IBSAT Sample Paper 1 is now available for download here. The IBSAT Sample Paper 1 consists of 140 multiple-choice questions divided into four sections—Verbal Ability, Reading Comprehension, Quantitative Aptitude, and Data Adequacy & Data Interpretation. Each question carries one mark, and there is no negative marking for incorrect answers.
IBSAT Sample Paper 1 Question Paper with Solutions PDF
Question 1:
GARNE
- (A) Pulverize
- (B) Marinate
- (C) Enthrall
- (D) Emblazon
- (E) Collect
Question 2:
IMPERIOUS
- (A) Domineering
- (B) Ravenous
- (C) Striking
- (D) Effervescent
- (E) Humdrum
Question 3:
CONTUMACIOUS
- (A) Pristine
- (B) Conservative
- (C) Disobedient
- (D) Optimistic
- (E) Opinionated
Question 4:
QUIESCENT
- (A) Serene
- (B) Concomitant
- (C) Dormant
- (D) Clammy
- (E) Hopeless
Question 5:
DISQUIETUDE
- (A) Easiness
- (B) Discussion
- (C) Passion
- (D) Anxiety
- (E) Salubrity
Question 6:
VITIATE
- (A) Trust
- (B) Deaden
- (C) Drain
- (D) Rectify
- (E) Amuse
Question 7:
TRITE
- (A) Peaceful
- (B) Powerful
- (C) Noiseless
- (D) Skeptical
- (E) Original
Question 8:
CONTRITE
- (A) Unrepentant
- (B) Expanded
- (C) Remorseful
- (D) Unresolved
- (E) Prevailing
Question 9:
SQUANDER
- (A) Depart
- (B) Preserve
- (C) Forfeit
- (D) Fortify
- (E) Destroy
Question 10:
INDIGENT
- (A) Modest
- (B) Impetuous
- (C) Profitable
- (D) Prosperous
- (E) Garish
Question 11:
Song : Cycle :: Sonnet :
- (A) Ballad
- (B) Melody
- (C) Rhyme
- (D) Sequence
- (E) Epic
Question 12:
Lumber : Bear :: Waddle :
- (A) Parrot
- (B) Pigeon
- (C) Goose
- (D) Hawk
- (E) Sparrow
Question 13:
Archipelago : Island :: Constellation :
- (A) Garden
- (B) Flower
- (C) Star
- (D) Valley
- (E) Mountain
Question 14:
Range : Mountains :: String :
- (A) Ribbons
- (B) Toys
- (C) Beads
- (D) Keys
- (E) Leaves
Question 15:
Bracket : Shelf :: Strut :
- (A) Bucket
- (B) Valve
- (C) Girder
- (D) Hammer
- (E) Rafter
Question 16:
If a nation is unable to come to _________ on interpreting its own past, it will be unable to _________ its national interests.
- (A) conclusion … plan
- (B) decision … comprehend
- (C) consolidation … meet
- (D) consensus … formulate
- (E) terms … design
Question 17:
Globalization _________ both prosperity and _________.
- (A) causes … development
- (B) reveals … doom
- (C) condemns … bliss
- (D) spreads … distress
- (E) transmits … generosity
Question 18:
Unscrupulous use of chemical insecticides to _________ the pests leads to pest _________.
- (A) aggravate … modification
- (B) disintegrate … mobility
- (C) rectify … revival
- (D) kill … stimulation
- (E) control … resurgence
Question 19:
A _________ relationship with Moscow will help New Delhi to _________ its ties with both Washington and Beijing.
- (A) robust … leverage
- (B) healthy … enhance
- (C) mutual … lose
- (D) perfect … ally
- (E) vigorous … cement
Question 20:
A judge tries to _________ his duties to the best of his _________.
- (A) fulfill … quality
- (B) discharge … capacity
- (C) execute … strength
- (D) perform … power
- (E) manage … ideas
Question 21:
Language cannot be static/ it must constant evolve/ to keep up with changing times/ and remain relevant. No error
- (A) static;
- (B) constant evolve
- (C) to keep up with changing times/
- (D) and remain relevant
- (E) No error
Correct Answer: (B) constant evolve
View Solution
Step 1: Identifying the error.
The phrase "must constant evolve" is incorrect. The correct expression should be "must constantly evolve," as "constantly" is the adverb modifying the verb "evolve."
Step 2: Conclusion.
The error is in option (B), where "constant evolve" should be "constantly evolve."
Quick Tip: When using verbs like "must," ensure the following verb is in its correct adverbial form, such as "constantly" instead of "constant."
Question 22:
If he would have taken rest/ as advised by the doctor,/ he might not have/ had a second heart attack. No error
- (A) If he would have taken rest/
- (B) as advised by the doctor/
- (C) he might not have/
- (D) had a second heart attack.
- (E) No error
Correct Answer: (A) If he would have taken rest/
View Solution
Step 1: Identifying the error.
The correct sentence should use the conditional past perfect tense. The phrase "If he would have taken rest" is incorrect. The correct phrase is "If he had taken rest," as the past perfect tense is used in conditional sentences.
Step 2: Conclusion.
The error is in option (A). The correct form should be "If he had taken rest."
Quick Tip: In conditional sentences, use the past perfect tense (e.g., "If he had taken rest") instead of "would have" in the if-clause.
Question 23:
The total allocation for education/ in this year's budget is Rs 34,400 crore,/ an amount that has gone up/ in 20 percent from last year. No error
- (A) The total allocation for education/
- (B) in this year's budget is Rs 34,400 crore,/
- (C) an amount that has gone up/
- (D) in 20 percent from last year.
- (E) No error
Correct Answer: (D) in 20 percent from last year.
View Solution
Step 1: Identifying the error.
The phrase "in 20 percent" is incorrect. The correct expression should be "by 20 percent" to indicate the increase. "By" is used when describing an amount of change or increase.
Step 2: Conclusion.
The error is in option (D), where "in 20 percent" should be "by 20 percent."
Quick Tip: When describing an increase or change, use "by" instead of "in" to indicate the amount of change (e.g., "by 20 percent").
Question 24:
Of the two cars/ that my friend has,/ the new Ford is without any question,/ the cheapest to run. No error
- (A) Of the two cars/
- (B) that my friend has/
- (C) the new Ford is without any question,/
- (D) the cheapest to run.
- (E) No error
Correct Answer: (D) the cheapest to run.
View Solution
Step 1: Identifying the error.
The phrase "the cheapest to run" is grammatically correct but lacks clarity. The sentence would flow better with the insertion of a clarifying phrase such as "of the two" to indicate a comparison. However, there is no actual grammatical error. The phrase itself is correct.
Step 2: Conclusion.
There is no error in the sentence, so the correct answer is (D).
Quick Tip: Make sure comparisons are clearly stated for better clarity, even when grammatically correct. In this case, "of the two cars" would improve clarity but doesn't constitute a grammatical error.
Question 25:
Although China is at present/ far ahead of India/ in terms of economic progress,/ it's education system is seriously flawed. No error
- (A) Although China is at present/
- (B) far ahead of India/
- (C) in terms of economic progress,/
- (D) it's education system is seriously flawed.
- (E) No error
Correct Answer: (D) it's education system is seriously flawed.
View Solution
Step 1: Identifying the error.
The error lies in the use of "it's" in the phrase "it's education system." The correct word should be "its," the possessive form, as "it's" is a contraction of "it is" or "it has," which doesn't fit the context.
Step 2: Conclusion.
The error is in option (D), where "it's" should be replaced with "its."
Quick Tip: Remember that "its" is the possessive form, while "it's" is a contraction of "it is" or "it has." Use "its" to indicate possession.
Question 26:
In many corporations, employees are replace by automated equipments so that to save money.
- (A) Are replace by automated equipments so that to
- (B) Are being replaced by automated equipment in order to
- (C) Were replaced by automated equipment so as to
- (D) Are replacing by automated equipment such that that
- (E) Replaces by automated equipment accordingly to
Correct Answer: (B) Are being replaced by automated equipment in order to
View Solution
Step 1: Identifying the error.
The sentence structure and tense are incorrect in the given sentence. The phrase “are replace” should be corrected to “are being replaced,” indicating an ongoing action in the present. Additionally, the phrase “so that to” is incorrect and should be replaced by “in order to,” which expresses the purpose more appropriately.
Step 2: Correcting the error.
The corrected sentence is: “In many corporations, employees are being replaced by automated equipment in order to save money.”
Step 3: Conclusion.
Therefore, the correct answer is (B).
Quick Tip: Use “are being replaced” to indicate an ongoing passive action in the present. Also, replace "so that to" with “in order to” for correct expression of purpose.
Question 27:
Tropical forests play a key role as the world’s carbon and wildlife reservoirs.
- (A) Play a key role as the world’s
- (B) Had played a key role in the world’s
- (C) Have been played a key role at the world’s
- (D) Has played a key role for the world’s
- (E) Plays a key role beside the world’s
Question 28:
Research shows that besides from obesity, Office Ergonomics are a leading factor that contributes to backache.
- (A) Besides from obesity, Office Ergonomics are a leading factor
- (B) Apart from obesity, Office Ergonomics is a leading factor
- (C) Along with obesity, Office Ergonomics were leading factors
- (D) Beside obesity, Office Ergonomics should be leading factor’s
- (E) Coupled with obesity, Office Ergonomics was leading factors’
Question 29:
Even as a series of bad news from the US has hit the global financial scene hard, the Indian IT companies have gone into stock taking mode.
- (A) Have gone into
- (B) Has gone for
- (C) Have been going to
- (D) Might have been going on
- (E) Are going in
Question 30:
A new study has found that almonds could help improving our digestion health by increasing levels of beneficial gut bacteria.
- (A) Could help improving our digestion
- (B) Can help improved our digestion
- (C) Could be helping to improve our digestive
- (D) Can help improved our digestive
- (E) Could help improve our digestive
Question 31:
P: Developed countries, including European economies and to a lesser extent
Q: Nevertheless, managed to maintain robust rates of economic growth
R: Developing countries have been affected as well, but they have
S: Japan, have been hit by the crisis in the US
- (A) QRSP
- (B) SRQP
- (C) RSQP
- (D) PSRQ
- (E) QSPR
Question 32:
P: Telescope arrays in the Northern and Southern hemispheres
Q: In Leh for an international collaboration that is
R: India plans to offer an astronomical site at Hanle
S: Exploring the possibility of setting up two large gamma-ray
- (A) PSQR
- (B) SPRQ
- (C) RQSP
- (D) QPRS
- (E) QSRP
Question 33:
P: Farmers of South India, particularly, Kerala
Q: Coconut is the major crop cultivated by small and marginal
R: Coconut is the cost and unavailability of laborers
S: For every farmer, the practical difficulty in carrying out plant protection in
- (A) SQRP
- (B) PRQS
- (C) SQPR
- (D) RQPS
- (E) QPSR
Question 34:
P: The environmental problems the world is facing
Q: As it is called, will not reverse global warming
R: Going dark has its uses, Earth Hour
S: But it is a good way to raise awareness about
- (A) PSQR
- (B) RQSP
- (C) SQPR
- (D) QPRS
- (E) QSRP
Question 35:
P: We should definitely move them
Q: To cooler climes and safer environments
R: If some species cannot survive in their current habitat
S: Due to global warming or human proximity
- (A) SPRQ
- (B) QRPS
- (C) SQPR
- (D) PRSQ
- (E) RSPQ
Question 36:
An action that is bad or unacceptable, but not very serious.
- (A) Felony
- (B) Etiquette
- (C) Misdemeanor
- (D) Repression
- (E) Concord
Question 37:
An animal or plant that lives in or on another animal or plant.
- (A) Sycophant
- (B) Bigot
- (C) Proselyte
- (D) Chauvinist
- (E) Parasite
Question 38:
To make someone angry by hurting the pride.
- (A) Pique
- (B) Quell
- (C) Nurture
- (D) Mitigate
- (E) Divulge
Question 39:
Harsh or insensitive in manner.
- (A) Stupendous
- (B) Abrasive
- (C) Venomous
- (D) Fecund
- (E) Odious
Question 40:
Having the habit of putting forward one’s own view noisily without any regard for the feelings of others.
- (A) Lissome
- (B) Gullible
- (C) Desolate
- (D) Naïve
- (E) Bumptious
Question 41:
She was sure to steal a march upon her rivals.
- (A) Oppose
- (B) Confront
- (C) Outshine
- (D) Avoid
- (E) Compromise
Question 42:
The carrot and stick policy pays dividends in every organization.
- (A) Rigorous training
- (B) Continuous vigilance
- (C) Democratic approach
- (D) Reward and punishment
- (E) Authoritative style
Question 43:
My friend has a bee in his bonnet.
- (A) Obsessed with something
- (B) Remains unaffected
- (C) Thinks a lot
- (D) Always busy
- (E) Be restless
Question 44:
If we give them this concession, it will be the thin end of the wedge.
- (A) The least we could do for them
- (B) The beginning of further concessions
- (C) Inadequate to fulfill their needs
- (D) A compromise on principle
- (E) Lead to more demands
Question 45:
Archana cut me dead in the street.
- (A) Deceived me
- (B) Abused me
- (C) Pushed me
- (D) Left me
- (E) Ignored me completely
Question 46:
From the following select the appropriate word to replace number 46 in the above passage.
- (A) Untrained
- (B) Skilled
- (C) Homogenous
- (D) Supplementary
- (E) Talented
Question 47:
From the following select the appropriate word to replace number 47 in the above passage.
- (A) Help
- (B) Utilize
- (C) Suffice
- (D) Apply
- (E) Call
Question 48:
From the following select the appropriate word to replace number 48 in the above passage.
- (A) Dispensable
- (B) Perfunctory
- (C) Inessential
- (D) Mandatory
- (E) Necessary
Question 49:
From the following select the appropriate word to replace number 49 in the above passage.
- (A) Destroyed
- (B) Cleared
- (C) Smothered
- (D) Diluted
- (E) Culled
Question 50:
From the following select the appropriate word to replace number 50 in the above passage.
- (A) Conserved
- (B) Eroded
- (C) Honored
- (D) Outmoded
- (E) Perforated
Question 51:
What is the most significant aspect noticed in his plays?
- (A) Absurdity
- (B) Manipulative effect
- (C) Fatal errors
- (D) Struggle for power
- (E) Linguistic agility
Question 52:
Select the synonym of the word ‘mordantly’ as used in the passage.
- (A) Complacently
- (B) Noticeably
- (C) Hauntingly
- (D) Deadly
- (E) Harshly
Question 53:
Pinter was the most imitated dramatist of his times because
- (A) His writings at once evoke a rare sensibility which is an endearing trait
- (B) He found the ominous in the everyday and the noise within silence
- (C) He was one of the few modern writers whose name became part of modern cultural vocabulary
- (D) He was publicly outspoken in his views on repression and censorship, not only at home but also abroad
- (E) His works depict violence though he does not look around for trouble
Question 54:
What was the most burlesqued aspect of Pinter’s writing?
- (A) Characters that are ready to hit but afraid to strike
- (B) The ‘pause’ which is used as an instructive note to actors
- (C) The consistent usage of ‘pause’ with rhythmic assurance
- (D) His focused performance and economy of gesture
- (E) Introducing ‘pause’ which has a violent effect
Question 55:
What was the tone of his plays?
- (A) Skeptical
- (B) Pessimistic
- (C) Candid
- (D) Critical
- (E) Unconvincing
Question 56:
Which of the following words, used in the passage, is a one-word substitute for the phrase, ‘a figure of speech in which an expression is used to refer to something that it does not literally denote in order to suggest a similarity’?
- (A) Weasel
- (B) Metaphor
- (C) Image
- (D) Pause
- (E) Space
Question 57:
What did he capture in his most celebrated works?
- (A) The anxiety and ambiguity of life in the latter half of the 20th century
- (B) The slipperiness of memory and human character
- (C) The struggle for power
- (D) The repression and censorship adopted by the US in the matter of Iraq
- (E) None of the above
Question 58:
How did Pinter describe The Birthday Party?
- (A) It is a very serious piece of work
- (B) It is supposed to be a comedy of errors
- (C) It is absurd and inglorious in its content
- (D) It is technically flawed in construction
- (E) It is a byword for strong and unspecified menace
Question 59:
Choose the meaning of ‘resilience’ as used in the passage.
- (A) Susceptible to criticism or persuasion or temptation
- (B) Good-natured tolerance of delay or incompetence
- (C) Able to withstand or recover quickly from difficult conditions
- (D) The distinct personality of an individual regarded as a persisting entity
- (E) An acute but unspecific feeling of anxiety, usually reserved for philosophical anxiety about the world or about personal freedom
Question 60:
The ‘New Woman’ emerged by
- (A) Relieving herself from all sorts of restrictions laid down by Indian men
- (B) Breaking all the shackles set forth by the society authoritatively as obligatory
- (C) Creating her own ‘space’ within the confines of the four walls of her home
- (D) Pushing herself against the norms and traditions prevailing in the Indian society
- (E) Receiving the right kind of education at the right time that helped her to emancipate herself
Question 61:
What according to the author is a sign of women empowerment?
- (A) Refusing to play stereotyped roles
- (B) Raising the voice against paradoxes
- (C) Earning more money than men
- (D) Seeking total liberation
- (E) Rebelling against the prevailing norms
Question 62:
Presently, what is the ‘New Woman’ engaged in?
- (A) She is claiming monetary independence so that she can enjoy greater autonomy
- (B) She realized the significance of freedom and equality and so is fighting for equal rights
- (C) She is contesting for her share of space which is of utmost importance to a woman
- (D) She is very busy building a self image for herself and in keeping up her identity against all odds
- (E) She is courageously treading uncharted paths which are dreaded even by her male counterparts
Question 63:
In the present days, what is the most terrifying actuality regarding a girl child?
- (A) Increasing school dropout rate
- (B) Gifting the girl child to temples
- (C) Low allocation of education budget
- (D) Domestic violence and molestation
- (E) Gender cleansing
Question 64:
According to the passage, which of the following statements is true?
- (A) A woman of substance is the one who meekly surrenders to male domination
- (B) Blogs and network sites are now used as effective tools to express a woman’s anger for denying her the freedom
- (C) Women writers articulate their experiences in a voice which is yet to be heard
- (D) The IT and travel sectors are the two upcoming fields that restricted growth opportunities for women
- (E) Ever since the days of freedom struggle, lack of sustained efforts by women organizations added to their already existing misery
Question 65:
The author highlights the fact that
- (A) Sons are at a premium in India
- (B) Girl child education is given utmost importance in urban areas
- (C) Discrimination extends to all areas including the food that is given to a girl
- (D) It is worrisome to note that the all-India sex ratio is declining rapidly
- (E) Daughters have choices of their own and are given total freedom
Question 66:
What is the central theme of the present passage?
- (A) What is ‘new’ for one woman maybe ‘old’ for another and some other woman might be facing severe male domination
- (B) There is tremendous diversity among the different groups of Indian women
- (C) Women are prone to violence in all walks of life and they are subjected to suppression right from their birth
- (D) Celebrating the New Age woman who scripts her own success stories
- (E) Dowry deaths are mostly prevalent in rural India and the girl child is neglected by the family members
Question 67:
What is the author’s gut feeling?
- (A) Scientists will invent a mechanism that might trigger a genome and convert it into the bacterium
- (B) Scientists will succeed in creating a synthetic genome which has the characteristics of a natural one
- (C) Scientists will improve upon the synthetic gene and find an alternative which is akin to the proto-cell of the bacterium
- (D) Scientists will prove that the DNA structure of a proto-cell is similar to that of an artificial one
- (E) Scientists will find a way to insert the bacterial genome into the proto-cell and somehow trigger it to make the bacterium itself
Question 68:
Which of the following words aptly substitutes ‘flummox’ as used in the passage?
- (A) Control
- (B) Petrify
- (C) Bewilder
- (D) Challenge
- (E) Demystify
Question 69:
Why does the author refer to Thomas Hardy’s poem?
- (A) To estimate the role played by direct properties attributable to one’s parentage
- (B) To underline the significance of the biological process whereby genetic factors are transmitted from one generation to the next
- (C) To emphasize the importance of the total of inherited attributes that rarely come by natural descent
- (D) To highlight the purpose of genetic endowment which can be traced through the family face
- (E) To evaluate the function of genes that are seldom present among the descendants of one individual
Question 70:
According to the passage, which of the following statements is not true?
- (A) Thomas Hardy’s poem, Heredity, reflects the DNA in a human being’s genome
- (B) Creating life in a lab will surely raise pertinent questions pertaining to ethics
- (C) Scientists, in future, will be able to create life under artificial conditions
- (D) Cloning of Dolly, the sheep, has invited the wrath of people because the sheep soon died a miserable death
- (E) Two centuries ago, urea was synthesized in a chemical laboratory
Question 71:
What did the scientists at JCVI do?
- (A) They circumvented nature’s constraint of direct descent
- (B) They bypassed nature’s laws and produced a natural gene
- (C) They invented an imperishable gene which is synthetic in nature
- (D) They ignored the theory of inheritance and created an intrinsic gene
- (E) They produced a gene which can be preserved permanently
Question 72:
A recently initiated technology, which is ethically acceptable, is
- (A) Assembling the complex biological molecule
- (B) Gene sequencing
- (C) Assisted reproduction
- (D) Stitching together of an artificial cell
- (E) Inserting a proto-cell into the bacterium
Question 73:
What was the outcome of their research?
- (A) They analyzed the DNA sequence of the synthetic gene in the laboratory for the first time
- (B) They contrasted the properties of a synthetic gene with that of a natural one
- (C) They created a gene sequence in artificial conditions which could undergo mutation
- (D) They produced the first synthetic genome in the laboratory which is analogous to the natural one
- (E) They studied the functions of a natural gene and a synthetic gene under controlled conditions of a laboratory
Question 74:
According to the author’s opinion, what would be the result of cloning a human being?
- (A) It will invite people’s indignation
- (B) It would be a wonderful prospect for humanity
- (C) It might change the face of the earth
- (D) It will be looked down as a sin
- (E) It will prove to be a global catastrophe
Question 75:
The DNA pieces of the synthetic genome were stitched together by using
- (A) The method of biochemical synthesis
- (B) The biochemical machinery of a host cell
- (C) The biochemical genome of a host cell
- (D) The DNA sequence of a host cell
- (E) The synthesized DNA pieces of a host cell
Question 76:
Which of the following statements is not true in context of the given passage?
- (A) There is a need for a new renaissance
- (B) The poor and needy are oppressed by modern man
- (C) Modern man is not an individualist
- (D) Western renaissance has held a great deal of promise for mankind
Question 77:
The author hopes that the present crisis can be solved by
- (A) Devoted individual efforts
- (B) Different political systems
- (C) Spiritual individuals
- (D) Purposeful and collective efforts
Question 78:
The author appears to be advocating which of the following approaches to be adopted by the society?
- (A) Capitalist
- (B) Communist
- (C) Humanistic
- (D) Socialist
Question 79:
The modern value systems encourage the importance of which of the following?
- (A) Craving for power and possession
- (B) Basic respect for all individuals
- (C) Spiritual development of an individual
- (D) Spirit of inquiry and knowledge
Question 80:
According to the passage, why has modern man turned out to be an enemy of everything that is non-human?
- (A) He hates and distrusts other human beings
- (B) He has been dominated by the drives of acquisitiveness and power
- (C) He consciously practices the spirit of cooperation
- (D) He is preoccupied with his own self
Question 81:
P, Q and E start a joint venture, where in they make an annual profit. P invested one-third of the capital for one-fourth of the time, Q invested one-fourth of the capital for one-half of the time and R invested the remainder of the capital for the entire year. P is a working partner and gets a salary of 10,000 per month. The profit after paying P’s salary is directly proportional to the sum each one has put and also to the square of the number of months for which each has put their sum in the venture. If in a year P earns 60,000 more than Q, then how much does P earn?
- (A) 1,00,000
- (B) 1,20,000
- (C) 1,35,000
- (D) 1,50,000
- (E) 1,80,000
Question 82:
Given \(A=x+y^{2}+z^{3}\). If x increases by 6300%, y increases by 700% and z increases by 300%, then what is the percentage increase in the value of A?
- (A) 12
- (B) 18
- (C) 26
- (D) 33
- (E) 63
Question 83:
What is the area of the square, if four vertices lie on the circumference of a circle where the area of the circle is four times its diameter in magnitude?
- (A) \(\dfrac{8}{\pi^{2}}\) sq.units
- (B) \(\dfrac{16}{\pi^{2}}\) sq.units
- (C) \(\dfrac{32}{\pi^{2}}\) sq.units
- (D) \(\dfrac{64}{\pi^{2}}\) sq.units
- (E) \(\dfrac{128}{\pi^{2}}\) sq.units
Question 84:
The charge for sending a telegram is constant for the first 10 or less words and an amount proportional to the number of words exceeding 10. If the charge for a 15 word telegram is ₹ 3.00 and that for a 20 word is ₹ 4.25, how much would it cost to send a 35 word telegram?
- (A) ₹ 8.00
- (B) ₹ 9.50
- (C) ₹ 10.50
- (D) ₹ 11.25
- (E) ₹ 12.50
Question 85:
If \(f(a,b)=a^{2}+b^{2}\) and \(g(a,b)=\dfrac{2}{b^{2}}\left[a^{2}+b^{2}\right]\), then what is the value of \(f(6,3)-g(8,4)\)?
- (A) 30
- (B) 35
- (C) 40
- (D) 45
- (E) 40
Question 86:
There are eight persons – P, Q, R, S, T, U, V and W – standing in a row and four distinct articles A, B, C and D are to be given to four people. No four neighboring persons receive an article. How many ways can this distribution be done?
- (A) 1680 ways
- (B) 1560 ways
- (C) 1440 ways
- (D) 1380 ways
- (E) 1320 ways
Question 87:
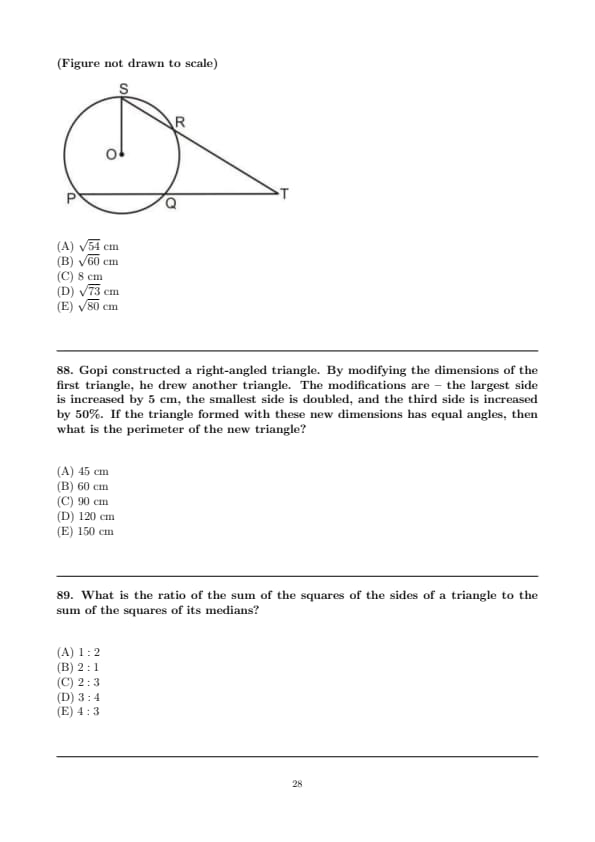
In the figure below, PT and ST are two secants. If O is the centre of the circle and PQ = 2QT = 8 cm, OS = 5 cm, then what is the measure of the line OT? (Figure not drawn to scale)
![]()
- (A) \(\sqrt{54}\) cm
- (B) \(\sqrt{60}\) cm
- (C) 8 cm
- (D) \(\sqrt{73}\) cm
- (E) \(\sqrt{80}\) cm
Question 88:
Gopi constructed a right-angled triangle. By modifying the dimensions of the first triangle, he drew another triangle. The modifications are – the largest side is increased by 5 cm, the smallest side is doubled, and the third side is increased by 50%. If the triangle formed with these new dimensions has equal angles, then what is the perimeter of the new triangle?
- (A) 45 cm
- (B) 60 cm
- (C) 90 cm
- (D) 120 cm
- (E) 150 cm
Question 89:
What is the ratio of the sum of the squares of the sides of a triangle to the sum of the squares of its medians?
- (A) \(1:2\)
- (B) \(2:1\)
- (C) \(2:3\)
- (D) \(3:4\)
- (E) \(4:3\)
Question 90:
The boat will sink when the weight on it increases beyond \(350\,\)kg. There is a hole through which water leaks in at \(0.4\) kg/s. The boat weighs \(1200\) kg, the boatman \(48\) kg, and there are four passengers weighing \(42.5,\,53.5,\,43.5,\,54.5\) kg. The boatman throws out water at \(0.04\) kg/s. How long will the boat float?
- (A) \(60\) hours
- (B) \(80\) hours
- (C) \(96\) hours
- (D) \(100\) hours
- (E) \(120\) hours
Question 91:
In an organization, there are four departments A, B, C and D with some accountants, managers, stenographers and office boys working together. Department A has 10 accountants, 8 managers, 7 stenographers and 3 office boys. The total monthly salary of all these employees is ` 2,37,500. Department B has 5 stenographers, 12 accountants, 6 managers and 7 office boys. The total monthly salary of all these employees is ` 2,31,500. Department C has 4 managers, 4 stenographers, 5 office boys and 7 accountants. The total monthly salary of all these employees is ` 1,51,000. If all the respective employees are paid equally in all the departments, then find the total monthly salary of 18 accountants, 11 managers, 10 stenographers and 10 office boys of department D?
- (A) 2,85,500
- (B) 3,25,500
- (C) 3,60,500
- (D) 3,85,500
- (E) 4,15,000
Question 92:
If \(\log_{a^{4}} 65536 = 2\), what is the value of `a’?
- (A) 2
- (B) 4
- (C) 6
- (D) 8
- (E) \(\sqrt{2}\)
Question 93:
A six-digit code is to be formed using 6 distinct numbers. Number in the first place is square of a prime number in third place. Numbers in 4th, 6th, 2nd and 1st place are consecutive numbers. If all odd digits except 1 are present in the code, what is the sum of all the digits?
- (A) 17
- (B) 21
- (C) 34
- (D) 38
- (E) 43
Question 94:
The functions f(x) and g(x) are related as f(g(x)) = xg(f(f(x))), where \( f(x) = \dfrac{x}{x - 1} \). What could be the functional form g(x)?
- (A) \(\dfrac{1}{x}\)
- (B) \(\dfrac{x}{x + 1}\)
- (C) \(\dfrac{x + 1}{x}\)
- (D) \(\dfrac{x}{x - 1}\)
- (E) \(\dfrac{x}{1 - x}\)
Question 95:
What is the unit’s digit of the expression \(77^{920} + 64^{165} + 53^{246}\) ?
- (A) 0
- (B) 1
- (C) 2
- (D) 3
- (E) 4
Question 96:
A blind man lives in an apartment containing 2 rooms. Each day before going to work he enters any one room randomly, picks up a bag and leaves home. One of the rooms contains 3 blue, 4 green and 5 red bags and the other contains 2 blue, 1 green and 3 red bags. What is the probability that he takes a green bag to his workplace?
- (A) \(\dfrac{1}{4}\)
- (B) \(\dfrac{1}{3}\)
- (C) \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)
- (D) \(\dfrac{2}{3}\)
- (E) \(\dfrac{3}{4}\)
Question 97:
There are three cans and a bucket. The cans each have a capacity of 5 litres, but are partially filled with water. The bucket also has some water in it. The sum of the water in the bucket and water in the first can is half of the total bucket capacity. When the first and third cans are emptied into the bucket, it contains 6 litres of water. Instead, when the second and the third cans are emptied into the bucket, it contains 7 litres of water. When water in all the cans are poured into the bucket, it is filled to its capacity. The first and second can contain a total of 7 litres. How many litres did the bucket already contain?
- (A) 1 litre
- (B) 2 litres
- (C) 3 litres
- (D) 4 litres
- (E) 5 litres
Question 98:
If the selling price of an article is five times the discount offered and if the percentage of discount is equal to the percentage profit, what is the ratio of the discount offered to the cost price?
- (A) 11 : 30
- (B) 4 : 15
- (C) 7 : 30
- (D) 1 : 6
- (E) 3 : 25
Question 99:
The dimensions of a triangle are 15 cm, 8 cm, and 17 cm. What is the area of a circle having radius \((r + 4)\) cm if ‘r’ is the inradius of the given triangle?
- (A) \(36\pi\) cm\(^2\)
- (B) \(49\pi\) cm\(^2\)
- (C) \(54\pi\) cm\(^2\)
- (D) \(64\pi\) cm\(^2\)
- (E) \(81\pi\) cm\(^2\)
Question 100:
What is the geometric mean of the sequence 1, 3, 9, 27, 81, …, \(3^n\)?
- (A) \(3^{\frac{n(n+1)}{2}}\)
- (B) \(3^{\frac{n}{2}}\)
- (C) \(3^{n}\)
- (D) \(3^{2n}\)
- (E) \(3^{n(n+1)}\)
Question 101:
Given quadratic equation is \(x^{2}-|x|-30=0\). Then which of the following statements is/are incorrect?
- (A) \(x-6=0\)
- (B) \(x+6=0\)
- (C) \(x+5=0\)
- (D) \(x+7=0\)
- (E) Both (c) and (d)
Question 102:
In a shooting competition, all shooters must hit the letter space where letter ‘A’ is written (small equilateral triangle of side \(3\) cm) on a target board shaped as a larger similar triangle of side \(12\) cm. What is the probability that the shooter will hit that space?
![]()
- (A) \(\,\dfrac{1}{16}\)
- (B) \(\,\dfrac{1}{12}\)
- (C) \(\,\dfrac{1}{8}\)
- (D) \(\,\dfrac{1}{4}\)
- (E) \(\,\dfrac{3}{4}\)
Question 103:
What is the value of \(\sqrt{\,42+\sqrt{\,42+\sqrt{\,42+\sqrt{\,42+\cdots}}}\,}\) ?
- (A) \(-7\)
- (B) \(-6\)
- (C) \(6\)
- (D) \(7\)
- (E) \(42\)
Question 104:
Rohit purchased a car and a plot at the same time. At the end of the first two years the value of the plot increased by \(30%\) and the value of the car decreased by \(10%\). At the end of next two years, the value of the car decreased by \(20%\) and the value of the plot increased by \(25%\). At the end of next two years, the value of the plot increased by \(20%\) and the value of car decreased by \(25%\). Had he sold both the car and the plot at the end of sixth year, he would have got \(56%\) more from the plot than from the car. How much less did he pay for the plot than the car when he purchased them?
- (A) 42%
- (B) 46%
- (C) 52%
- (D) 54%
- (E) 56%
Question 105:
An electronic company conducts a survey of 1500 houses for their products. The survey suggested that 862 houses own TV, 783 houses has AC and 736 houses has washing machine. There were 95 houses having only TV, 136 houses having only AC and 88 houses having only washing machine. There were 398 houses having all the three equipments. How many houses have only TV and washing machine but not AC?
- (A) 65
- (B) 119
- (C) 184
- (D) 185
- (E) 213
Question 106:
A series is formed in such a manner that the first term is the first natural number, the second is the square of the first term, the third term is the third natural number and fourth is the square of the third term and so on. What is the sum of the first 50 terms of the series?
- (A) 19825
- (B) 19450
- (C) 20825
- (D) 21450
- (E) 22825
Question 107:
Anu collected certain number of coins of denominations ₹1, ₹2, and ₹5. She has certain number of ₹2 coins, 4 times as many ₹1 coins as ₹5 coins, and 15 more ₹2 coins than ₹1 coins. If the total value is ₹490, how many ₹2 coins are there?
- (A) 11
- (B) 20
- (C) 35
- (D) 60
- (E) 70
Question 108:
What is the probability that a two-digit positive integer N has the property that the difference of N and the number obtained by reversing the order of its digits is a perfect cube?
- (A) 4/45
- (B) 5/15
- (C) 6/45
- (D) 7/45
- (E) 8/45
Question 109:
Given quadratic equation is \(x^{2}-|x|-30=0\). Then which of the following statements is/are incorrect?
- (A) \(x-6=0\)
- (B) \(x+6=0\)
- (C) \(x+5=0\)
- (D) \(x+7=0\)
- (E) Both (c) and (d)
Question 110:
In a shooting competition, all shooters must hit the letter space where letter ‘A’ is written (small equilateral triangle of side \(3\) cm) on a target board shaped as a larger similar triangle of side \(12\) cm. What is the probability that the shooter will hit that space?
![]()
- (A) \(\,\dfrac{1}{16}\)
- (B) \(\,\dfrac{1}{12}\)
- (C) \(\,\dfrac{1}{8}\)
- (D) \(\,\dfrac{1}{4}\)
- (E) \(\,\dfrac{3}{4}\)
Question 111:
In the figure below, what is the area of the smaller circle?
![]()
Statement 1: The two larger circles have the same radii of 8 cm each and \( O'O'' = 12 \, cm \).
Statement 2: The centres \( O, O' \) and \( O'' \) of the three circles are collinear.
- (a) If the data in statement (1) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (b) If the data in statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (c) If the data in both the statements together are needed to answer the question
- (d) If either statement (1) alone or statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (e) If neither statement (1) nor statement (2) suffices to answer the question
Question 112:
What is the unit’s digit of the number \( (8pqr)^{64} \) where p, q, and r are the hundredth, tenth, and unit digits of the number?
Statement 1: The product of \( p \) and \( q \) is 12.
Statement 2: The product of \( q \) and \( r \) is 24 and \( r \) is greater than 4.
- (a) If the data in statement (1) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (b) If the data in statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (c) If the data in both the statements together are needed to answer the question
- (d) If either statement (1) alone or statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (e) If neither statement (1) nor statement (2) suffices to answer the question
Question 113:
Which has the greater length, \(AB\) or \(CD\)?
Statement 1: \(CD\) is the diameter of the circle.
Statement 2: \(AB\) is the length of the side of a square inscribed in a circle whose radius is half of \(CD\).
- (a) If the data in statement (1) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (b) If the data in statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (c) If the data in both the statements together are needed to answer the question
- (d) If either statement (1) alone or statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (e) If neither statement (1) nor statement (2) suffices to answer the question
Question 114:
Ritu, Deep, Lakshya, Krish, Suja, Adi and Anu are seven friends and belong to the same family. Ritu has a son and a daughter. Krish and Deep are males. Suja and Lakshya are females. What is the relationship between Suja and Adi?
Statement 1: Ritu has a grandson and a granddaughter and Anu is Krish’s niece.
Statement 2: Suja is Lakshya’s sister-in-law and Deep has two children Adi and Anu.
- (a) If the data in statement (1) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (b) If the data in statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (c) If the data in both the statements together are needed to answer the question
- (d) If either statement (1) alone or statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (e) If neither statement (1) nor statement (2) suffices to answer the question
Question 115:
Are \(\triangle ABC\) and \(\triangle PQR\) congruent?
Statement 1: The triangles are right-angled triangles.
Statement 2: The base and heights of two triangles are equal.
- (a) If the data in statement (1) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (b) If the data in statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (c) If the data in both the statements together are needed to answer the question
- (d) If either statement (1) alone or statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (e) If neither statement (1) nor statement (2) suffices to answer the question
Question 116:
A survey on games played by 400 college students shows: 15% Hockey, 25% Football, 30% Cricket, 15% Basketball, 15% Tennis. What is the ratio of the minimum number of students from college A who play Basketball to the number from college A who play Football?
Statement 1: Students from college A comprise 20% of total students surveyed.
Statement 2: 15% of the total students who play Basketball and Football are from college A.
- (a) If the data in statement (1) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (b) If the data in statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (c) If the data in both the statements together are needed to answer the question
- (d) If either statement (1) alone or statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (e) If neither statement (1) nor statement (2) suffices to answer the question
Question 117:
If ‘a’ and ‘b’ are integers, is \( \left(\dfrac{a}{6}+\dfrac{b}{5}\right) \) an integer?
Statement 1: ‘a’ is divisible by 5 and ‘b’ is divisible by 6.
Statement 2: ‘a’ is a multiple of 6 which is one–tenth the value of ‘b’.
- (a) If the data in statement (1) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (b) If the data in statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (c) If the data in both the statements together are needed to answer the question
- (d) If either statement (1) alone or statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (e) If neither statement (1) nor statement (2) suffices to answer the question
Question 118:
A, B, C, D, E and F are six whole numbers. Is the 6-digit number “ABCDEF” divisible by \(132\)?
Statement 1: The last four digits of the number have a factor \(4\) and \(A+C+E=12(B+D+F)\).
Statement 2: Sum of all the digits of the given number is divisible by \(24\).
- (a) If the data in statement (1) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (b) If the data in statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (c) If the data in both the statements together are needed to answer the question
- (d) If either statement (1) alone or statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (e) If neither statement (1) nor statement (2) suffices to answer the question
Question 119:
What was A’s score in fourth aptitude test?
Statement 1: A’s score in the fourth test was 12 points higher than the average score in the first three tests written.
Statement 2: A’s score on the fourth test raised the average test score from 80 to 85.
- (a) If the data in statement (1) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (b) If the data in statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (c) If the data in both the statements together are needed to answer the question
- (d) If either statement (1) alone or statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (e) If neither statement (1) nor statement (2) suffices to answer the question
Question 120:
What is the value of \(xyz\)?
Statement 1: \(x^{a}=y^{b}=z^{c}\) and \(ab+bc+ca=0\) where \(a, b, c\) are non-zero integers.
Statement 2: \(a^{x}=b^{y}=c^{z}=a\) where \(a, b, c\) are non-zero integers.
- (a) If the data in statement (1) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (b) If the data in statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (c) If the data in both the statements together are needed to answer the question
- (d) If either statement (1) alone or statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (e) If neither statement (1) nor statement (2) suffices to answer the question
Question 121:
In \(\triangle ABC\), \(AB=2\) cm and \(BC=4\) cm. What is the length of \(AC\)?
Statement 1: The three sides of the triangle are in geometric progression.
Statement 2: \(\angle ABC = 30^\circ\).
- (a) If the data in statement (1) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (b) If the data in statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (c) If the data in both the statements together are needed to answer the question
- (d) If either statement (1) alone or statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (e) If neither statement (1) nor statement (2) suffices to answer the question
Question 122:
Is \(xy\) negative?
Statement 1: \(\ (x+y)^2 < (x-y)^2\).
Statement 2: \(\ (x-y)\) is positive.
- (a) If the data in statement (1) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (b) If the data in statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (c) If the data in both the statements together are needed to answer the question
- (d) If either statement (1) alone or statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (e) If neither statement (1) nor statement (2) suffices to answer the question
Question 123:
a, b, and c are three positive integers. What is the value of \(a^2 + b^2 + c^2\)?
Statement 1: \(a^2 + b^2 = 17\) and \(c\) is the arithmetic mean of \(a\) and \(b\).
Statement 2: The geometric mean of \(a\) and \(b\) is \(2\).
- (a) If the data in statement (1) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (b) If the data in statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (c) If the data in both the statements together are needed to answer the question
- (d) If either statement (1) alone or statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (e) If neither statement (1) nor statement (2) suffices to answer the question
Question 124:
What is today’s date?
Statement 1: Three days before it was Friday.
Statement 2: One week before it was the first Tuesday in April 2007.
- (a) If the data in statement (1) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (b) If the data in statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (c) If the data in both the statements together are needed to answer the question
- (d) If either statement (1) alone or statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (e) If neither statement (1) nor statement (2) suffices to answer the question
Question 125:
A right circular cone (PQR) is cut into two parts, cone (C) and frustum (F), by a plane parallel to the base. What is the ratio of the volume of C to the volume of F?
Statement 1: PQR is twice the radius of C.
Statement 2: PQR has been cut off at the middle of its height.
- (a) If the data in statement (1) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (b) If the data in statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (c) If the data in both the statements together are needed to answer the question
- (d) If either statement (1) alone or statement (2) alone is sufficient to answer the question
- (e) If neither statement (1) nor statement (2) suffices to answer the question
Question 126:
![]()
If the given highest scores are taken, what is the least % share of Australia in the total scores of each Cup?
- (A) 21%
- (B) 23.9%
- (C) 24.7%
- (D) 26.8%
- (E) 31.8%
Question 127:
In which Cup is the % increase in Sri Lanka’s highest score the greatest compared to its highest score in the previous Cup?
- (A) Cup A
- (B) Cup B
- (C) Cup C
- (D) Cup D
- (E) Cups B and D
Question 128:
After the completion of tournament for Cup A, each team is given a rank based on their highest scores. If the highest score of India is the same as the highest score of South Africa playing for Cup C, what is the rank of team India playing for Cup A?
- (A) 1
- (B) 2
- (C) 3
- (D) 4
- (E) None
Question 129:
If the highest scores of all teams in each cup are taken, what is the ratio of total runs scored by Sri Lanka and India in all the cups?
- (A) 218 : 243
- (B) 238 : 249
- (C) 218 : 249
- (D) 1215 : 1159
- (E) 1090 : 1229
Question 130:
If the runs scored by Australia and South Africa for Cup B are of a final match, what is the required run rate of Australia to win the match playing all the stipulated overs?
- (A) 6.1
- (B) 6.15
- (C) 6.22
- (D) 6.34
- (E) 6.44
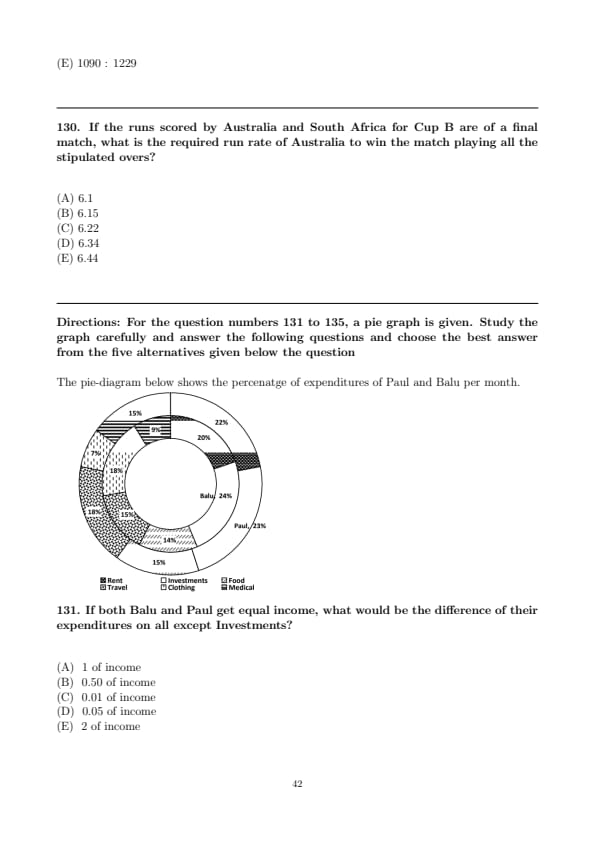
Question 131:
![]()
If both Balu and Paul get equal income, what would be the difference of their expenditures on all except Investments?
- (A) ₹ 1 of income
- (B) ₹ 0.50 of income
- (C) ₹ 0.01 of income
- (D) ₹ 0.05 of income
- (E) ₹ 2 of income
Question 132:
If Paul’s income was ₹13,500, what would be his average expenditure on Investments, Rent, and Travelling?
- (A) 2540
- (B) ₹ 2125
- (C) ₹ 2490
- (D) ₹ 2650
- (E) ₹ 2700
Question 133:
If the salary of Balu is ₹15,000, what would be the expenditure on Investments and Food?
- (A) ₹ 5450
- (B) ₹ 4200
- (C) ₹ 4560
- (D) ₹ 5700
- (E) ₹ 5900
Question 134:
What is the sum of the angles subtended by Paul’s expenditures on Travel, Rent and Medical?
- (A) \(207.2^\circ\)
- (B) \(165.8^\circ\)
- (C) \(157.5^\circ\)
- (D) \(207^\circ\)
- (E) \(187.2^\circ\)
Question 135:
If both Balu and Paul get equal income, what is the ratio of their expenditures on Food and Clothing?
- (A) \(1:1\)
- (B) \(1:2\)
- (C) \(3:1\)
- (D) \(2:3\)
- (E) \(16:11\)
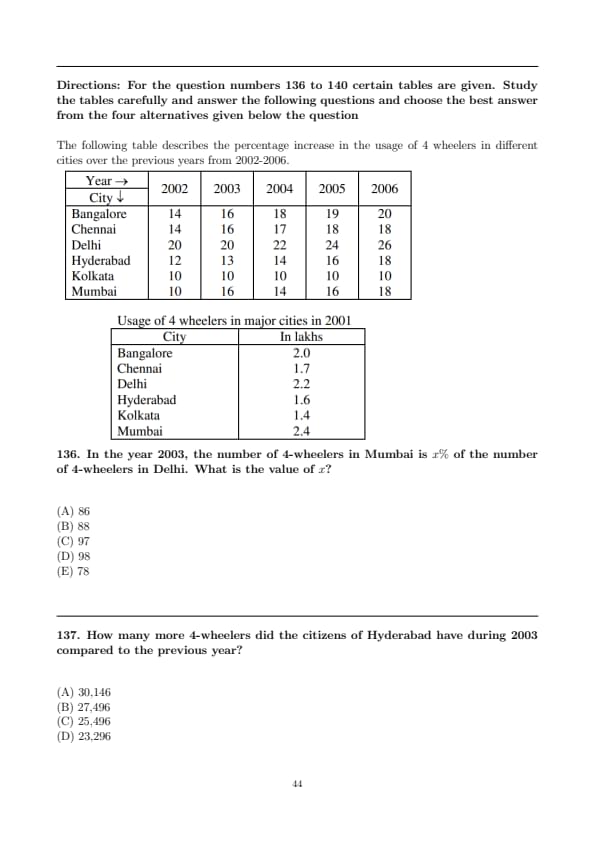
Question 136:
![]()
In the year 2003, the number of 4-wheelers in Mumbai is \(x%\) of the number of 4-wheelers in Delhi. What is the value of \(x\)?
- (A) 86
- (B) 88
- (C) 97
- (D) 98
- (E) 78
Question 137:
How many more 4-wheelers did the citizens of Hyderabad have during 2003 compared to the previous year?
- (A) 30,146
- (B) 27,496
- (C) 25,496
- (D) 23,296
- (E) 21,498
Question 138:
In Kolkata, the number of 4 wheelers in the year 2004 is exactly 70% of the number of 4 wheelers in the year 2007. How many 4 wheelers were there in 2007 in the city?
- (A) 2,44,320
- (B) 2,66,200
- (C) 2,12,460
- (D) 2,56,210
- (E) 2,65,114
Question 139:
How many 4 wheelers does the city Chennai have in the year 2003?
- (A) 2,24,808
- (B) 2,23,316
- (C) 2,10,248
- (D) 1,80,456
- (E) 1,74,555
Question 140:
What is the approximate ratio of 4 wheelers in Bangalore in the year 2005 to that in the year 2003?
- (A) 7 : 5
- (B) 9 : 5
- (C) 8 : 5
- (D) 6 : 5
- (E) 7 : 9






















































Comments