Jasmine Grover Study Abroad Expert
Study Abroad Expert
Habitat is a natural home, location where a living organism survives, resides, or exists. An organism chooses to reside in a place as per its suitability. For example, a fish will reside in the waters and not in the land, a polar bear is made in such a way that it can easily survive in extremely cold conditions while a house cat cannot survive in that same environment. Certain characteristics of living organisms which enables them to survive in their surrounding are known as adaptation in living organism. This is the reason why we find certain animals in certain environments. Some animals have also evolved themselves to survive in extreme conditions.
Key Terms: Habitat, adaptation, terrestrial habitat, aquatic habitat, abiotic factors, biotic factors, deserts, mountains, grassland, oceans, ponds, lakes, reproduction, Growth
Types of Habitat
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Adaptation of a living organism in a particular habitat is a slow process. Over a thousand years of duration, the abiotic factors undergo changes. Sometimes the living organisms modify themselves to adapt and survive in the changing environment. The organisms which fail to adapt themselves in that habitat eventually die out. New organisms replace them and try their best to survive and adapt to that environment. Due to this we can find a particular type of living organism more in number in its suitable habitat.
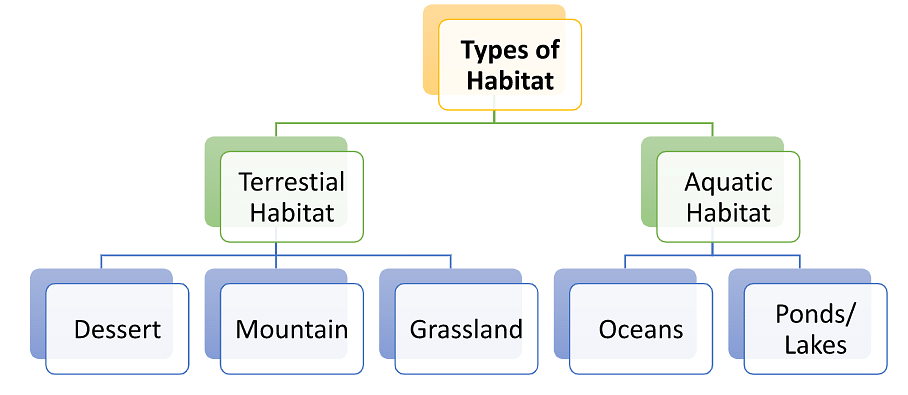
Living things that are biotic components and nonliving things that are abiotic components both co-exist together to form a particular habitat. Types of habitat are mainly divided into two main classifications, terrestrial habitat, and aquatic habitat.
Also Read:
Terrestrial Habitat
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Terrestrial habitat is where land animals and plants survive. Different types of land animals share one terrestrial habitat. This is further classified into desert, mountain, and grasslands based on its distinct difference in climate change, environmental conditions, and animal adaptation.
Desert: Deserts are places with extreme temperatures. The environment lacks moisture. At day time the temperature can rise up to approximately 390C while at night the temperatures can fall approximately to -3.90C. For adapting to such an extreme environment, small animals like rats, scorpions, snakes, makes burrows inside sand and come out at night for hunting.

Desert Ecosystem
Camels have long legs which helps them to stand quite above the hot sand. They have excellent ability to store water and prevent excretion of water. The plants in the desert have thick waxy layered stems which prevents the evaporation of water. They have deep and long roots which travel deep below the ground in search of water. In this way the plants and the animals have adapted themselves to the extreme desert habitat.
Read More: Biodiversity Hotspot
Mountains: The mountainous regions are cold and windy. One can also find snowfall during the winter season on some mountains. As seen in the above pictures, tall cone-shaped trees with needle-like leaves have adapted to this environment. The distinct shape of these trees helps them to let the rainwater and snow slide off easily.
Mountain Habitat
Animals which are found here have thick fur or skin to protect themselves from cold. The mountain goat has strong and angular hooves which helps it to balance and climb higher heights. Yaks have long thick fur; snow leopards have fur covered throughout its tail and paws. Different adaptations can be seen as we scale higher in the mountains.
Read More: Catabolism and Anabolism
Grassland: There are different animals including carnivorous, herbivorous, omnivorous, scavengers, etc in the grassland. The grassland has comparatively good environmental conditions for animals and plants to survive and flourish. But here we can see the struggle of surviving between the predator and the prey. The predators are the animals who hunt down other animals for food, eg- lions, tigers, cheetahs, wild cats, leopards, etc. Prey are the animals that are hunted down by the predator, eg, deer, boar, giraffe, rabbits, etc.

Grasslands
The body of the prey and the predator are uniquely designed for enhancing their survival rates. The prey have long ears, eyes on the side of the head to look out for predators in all directions while the predator has skin colour which enables it to camouflage among tall grass. In this way the animals and the plants have adapted themselves to grassland habitat.
Read More: Ecosystem
Aquatic Habitat
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
Aquatic habitat is the underwater ecosystem where fish, corals, and other aquatic plants survive. The underwater environment is completely different to that of the land. The aquatic environment differs for different parts of the earth. The Oceans have great differences in the aquatic environment as it is spread over large areas. They also have varying depths of ocean floor which promote different habitats. Thus the Aquatic Habitat is further classified into Oceans and Ponds/ Lakes.
Oceans: Oceans hold about 96.5% of the earth’s water. Thus most of the aquatic animals belong to the oceans. Fish have streamlined bodies, designed in such a way for swimming and breathing underwater. They respire the dissolved oxygen in the water through their gills.

Ocean habitat
Octopus and jellyfish do not have a streamlined body like the fishes, yet they can swim effectively, they stay close to the seafloor and catch the prey which swim close by. The size of fish can greatly vary as per their adaptability to the aquatic habitat.
Read More:Chordates and Non-chordates
Ponds/ Lakes: Ponds and lakes are comparatively smaller water bodies than the ocean. Small organisms like frogs, small fish, dragonflies, lotus, water lilies, algae, etc thrive in a pond/ lake habitat. In shallower waters, the plants tend to have their roots fixed on the lake’s floor and grow upwards. Aquatic plants have smaller roots than terrestrial plants. Some plants completely grow underwater. The small fish and insects feed on them.
Pond ecosystem
Frogs are amphibians and live inside and outside the water. Their webbed feet and strong back muscles are designed in such a way that they can be used to swim as well as jump longer distances. The fishes found in ponds/ lakes are comparatively smaller in sizes than the average fishes of the ocean.
Read More: Respiration and Combustion
Characteristics of Living Organisms
[Click Here for Previous Year Questions]
Despite the animals being adaptive to diverse habitats, all the living things have the following characteristics in common.
- All living organisms need food to grow and survive.
- They all respire, intake of carbon dioxide by the plants and oxygen by animals.
- They all reproduce to prevent extinction of their species.
- There is continuous growth in the bodies of the living organisms.
- All living creatures excrete to dispose of the waste of their body.
Things to Remember
- Living things have certain common characteristics — they need food, they respire and, excrete, respond to their environment, reproduce, grow and show movement.
- Human beings are the advance form of animals
- Extinction and changes in abiotic factors happen even in the current age
- Rocks, soil, air, water, light, and temperature are some of the abiotic components of our surroundings.
Learn More About:
Sample Questions
Ques. How are cacti adapted to survive in a desert? [3 marks]
Ans. Cactus are able to survive in the extreme temperatures in the desert because they have long and deep roots which are used to absorb water. In spite of such scarcity of water, cactus manage to survive with the help of these long roots. The leaves of the cactus are in the form of spines which restricts the water loss by the process of transpiration. The thick and green stem of the cactus is covered with a thick waxy layer which helps to retain water. The stem collects maximum water when water is available, this stored water helps the cactus to survive when water is not available. The cactus carries out photosynthesis in its stem.
Ques. What is a habitat? How do animals adapt to it? [5 marks]
Ans. A Habitat is a natural home, location where a living organism survives, resides, or exists. An organism choses to reside in a place as per its suitability. For example, a fish will reside in the waters and not in the land, a polar bear is made in such a way that it can easily survive in extreme cold conditions while a house cat cannot survive in them. Living things that are biotic components and nonliving things that are abiotic components both co-exists together to form a particular habitat. Types of habitat are mainly divided into two main classifications, terrestrial habitat, and aquatic habitat.
Adaptation of a living organism in a particular habitat is a slow process. Over a thousand years of duration, the abiotic factors undergo changes. Sometimes the living organisms modify themselves to adapt and survive in the changing environment. The organisms which fail to adapt themselves in a particular habitat eventually die out. New organisms replace them and try their best to survive and adapt to that environment. Due to this we can find a particular type of living organism more in number in its suitable habitat.
Ques. How do camels survive in the desert? [3 marks]
Ans. Deserts are known for having extreme temperatures. The camels naturally have thick coats of hair which protects them from the scorching heat of the day as well as provide the required heat by night. They have large feet that help them to walk effectively on the sliding sand of the desert. Camels have a special hump in their back where they store fats, that is they store food and water for surviving the times when it is scarce. They also have bushy and thick eyebrows which prevents the sand from entering their sensitive eyes during a sandstorm. They also have two-sets of eyelashes along with hairy ears. They have three eyelids to prevent the dust from entering their eyes. They also have a naturally adaptive temperature regulation system. They have thick leathery skin which prevents bruises while sitting and kneeling on the hot sand. A camel can go for about six to seven months without food and water. Due to all of these adaptive qualities, camels survive in the desert.
Ques. Explain the natural habitat of humans. [3 marks]
Ans. In simple terms, a human habitat can be described as a place where people choose to live, a place where they find all the basic amenities in reach and in abundance. Humans have adapted to live in grasslands, mountains, and deserts. They use the natural resources available in these habitats to fulfill their needs. They create shelters as per the climate of the habitat. Most of the human settlements are found near water bodies and in plain areas where there are plenty of resources. Wherever humans settle they focus on the food, water, shelter, suitable temperature, resources to ward off predators, etc to call that place as a habitat.
Ques. Compare Adaptation and Evolution. [3 marks]
Ans.
| Adaptation | Evolution |
|---|---|
| A form or structure modified to fit a changing environment. | A change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations |
| A change in the phenotypic level | A change in the genotypic level |
| A reversible change | An irreversible change which occur over generations |
| Occurs under the effect of environmental conditions | Occurs due to speciation |
Ques. Explain Amphibians. [3 marks]
Ans. Amphibians are animals which can survive both inside and outside the water. Mostly they require a moist atmosphere to live. The best example is frogs. They are born underwater and grow there. As they grow to become adults, they spend most of their time on the land. They feed on insects, small rats, small fishes, etc. They have bare skin with no hairs and scales on them. Most of them have four legs and webbed feet. Like a fish, amphibians breathe through gills when they are small. As they grow, they develop lungs which are capable of breathing air on the land.
Ques. What are Endangered animals? [3 marks]
Ans. Endangered animals are animals which are on the verge of extinction. These animals have the possibility of completely vanishing away from the face of earth with no species left behind. This happens when their food source is depleting or when there is sudden change in their habitat. The sudden changes and shortage of food forces these animals to die. The Giant Panda, Tiger, etc are endangered animals.
Ques. Distinguish between grassland animals and mountain animals. [3 marks]
Ans.
| Grassland Animals | Mountain Animals |
|---|---|
| Animals don’t have thick coats of fur | Animals have thick coats of fur |
| Animals have strong muscular legs that allow them to run quickly | Animals have powerful hooves that can run up steep slopes |
| They have brown skin that allows them to blend in with its surroundings | To blend in with the environment skin is either white or black |
| Strong and keen hearing aid in detection of predators and prey | Ears are also coated in fur to protect themselves from cold environments |



Comments