
Content Curator
Paper Chromatography is a cheap method to know about the properties and detection of substances in a solvent by keeping a strip of a paper sheet as the adsorbent through which the solution is made to pass. Here, the paper tends to be in the stationary phase. Besides, it is used for the detection of substances in different solvents as well as in humans and animals and uses a very less quantity of the sample material. This is an effective technique to know about the behaviour of substances and their property by calculating their migration rate through a strip of paper.
Also Read: Column Chromatography
| Table of Content |
Key Takeaways: Chromatography, Column Chromatography, Partition, Adsorption, Spotting, Biological Separation
What is Paper Chromatography?
[Click Here for Viva Questions]
Paper chromatography is a technique that uses strips or sheets of paper as the adsorbent through which a solution is made to pass. This is a type of chromatography which makes use of less amount of the sample material. Mostly, this procedure is used because of its cost-effectiveness. It can separate dissolved chemical substances using sheets of paper.
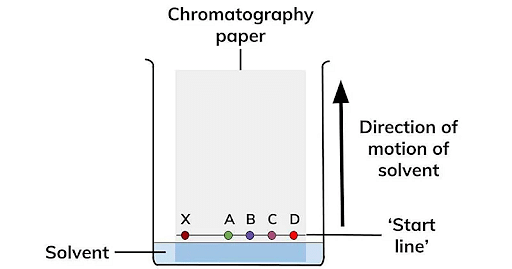
Paper Chromatography
In addition to that, this is used as an analytical tool. Paper chromatography is the most popular technique that is used for research works. It was discovered by Martin and Synge in 1943.
Read More: Adsorption Chromatography
Principle of Paper Chromatography
[Click Here for Viva Questions]
Paper Chromatography is based on the principle of Partition. Here, the substances are distributed through the liquid phase and the adsorbent paper acts as the stationary phase whereas the solvent acts as the mobile phase. Based on the capillary action of the pores in the strip of paper, the compounds in the sample material move depending on their affinity towards the stationary or mobile phase. Thus the compounds in the mixture get separated when the mobile phase moves.

Principle of Paper Chromatography
Read More: Thin Layer Chromatography
Types of Paper Chromatography
[Click Here for Viva Questions]
The different types of paper chromatography are given below.
Ascending Paper Chromatography: It is called ascending because the solvent moves in an upward direction.
Descending paper Chromatography: It is called descending because the flow of solvent is downwards due to gravitational pull.
Ascending and Descending Paper Chromatography: In this case, the solvent is moving in two directions after a particular point. Thus, it is called ascending and descending paper chromatography.
Radial paper chromatography: In this case, the solvent is deposited at the centre of the paper and results in a radial deposition of the ink. Thus, it is called circular or radial paper chromatography.
Two Dimensional Paper Chromatography: This is a specific technique for those substances that can have the same rf values.
Read More: Differential Extraction ChromatographyProcess of Paper Chromatography
[Click Here for Viva Questions]
Selection: Selection is based on the mixture, paper, and solvent. In the case of radial paper chromatography, it is easy to perform because it is a less time-consuming process.
Filter paper: Selection of filter paper is based on two things which are sample quality and the size of the pores.
Sample preparation: It is a simple process wherein the mobile phase must be prepared in a suitable solvent.
Spotting: It is necessary that the sample should be spotted at a proper position on the paper. This process is completed using a capillary tube.
Development of chromatogram: It is spotted by immersing the paper in the mobile phase. It happens because of the capillary action of paper.
Drying and compound detection: After the development of the chromatogram, it is dried and the detecting solution is sprayed on it for identification of the developed spots.
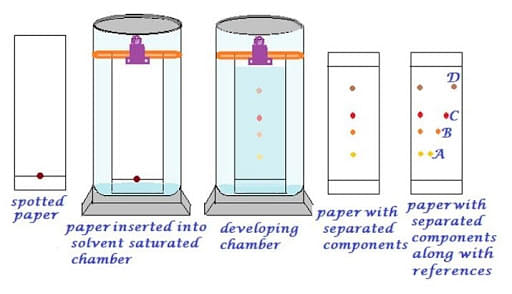
Process of Paper Chromatography
Applications of Paper Chromatography
[Click Here for Viva Questions]
Some of the applications of paper chromatography are as follows.
- Paper Chromatography is used in the biological separation of amino acids, peptides, alkaloids, sugars, lipids etc.
- It is sometimes used in the preparative method.
- Paper Chromatography is used to detect the contaminants in foods and drinks.
- Analysis of blood, haemoglobin, urine, etc. and other diagnoses also involves the usage of paper chromatography.
- Paper Chromatography is used to determine dopes in humans.
- Assessment of the level of pollutants in the water supply can be determined using paper chromatography.
- Paper Chromatography is also used to detect alcohol levels in the blood.

Paper chromatography used in laboratory process
Read More: Separation of Plant Pigment through Paper Chromatography
Things to Remember
- Paper Chromatography is a basic technique to know about the properties and detection of substances in a solvent.
- Paper Chromatography is a less costly technique to know about the behaviour of substances and their property.
- This technique uses strips or sheets of paper as the adsorbent through which a solution is made to pass.
- The types of paper chromatography are ascending, descending, radial and two-dimensional paper chromatography.
- Paper chromatography is used to detect adulterants in compounds and solutions.
- It is widely used in varied fields of chemistry, biology and the food industry.
Sample Questions
Ques. What is chromatography? (2 marks)
Ans. It is a technique for rapid and efficient separation of components of a mixture and purification of compounds. It is based on differential migration of the various components of a mixture through a stationary phase under the influence of a moving phase.
Ques. What is the basis (principle) of the chromatographic process? (2 marks)
Ans. It is based on the differential migration of the individual components of a mixture through a – stationary phase under the influence of a moving phase.
Ques. What is meant by the term developing in chromatography? (2 marks)
Ans. During chromatography, if the components to be separated are colourless, then these separated components on the chromatogram are not visible. Their presence is detected by development, which involves spraying a suitable reagent (called developing reagent) on the chromatogram, or placing the chromatogram in an iodine chamber when various components become visible. This process is called the development of the chromatogram.
Ques. What is meant by the term Rf value? (2 marks)
Ans. Rf (retention factor) of a substance is defined as the ratio of the distance moved up by the solute from the point of its application to the distance moved up by the solvent from the same point.
Ques. What are the essential characteristics of the substance used as a developer? (2 marks)
Ans.
- It should be volatile.
- It should impart colour to the different spots.
- It should not react with various compounds which are being separated.
Ques. What- is loading (or spotting)? (2 marks)
Ans. The application of the mixture as a spot on the original line on the filter paper strip or addition of mixture to the column is called loading (or spotting)
Ques. What is loading adsorption chromatography? (2 marks)
Ans. In this type, the mixture is dissolved in some suitable solvent such as alcohol, ether, benzene etc. and the resulting solution is poured down a vertical column filled with adsorbing material such as alumina, chalk, charcoal, silica gel, etc. The process of addition of the mixture to the column is called loading. Depending upon the rate at which different components of the mixture are adsorbed, different zones or bands are formed down the column; the substance that is adsorbed most remains at the top of the column. Later, the constituents are washed down and collected separately, with a suitable solvent. This process is called ‘elution’.
Ques. Describe briefly Paper Chromatography with a suitable diagram. (5 marks)
Ans. It is mainly a type of partition chromatography in which a special adsorbent paper is used instead of a column. Moisture adsorbed by this acts as a stationary phase and the solvent as a moving phase. The mixture to be separated or analysed is put at one end of the paper strip as a small spot. The paper is placed in a container, with a suitable solvent, vertically in such a way that the lower end (where the mixture spot is put) dips in the solvent and the spot remains slightly above the solvent level (Fig). The solvent rises up the paper due to capillary action and the components of the mixture rise up at different rates and thus get separated from one another as shown in Fig.
This type of paper chromatography in which the solvent rises up is called Ascending paper chromatography. Alternatively, the solvent may be taken on the top in a container and be allowed to come down in which case it is termed as ‘Descending paper chromatography.

Ques. What are the applications of Paper Chromatography? (3 marks)
Ans.
- It is used in the biological separation of amino acids, peptides, alkaloids, sugars, lipids etc.
- It is sometimes used in the preparative method.
- It is used to detect the contaminants in foods and drinks.
- It is used in the analysis of blood, haemoglobin, urine, etc. and thus helps in diagnosis.
- To determine dopes in humans.
- It is used to assess the level of pollutants in the water supply.
- It is also used to detect alcohol levels in the blood.
Ques. What are the types of Paper Chromatography? (5 marks)
Ans. Ascending Paper Chromatography: It is called ascending because the solvent moves in an upward direction.
Descending paper Chromatography: It is called descending because the flow of solvent is downwards due to gravitational pull.
Ascending and Descending Paper Chromatography: In this case, the solvent is moving in two directions after a particular point. Thus, it is called ascending and descending paper chromatography.
Radial paper chromatography: In this case, the solvent is deposited at the centre of the paper and results in a radial deposition of the ink. Thus, it is called circular or radial paper chromatography.
Two Dimensional Paper Chromatography: This is a specific technique for those substances that can have the same rf values.
Read More:
| Brown Ring Test | Zone Refining | Homogeneous Mixtures |
| Types of Solutions | Non-Electrolytes | Classification of Colloids |
| Principle of Homogeneity | Homogeneous Equilibria | Acid Test |
Related Links:





Comments