Collegedunia Team Content Curator
Content Curator
Matter can be described as an acronym of the physical substances existing around us. In simple words, matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. But, what is mass? Basically, mass is the amount of matter present in an object. Every object, starting from clothes to air, is mainly composed of matter. Matter can also be broken down into its building blocks, which are atoms. Atoms, that are elementally composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons, are known to be the building blocks of all matter existing around the universe.
| Table of Content |
Key Takeaways: Solid, Liquid, Gas, Matter and Atoms
Definition of Matter
Matter can be defined as anything that takes up space and also has mass. It is any physical substance that exists around all of us.
Matter, in brief, is also supposed to be composed of an element or component. Which is to say, matter is composed of building blocks called atoms. Atoms are elementally composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Matter can normally be visible or invisible to our naked eyes.
Also Check:
Different States of Matter
Matter can be classified into three main segments, which are, solid, liquid and gas. Every phase of matter has been bound with an atomic bond, wherein, some have a tight atomic bonding, while others have a loose atomic bonding.
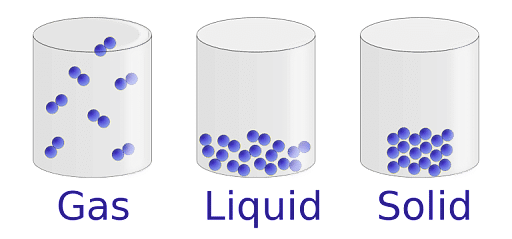
Three Different States of Matter
Solids:
- Solids are known to have a definite mass and volume which results in a rigid form.
- Solids, as can be already guessed, have a tight atomic bonding, with very high viscosity. It is one reason behind why solids have a rigid shape and form.
- In addition, the intermolecular distances between the particles of solid are very compressed, which apparently results in the attractive forces to be high.
- Most of the solid objects have a crystalline, three-dimensional structure.
- In fact, the atoms of a typical solid object have a fixed position, which gives an idea about why they can physically oscillate in their main position.

Solid Molecules
Liquids:
- Liquid molecules are generally also closely packed, but not as much as the molecules of solids.
- It has weaker intermolecular forces, which consequently gives it a non-rigid form. The molecules of liquids are weaker than solid materials, but are apparently stronger than gases.
- Liquids tend to flow with ease since there is minimal space between the molecules of it.
- Liquids are capable of taking the shape or form of any container it is reserved in. For example, when you pour a liquid substance into a jar, it tends to reshape itself into the form the jar is in. Liquids, in a nutshell, have a fixed volume.
- The compressibility and thermal expansion in quid substances are typically higher than solids, like water or juice.
Liquid Molecules
Gasses
- The gaseous state, of all phases of matter, has the weakest intermolecular forces of attraction.
- The particles of gasses are quite distant from one another, which contributes to it having a loosely packed atomic bonding.
- Gas particles tend to be highly compressible since they have larger empty spaces between each particle.
- Gasses usually have a lower density than solids and liquids.
- They tend to expand in any container they are seemingly placed inside due to their volume.
- Gasses also are capable of diffusion. They are likely to blend with other substances in every proportion.

Gas Molecules
Can Matter Change Its State?
Matter, of any form, is capable of changing its state from one particular phase to another. As a general idea, when increasing the temperature of solids, the kinetic energy usually also increases with it. As a result, the particles begin vibrating with an increased speed.
For instance, water, which is a liquid, starts to solidify and become ice upon freezing. Similarly, water can also evaporate, which is typically a gaseous state, upon heating. The components that bind the water do not really change, but its shape or form or volume definitely does upon transformation. The change really does depend on various factors, like climatic behaviors, humidity, temperature and the kind of matter it is.
Law of Conservation
The law of conservation generally outlines the idea that matter can neither be created nor be destroyed. In the physical world, the law of conservation ideates energy, matter, angular momentum, mass and more. The law of conservation of matter mainly claims that the amount of matter usually remains the same, but undergoes change in its state. Matter, as stated prior, cannot be automatically created or destroyed by us or nature. It only just changes its shape, form, and volume.
Points to Remember
- Matter is anything that occupies space, mass and volume. Anything from books to air is composed of matter.
- Matter can be broken down to its building blocks called Atoms. Atoms, which are elementally composed of electrons, neutrons and protons, are what forms matter.
- Liquids, however, are not as closely packed as solids are, giving it a flowy form that can take up the shape of any container it is poured in.
- The particles of gasses are highly distant from one another, which contributes to it having the most loosely packed atomic bonding.
- The law of conservation generally outlines the idea that matter can neither be created nor be destroyed.
Also Read:
Sample Questions
Ques. Write a short note on Matter. (2 marks)
Ans. Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. It is the building block of the entire universe. It is known to be composed of atoms, which basically are the building blocks of matter itself. These apparently are known to give matter its physical and chemical properties, along with giving matter several states, like solids, liquids and gasses. In fact, the force of attraction between these atoms is what binds them to have a shape and form.
Ques. What are the three different states of matter? (3 marks)
Ans.Matter can be classified into three main segments, which are, solid, liquid and gas,
- Solids: Solids are crystalline structures that have the highest intermolecular force. Solids are known to have a definite mass and volume which results in a rigid form. Solids have a tight atomic bonding, with very high viscosity. It is one reason behind why solids have a rigid shape and form.
- Liquids: Liquid molecules are generally also closely packed, but not as much as the molecules of solids. It has weaker intermolecular forces, which consequently gives it a non-rigid form.
- Gasses: The gaseous state has the weakest intermolecular forces of attraction. The particles of gasses are quite distant from one another, which contributes to it having a loosely packed atomic bonding.
Ques. “Matter can exist in two states at once.” Is the statement true or false? (2 marks)
Ans. Matter can definitely exist in two states at once. Which is to say, pressure is responsible to turn matter from one state to another. However, there are distinct matter forms that tend to vary, but can still be seen in two states at once. Mainly, for matter to travel through the three distinct stages, it needs a technical or natural trigger, like condensation, evaporation, fusion and more. Water is the only substance in all of earth that can be found in all the three stages of matter.
Ques. What is the Law of Conservation? (2 marks)
Ans. The law of conservation gives the idea that matter can neither be created nor be destroyed. The principle of Law of Conservation asserts that a certain measurable property is not capable of change in the period of time within a singular physical system. The law of conservation ideates energy, matter, angular momentum, mass and more. The law of conservation of matter claims that the amount of matter usually remains the same, but undergoes change in its state. For example, when water freezes over time and forms ice.
Ques. Define Intermolecular forces (MF). (2 marks)
Ans. Intermolecular force, or simply IMF, is the force that influences interaction between particles, typically molecules. It acts as the mediator of attraction or repulsion that surfaces between the respective molecules and binds them either together or away. For example, solids usually have the strongest intermolecular force which gives them a rigid shape and form while gasses have the weakest, giving them a non-rigid form. Gasses, unlike solids, have loosely packed atomic bonding.
Ques. Define briefly the State of Liquid in Matter.
Ans. The state of liquid in matter are:
- Liquids typically have weaker intermolecular forces, which gives it a non-rigid form. The molecules of liquids are weaker than solids, but are stronger than gases.
- Liquids are likely to flow with ease since there is minimal space between the molecules of it. The intermolecular forces between them are weak.
- Liquids are capable of taking the shape or form of any container it is reserved in. For example, when you pour a liquid substance into a jar, it tends to reshape itself into the form the jar is in. Liquids, quite clearly, have a fixed volume.
Ques. Define briefly the State of Gases in Matter. (5 marks)
Ans. State of Gases in Matter are:
- Gas particles are apparently distant from one another, which is why it has loosely packed atomic bonding.
- They tend to be highly compressible since they have larger empty spaces between each particle.
- Gasses have a lower density than solids and liquids both.
- They are likely to expand in any container they are seemingly placed inside due to their volume.
- Gasses also are capable of diffusion. They tend to blend with other substances in every proportion.



Comments