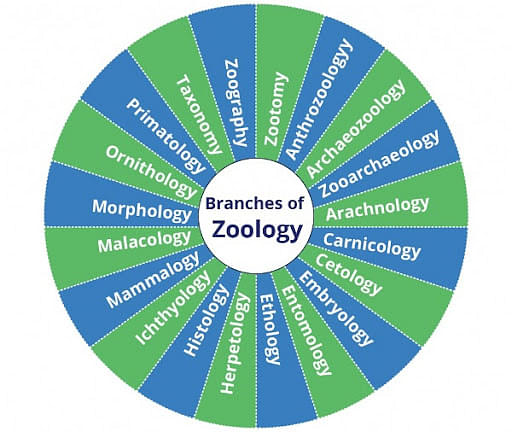
Branches of Zoology
Also Read:
| Related Links | ||
|---|---|---|
| Invertebrates | Animal Kingdom MCQs | Phylum Hemichordata |
| Gemmule Formation | Difference Between Chordates and Non-Chordates | Phylum Arthropoda |
| Benthic Zone | Coelom | Phylum Annelida |
Things to Remember
- Genetic diversity is diversity at the genetic level. For example the Rauwolfia vomitoria growing in different Himalayan ranges shows the genetic variation i.e due to the concentration of the active chemical (reserpine) that the plant produces.
- Species diversity is the diversity at the species level. For example, the Western Ghats have a greater amphibian species diversity than the Eastern Ghats.
- Ecological diversity is diversity at the ecosystem level. For example, the different type of ecosystems within India are deserts, rain forests, mangroves, coral reefs, wetlands, estuaries.
- Ex-situ Conservation is the conservation of threatened animals and plants outside their natural habitat. Examples are Zoological parks, botanical gardens and wildlife safari parks.
- Biodiversity plays a major role in ecosystem services. Amazon forest through photosynthesis produces 20 percent of the total oxygen in the earth’s atmosphere.
Also Read:
Previous Years questions
- In which of the following animals, haemocyanin pigment is found?...[NEET 2001]
- Transfer of Taenia to secondary host occurs as….[NEET 1989]
- Jelly fish belongs to class...[NEET 1989]
- Choose the correct match showing division of labour with animal example....[KCET 2013]
- Which one of the following groups of three animals is correctly matched with their one characteristic morphological feature?.[KCET 2013]
- The diagram of Labeo rohita is given below. Identify the parts labelled A, B, C, D, E, F, G....[KCET 2010]
- Column I contains larval stages and column II contains the group to which it belongs. Match them correctly and choose the right answer. ...[KCET 2011]
- In which of the following organisms, self fertilization is seen ?...[KCET 2007]
- Select the correct order of classification of Ranatigrina upto genus...[KEAM]
- Which one of the following is not a characteristic feature of the subphylum Vertebrata ?...[KEAM]
- Which one of the following is correctly paired ?...[KEAM]
- Animals which have well developed echolocation system like that of bats are…...[KEAM]
- Which of the following is modification of leaf?...[KEAM]
- A list of animals is given below. Identify the animals with open circulatory system and choose the correct answer. (a) Ascidia (b) Cockroach (c) Earthworm (d) Prawn (e) Silverfish (f) Snail (g) Squid.….[KEAM]
- "Triploblastic, unsegmented, acoelomate exhibiting bilateral symmetry and reproducing both asexually and sexually with parasitic forms". The above description is characteristic of phylum...[KEAM]
Sample Questions
Ques. Who is the father of zoology? (1 Mark)
Ans. Aristotle is considered the father of zoology because of his major contributions to zoology which include a huge amount of information regarding the variety, structure, behavior of animals.
Ques. What is biology's definition? (2 Marks)
Ans. Biology is the study of all the formulas of the natural science of life and living organisms. It consists of living organisms' important molecular interactions, physical structure, physiological mechanisms, chemical processes, development, and evolution. Biology also tells us how cells and organisms work.
Ques. What is animal behavior and its types? (2 Marks)
Ans. Behavior can be anything like an animal action that involves a response to a stimulus. Blinking, walking, flying, eating, vocalizing, and huddling are all various examples of behaviors. Behaviour is known as the way an animal acts. Swimming is also a kind of example of behavior.
Ques. What are the 5 tasks a zoologist must do? (2 Marks)
Ans. The Five tasks a zoologist must do are mentioned below:
- Studying the interaction of animals and animal behavior in their ecosystems
- Writing the reports as well as scholarly articles and also contributing to scientific journals
- Identifying and Collecting zoological data
- Performing and Preparing for the research projects
- Extraordinary animal conservation efforts
Ques. List identifying features of Arthropoda & give examples. (3 Marks)
Ans. The identifying features of Arthropoda are:
(i) Animals with jointed appendages;
(ii) Triploblastic, coelomate, and bilaterally symmetrical animals;
(iii) The body of animals is covered by a chitinous cuticle (hard exoskeleton), and segments are not separated by septa.
(iv) Arthropods are unisexual animals.
(v) Examples include Crab, Apis, Spider and Anopheles.
Ques. What are protochordates? How is it classified? (3 Marks)
Ans. Protochordate is an organism that belongs to the lower chordates and is generally found in marine water. Their body is bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, and coelomate. At a certain stage of their lives, their bodies develop a long, rod-like structure called the notochord. There are three subphyla: -
(i) Hemichordata (Half chordate)
Example: Balanoglossus
(ii) Urochordata (Tail cord)
Example: Salpa & Herdmania
(iii) Cephalochordata (Head cord)
Example: Amphioxus
Ques. “Mammals are the most successful & dominant animals today” Give evidence. (4 Marks)
Ans. Mammals are the most successful and dominant animals on the planet today. They thrive in the majority of the world's environments. The unique characteristics of mammals are:
(i) Body covered with hair.
(ii) Presence of sweat and sebaceous glands in the skin.
(iii) Presence of mammary glands in females that produce milk.
(iv) Presence of a pair of external ears and three ear ossicles i.e., malleus, incus and stapes.
(v) The heart has four chambers.
(vi) RBCs are biconcave and lack a nucleus (enucleated).
(vii) The testis is located outside the abdomen in a special pouch called the scrotum.
(viii) Mostly viviparous (produces young ones).
(ix) The embryo is attached to the uterine wall with the help of the placenta.
(x) The skull is dicondylic, i.e., it has two occipital condyles.
Ques. What is the basis of the classification of Animalia? (4 Marks)
Ans. The basis of classification of Animalia are: -
(i) Notochord: It is a rod-like structure found in the chordates. It is not found in non-chordates.
(ii) Symmetry: It is the plan of arrangement of body parts. They are of three types: - Asymmetrical, radially symmetrical, and bilaterally symmetrical.
(iii) Organisation: Animals have a cellular grade of organisation. Their bodies are made up of cells, while others have tissues, organs, and organ systems.
(iv) Embryonic layers: Ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm are three embryonic layers that give rise to different organs in the body. These are also called germinal layers. Some animals are diploblastic, for example-sponges, but others are triploblastic having three germinal layers.
Ques. What are career options in zoology? (4 Marks)
Ans. It is a good career option for those who have a zeal to explore biodiversity and are ready to accept challenges. Students with higher education in zoology and work experience in this field can get a decent pay scale.
If you're wondering what else you can do with a zoology degree, here are a few other job options for graduates:
- Environmental consultant
- Animal nutritionist
- Science writer
- Environmental education officer
- Toxicologist
- Veterinary nurse
- Research scientist
- Biomedical scientist
Do Check Out:








Comments