Jasmine Grover Content Strategy Manager
Content Strategy Manager
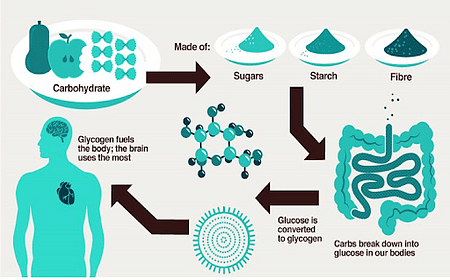
Sources of Carbohydrates include sugar, starch, and fibers such as bread, milk, beans, potatoes, soft drinks, corn, etc. Carbohydrates are biomolecules consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. They provide glucose to the human body so that it can carry out its functions properly. Carbohydrates are essential nutrients that include fibres, sugar and starches. They are found in vegetables, fruits, grains and milk. Carbohydrates function by storing energy and help in the preservation of our muscles. The food with carbohydrates is converted into blood sugar or glucose during the process of digestion by our digestive system.
| Table of Content |
Key Terms: Carbohydrates, Sources of Carbohydrates, Biomolecules, Muscles, Water, Human Body, Energy, sugar, starch, fibers
What are Carbohydrates?
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The word ‘Carbohydrate’ is derived from the French word ‘Hydrate de Carbone which means hydrate of carbon. The general formula for these compounds is Cn(H2O)n. Biomolecules that include the atoms of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen at their chemical level are known as Carbohydrates. It is similar to water as the ratio of Hydrogen and Oxygen is 2:1 in Carbohydrates too as in the case of water. Carbohydrates are among the three micronutrients through which the human body gets energy. They are converted to sugar and this sugar is used as energy by the cells.

Also check: Food Where Does it Come From?
Sources of Carbohydrates
[Click Here for Previous Years Questions]
The compounds present in food that provide us with energy for growth and repair are known as Nutrients. Carbohydrates are present in both healthy and unhealthy food. They are present in different forms such as sugars, starch, and fibers. Carbohydrates are not present naturally in the human body, hence they must be taken in through diet.
Healthy Sources of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates in healthy food consisting of both animal and plant sources which include:
- Corn
- Potatoes
- Milk Products
- Fresh Fruits
- Vegetables
Unhealthy Sources of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates in Unhealthy food include:
- White Bread
- Artificial Sugar
- Pastries
- Soda
- Other Highly Processed Foods
Read More:
| Chapter Related Topics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D Deficiency | Test for Fats | Test for Starch |
| food deficiency | dietary fibre significance | balanced diet |
Functions of Carbohydrates
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The functions of Carbohydrates are as given below:
- Carbohydrates are the primary or the main sources of energy in our human body.
- They are also involved in fat metabolism.
- Carbohydrates prevent ketosis.
- They are a part of connective tissues.
- Carbohydrates maintain the digestive system of the body.
- Blood cholesterol can be lowered due to the fibers in Carbohydrates.
- Carbohydrates are used to build and repair tissues because it retains protein from being burned.
- Carbohydrates give energy to the central nervous system.
- They are found in different forms such as sugar, glucose, starch, and fibers.
Read More:
| Related Articles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Structure of Glucose and Fructose | Maltose | Vitamins |
| Enzymes | Test for Starch | Carbohydrate Metabolism |
| Test for Protein | Hormones | Macromolecules |
Types of Carbohydrates
[Click Here for Previous Years Questions]
The different types of Carbohydrates are as follows:
- Simple Carbohydrates: Simple Carbohydrates have just one or two molecules of sugar in them. They are called empty calories as they don’t have vitamins and minerals. These Carbohydrates are present in food which includes artificial sugars. These are present in fresh fruits like apples, oranges, bananas, pineapples, sweet potatoes, and berries. Milk is also the main source of carbohydrates of this type. These are further divided into 3 types – Monosaccharides, Disaccharides, and Oligosaccharides.
- Complex Carbohydrates: Complex Carbohydrates have two or more molecules of sugar present in them. They include starch and fiber. Complex carbohydrates are good carbohydrates. Complex carbohydrates do not spike sugar levels in the blood. They help to maintain minimal sugar levels in the blood. These carbohydrates include beans, peas, whole grains, barley, oats, wild rice, brown rice, and many more.

- Starchy Carbohydrates: Foods rich in carbohydrates are known as starchy carbohydrates such as beans, potatoes, sweet potatoes, and some nuts. Grains and Cereals are the primary sources of starchy carbohydrates. These also include whole grain, grain bread, and many more.
- Fibrous Carbohydrates: Fibrous Carbohydrates are concentrated sources of energy. These carbohydrates are found in fresh vegetables such as pumpkin, carrot, tomatoes, beans, broccoli, peas, sprouts, cucumbers, squash, and many more.
Read More:
| Important Topics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Beriberi | obesity | difference between vitamin d and d3 |
| scurvy | Vitamin K | Fats |
| Structure of Glucose and Fructose | Maltose | Test for Protein |
Things to Remember
- Biomolecules that include the atoms of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen at their chemical level are known as Carbohydrates.
- The Compounds present in food that provide us with energy for growth and repair are known as Nutrients.
- Carbohydrates are the primary or the main sources of energy in our human body.
- Blood cholesterol can be lowered due to the fibers in Carbohydrates.
- Simple carbohydrates have one or two molecules in them.
- Complex carbohydrates include starch and fiber.
- Foods rich in carbohydrates are starchy carbohydrates such as beans, potatoes, sweet potatoes, and some nuts.
- Fibrous Carbohydrates are concentrated sources of energy.
Also Read: Complex Carbohydrates
Previous Years Questions
- Which of the following carbohydrates are branched ...[UPSEE 2019]
- the following statements is not true regarding (+) Lactose…?
- What will happen when D-(+)-glucose is treated with ….
- Stachyose is a…
- When glucose reacts with bromine water….
- Fructose reduces Tollen's reagent due..
- Which of the following is ketohexose ?
- Two forms of D-glucopyranose, are called...[JEE Advance 2005]
- disaccharide is...[JEE Advance 2010]
- Which of the following is the sweetest sugar?
- The two functional groups present in a…
- The letter D in-carbohydrates represents…. [KEAM]
- The \(\alpha\)- and \(\beta\)- forms of glucose are…[KEAM]
- The two functional groups characteristic of sugars are… [NEET 2018]
Sample Questions
Ques. What are Monosaccharide carbohydrates? (2 marks)
Ans. These carbohydrates are a type of simple carbohydrates and glucose is an example of these carbohydrates. It is further divided into 5 types – Trioses, Tetroses, Pentoses. Hexoses, and Heptoses.
Ques. Mention some examples of carbohydrates? (2 marks)
Ans. Some basic examples of carbohydrates include Glucose, Galactose, Maltose, Fructose, Sucrose, Lactose, Starch, Cellulose, Chitin, and many more.
Ques. How are simple carbohydrates different from complex carbohydrates? (1 mark)
Ans: Simple carbohydrates include one or two sugar molecules in them, whereas complex molecules have two or more sugar molecules present in them.
Ques. Are carbohydrates important to the human body? (2 marks)
Ans: Carbohydrates are meant to provide energy to the human body as they are broken down into the particles of glucose that enter the blood. Glucose is utilized by the cells of the body that produces ATP.
Ques. How are the carbohydrates digested? (1 mark)
Ans: During the action of salivary amylase, carbohydrates start to get digested in the mouth. These are completely broken down in the intestine, not in the stomach.
Ques. State three functions of carbohydrates. (3 marks)
Ans. The functions of carbohydrates are:
- Blood cholesterol can be lowered due to the fibers in Carbohydrates.
- Carbohydrates maintain the digestive system of the body.
- They are also involved in fat metabolism
Ques. What are the 4 types of Carbohydrates? (3 marks)
Ans. The 4 types of carbohydrates are:
- Monosaccharides
- Disaccharides
- Oligosaccharides
- Polysaccharides
For Latest Updates on Upcoming Board Exams, Click Here: https://t.me/class_10_12_board_updates
Check-Out:





Comments